
Whereas an excess of chlorine favors formation of chloroform and carbon tetrachloride. Add distilled water to make 1 liter and mix thoroughly.
1 with phosphorus pentachloride yields acetone chloride CH32CCl2 2 with hydrogen chloride dry yields both mesityl oxide CH3COCHCCH32 liquid bp 132 C and phorone CH32CCHCOCH.
Chlorination of methylene chloride. Methylene Chloride is derived from the chlorination of methane during which other chlorinated methane derivatives may be formed. Propylene oxide cyclohexane andor 2-methyl-2-butene are added as stabilizers. Purity depends on the amount of C2 and higher hydrocarbons in the methane and the extent of chlorination.
Small amounts of several other chlorinated compounds may be present. Methylene Chloride is a clear colorless nonflammable volatile liquid chlorinated hydrocarbon with a sweet pleasant smell and emits highly toxic fumes of phosgene when heated to decomposition. Methylene chloride is primarily used as a solvent in paint removers but is also used in aerosol formulations as a solvent in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals as a degreasing agent in.
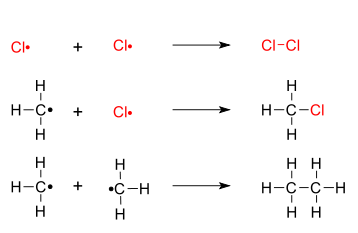
The chlorination of methane shown below provides a simple example of this reaction. In the case of methane a large excess of the hydrocarbon favors formation of methyl chloride as the chief product. Whereas an excess of chlorine favors formation of chloroform and carbon tetrachloride.
CH 4 Cl 2 energy CH 3 Cl CH 2 Cl 2 CHCl 3 CCl 4 HCl. The following facts must be. Oxalyl chloride C2Cl2O2 CID 65578 - structure chemical names physical and chemical properties classification patents literature biological activities safetyhazardstoxicity information supplier lists and more.
Public health information CDC Research information NIH SARS-CoV-2 data NCBI Prevention and treatment information HHS Español. Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them.
Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent. Among the elements it has the highest electron.
The chlorination reaction proceeds stepwise via benzyl chloride and benzal chloride. Sarcomas at the injection site were observed in rats. Sulfur mustard H mustard gas Sulfuryl fluoride.
Store in a dry place no lower in temperature than Alkyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride C12 40 C14 50 C18 10 can be found in 0 products. Manufacture of benzyl compoundsperfumespharmaceuticals. Thionyl chloride has a nauseating sickly-sweet odor to it that imprints itself forever upon your memory.
One accident that occurred during my time as a TA involved a student dropping a flask with 5 mL of thionyl chloride into a rotovap bath outside the fume hood. The cloud of SO2 and HCl that formed cleared the teaching lab for half an hour. Searching for NSF Certified Drinking Water Treatment Chemicals is quick and easy.
If you have any problems please contact NSF. Learn more about NSF Internationals services for treatment chemicals. Trichloroethylene Perchloroethylene Methylene Chloride Banner Chemicals UK supply GLOBALLY and EXCLUSIVELY of all grades of PERKLONE PCE Perchloroethylene and TRIKLONE TCE Trichloroethylene including TRIKLONE-LE and TRIKLONE-N and.
Chlorination and sulfochlorination Chlorinated Polyethylene PE-C is an inexpensive material having a chlorine content from 34 to 44. It is used in blends with PVC because the soft rubbery chloropolyethylene is embedded in the PVC matrix thereby increasing the impact resistance. The catalyst used in the preparation of an alkyl chloride by the action of dry HCl on an alcohol is a anhydrous AlCl 3 b FeCl 3 c.
Chlorination c hydrogenation d dehydrohalogenation. An alkyl halide by formation of its Grignard reagent and heating with water yields propane. What is the original alkylhalide.
A Methyl iodide b Ethyl iodide c Ethyl bromide. Free radical chlorination or bromination of alkanes gives a complex mixture of isomeric mono- and polyhaloalkanes which is difficult to The hydroxyl group of an alcohol is replaced by halogen on reaction with concentrated halogen acids phosphorus halides or thionyl chloride. Example of Unit operation.
Example 1 Distillation of Methylene Di Chloride with water Explanation In a process the separation of Methylene Di Chloride with water using a liquid-liquid separation technique can be called as a unit operation Explanation In the above process only separation is taking place which will be done base on density difference. The following spent halogenated solvents. Tetrachloroethylene methylene chloride trichloroethylene 111-trichloroethane chlorobenzene 112-trichloro-122-trifluoroethane ortho-dichlorobenzene trichlorofluoromethane and 112 trichloroethane.
All spent solvent mixturesblends containing before use a total of ten percent or more by volume of one or more of the above halogenated. Cyanides Amenable to Chlorination after Distillation H. Cyanides Amenable to Chlorination without Distillation Short-Cut Method I.
Weak Acid Dissociable Chloride J. Spot Testing for Sample Screening L. Total Cyanide after Distillation by Flow Injection Analysis O.
Total Cyanide and Weak Acid Dissociable Cyanide by Flow Injection Analysis. Free radical chlorination hν Cl 2 Free radical bromination hν. I cant seem to access conversion to esters in the acid chloride section.
November 20 2012 at 215 am. I mean in the acyl halide section. November 20 2012 at 225 am.
Never-mind it was a problem with my browser. January 25 2013 at 1151 am. The numbers under the column headed CASRN are the Chemical Abstracts Service Registry Numbers for each hazardous substanceThe Statutory Code column indicates the statutory source for designating each substance as a CERCLA hazardous substance.
1 indicates that the statutory source is section 311b2 of the Clean Water Act 2 indicates that the source is section 307a. Ammonium chloride NHCl 6. Magnesium sulfate MgSO7HO 7.
Calcium chloride CaCl2 anhydrous 8. Ferric chloride FeCl3-6H 0 PREPARATION Phosphate Buffer Solution 1. Dissolve 85 grams KH2P04 2175 grams K2HP04 334 grams Na2HP047H20 and 17 grams NfyCl in about 500 mis distilled water.
Add distilled water to make 1 liter and mix thoroughly. Stable for about 1 month. Chloride occurs naturally in ground water as a component of deposited salts in geologic formations.
The levels of chloride may vary in water wells depending on the type of rock the ground water moves through and how long the ground water is in contact with the rock and has the ability to dissolve minerals. Deeper wells may have higher levels of chloride because the ground water has dissolved. The following spent halogenated solvents.
Tetrachloroethylene methylene chloride trichloroethylene 111-trichloroethane chlorobenzene 112-trichloro-122-trifluoroethane ortho-dichlorobenzene trichlorofluoromethane and 112-trichloroethane. All spent solvent mixturesblends containing before use a total of ten percent or more by volume of one or more of the above. CWA-equivalent treatment means biological treatment for organics alkaline chlorination or ferrous sulfate precipitation for cyanide precipitation sedimentation for metals reduction of hexavalent chromium or other treatment technology that can be demonstrated to perform equally or greater than these technologies.
Radioactive wastes mixed with K141-K145 and K147-K151 are also prohibited. Acetone reacts with many chemicals in a marked manner. 1 with phosphorus pentachloride yields acetone chloride CH32CCl2 2 with hydrogen chloride dry yields both mesityl oxide CH3COCHCCH32 liquid bp 132 C and phorone CH32CCHCOCH.
CCH32 yellow solid mp 28 C 3 with concentrated H2SO4 yields mesitylene C6H3CH33 135 4 with NH3 yields acetone. The observed effect was caused by easier CH activation of terminal methyl group as compared to the internal methylene fragment. In addition to that the steric effect of substituents at the β-position to alkene was also noticed to prevent the activation of internal methylene unit and therefore to increase the reaction yield.
Methylenecyclopropane moiety of 220 was involved. An efficient copper-catalyzed cascade reaction of 2-aminophenylmethanols with aldehydes using the combination of cerium nitrate hexahydrate and ammonium chloride leads to a wide range of 2-substituted quinazolines in good yields. The method tolerates a various functional groups and represents a convenient and practical strategy for synthesis of 2-substituted quinazoline derivatives.