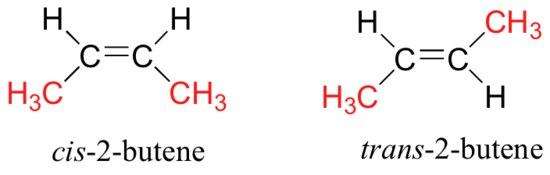
Difference Between Cis and Trans Cis-trans isomerism consists in the possibility of placing substituent groups on one or on different sides of a double bond plane or a non-aromatic cycle. Cis-2-butene trans-2-butene Anti-cancer drug Toxic.
The concentration of trans-2-butene was then determined to be 050 M.
Cis 2 butene. Except where otherwise noted data are given for materials in their standard state at 25 C 77 F 100 kPa. What is Infobox references. 2-Butene is an acyclic alkene with four carbon atoms.
It is the simplest alkene exhibiting cistrans-isomerism also known as EZ-isomerism. That is it exists as two. For cis-2-butene USEPAOPP Pesticide Code.
606666 there are 0 labels match. Not registered for current use in the US but approved pesticide uses may change periodically and so federal state and local authorities must be consulted for currently approved uses National Pesticide Information Retrieval Systems Database on cis-2-Butene 590-18-1. Available from as of January 24.
Cis-2-Butene Isobutane Isobutylene IsoPentane Mixed-2-Butenes n-Butane n-Pentane 1-Pentene Propane Propylene R290 UL Classified R600a UL Classified R600 Trans-2-Butene. Carbon Monoxide CNGLNG Ethane Ethylene HCL Anhydrous Hydrogen Methane Nitrogen. Ethane Ethylene LNG Methane.
Other Gases on Request. Welcome to GI. A quantity of cis-2-butene is added toa2Literflaskandheated to 400C for 2 years.
The concentration of trans-2-butene was then determined to be 050 M. What is the concentration of cis-2-butene in the flask. Generic Equilibrium Constant a A b B c C d D Constant for a given temperature Ratio of equilibrium concentrations of products over reactants Concentrations raised to the.
So weve talked about cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene. Theyre both di-substituted alkenes. So it turns out that trans-2-butene is the more stable of the two.
So this one is more stable. And we can think about that in terms of steric hindrance. If we look at cis-2-butene we have these methyl groups relatively bulky and they would sterically interfere with each other if theyre on the same.
K Ae E a RT Both A and E a are specific to a given reaction. K is the rate constant. E a is the activation energy.
R is the ideal-gas constant 8314 JKmol. T is the temperature in K. In addition to carrying the units of the rate constant A relates to the frequency of collisions and the orientation of a.
ISO 6976 1995 Natural gas - Calculation of calorific values density relative density and Wobbe index from composition. 2Optical isomerism Those stereoisomers which are mirror images of each other or differ in optical activity are known as optical isomers and this phenomenon is known as optical isomerism. Conditions for optical isomerism 1.
In optical isomers carbon atoms are attached to four different atoms or groups. 1 cis-2-butene 2 1-butene 3cyclohexene A 3. Which of the following compounds is an E isomer.
A are relatively polar compounds B have lower boiling points than alcohols of similar molecular weight C are reasonably soluble in water D both A and B E none of the above. Which of the alkyl chlorides listed below undergoes. Electronic Fluorocarbons To be your premier global supplier of high quality specialty gases and advanced materials.
Providing innovative solutions utilizing novel chemistry and leading technologies with a total commitment to our customers employees and the environment. Cis-2-butene has both methyl groups on the same side of the molecule. Trans-2-butene has the methyl groups on opposite sides of the molecule.
Their structural formulas are as follows. Models of left Cis-2-Butene and right Trans-2-Butene. Note however that the presence of a double bond does not necessarily lead to cis-trans isomerism Figure PageIndex4.
The right gas gets more done. At Praxair we believe the right gas can help you do more than run an application. It can promise more uptime lower long-term costs raise productivity and increase operational flexibility so you can do more with less.
So we have cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene. These are different molecules with different properties. If you want to use cistrans terminology youre looking for two identical groups and you are comparing them.
So lets look at these next two examples here and figure out which one is cis and which one is trans. Were looking for identical groups. So over here we have an ethyl group attached to.
N-Butane Isobutane cis-2-Butene trans-2-Butene 1-Butene Isobutylene 13-Butadiene Ethyl Acetylene in Nitrogen Portables. Pentane Oxygen in Nitrogen Portables. Gases and Gas Mixtures for Specific Applications.
EPA Protocol and Calibration Mixes. EPA Protocols are available as binary mixtures or multi-component mixtures. All MATHESON EPA Protocol Mixtures are certified using EPA.
Difference Between Cis and Trans Cis-trans isomerism consists in the possibility of placing substituent groups on one or on different sides of a double bond plane or a non-aromatic cycle. Cis-trans isomers belong to diastereomers since they are not mirror reflections of each other. Cis and trans isomers are found both among organic and inorganic compounds.
Our services are extensive and include cleaning purging drying emergency oxygenated aeration inerting cooling blanketing displacement pneumatic testing pressure leak detection inspection for piping and storage tanks and more. Cis-2-butene trans-2-butene Anti-cancer drug Toxic. Stereoisomers optical isomersare nonsuperimposable mirror images of each other.
Mirror a tetrahedral molecule with four different groups no rotation allows the two molecules to be superimposed Optical isomers are said to be chiral not superimposable. A chiral molecule and its mirror image form a pair of enantiomers. For example cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene etc.
While structural isomers are molecules having the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. They have different arrangements of the same groups. For example n-butane and 2-methyl propane isobutane etc.
What is the difference between - and isomers. - isomers are also called levorotatory because they rotate plane. C8H16 cis-2-butene C4H8 cis-2-pentene C5H10 cis-decalin C10H18 cyclohexane C6H12 cyclooctane C8H16 cyclopentadiene C5H6 cyclopentane C5H10 cyclopropane C3H6 ethane C2H6 ethylbenzene C8H10 ethylcyclohexane C8H16 ethylcyclopentane C7H14 ethylene C2H4 exotetrahydrodicyclopentadiene C10H16 hexamethylbenzene.
Except where otherwise noted data are given for materials in their standard state at 25 C 77 F 100 kPa. What is Infobox references. Isobutylene or 2-methylpropene is a hydrocarbon with the formula CH 3 2 CCH 2.
It is a four-carbon branched alkene olefin one of the four isomers of butylene. It is a colorless. In each case the alkene has a boiling point which is a small number of degrees lower than the corresponding alkane.
The only attractions involved are Van der. At these temperatures the cis-2-butene is not isomerized over the catalyst pellets. At t 0 the feed stream containing 2 vol cis 2-butenein helium is switched to a stream ofpure helium at the same total flow rate.
Reac tion rates for the isomerization of cis-2-buteneinto I-buteneand trans-2-buteneare to be. Cis-2-Butene C4H8 SSSS SSSSSSSS U SSSSS Trans-2-Butene C4H8 SSSS SSSSSSSS U SSSSS Carbon Dioxide CO2 SSSS SSSSSSSSSSSSSS Carbon Monoxide CO SSSS SSSSSSSSSS I SSS Carbonyl Sulfide COS SSSS I SSSSSSS I I S I I I Chlorine Cl2 U S S UU U SSSSS U U SS U U U Deuterium D2 SSSS SSSSSSSS I SSSSS Diborane B2H6 SSSS I SSSSS I I I SIIII Dichlorosilane H2SiCl2 I S S I I I SSSSS I I SIIII Dimethyl. Bromination of cis-2-butene via the bromonium ring leads to enantiomeric products actually the d and l diastereomer pair.
Top is RR the bottom is SS. The ring must be opened via S N 2 reaction leading to an anti arrangement of bromines in the final product. 31 The same bromination reaction with trans-2-butene leads to an anti dibromide which is the achiral meso diastereomer RS.