Systematic names are more useful however because a systematic name specifies the actual structure of the compound. Systematic names are more useful however because a systematic name specifies the actual structure of the compound.

Cox-1Aspirin USAN also known as acetylsalicylic acid is a salicylate drug often used as ananalgesic to relieve minor aches and pains as an antipyretic to reduce fever and as an anti-inflammatory medication.
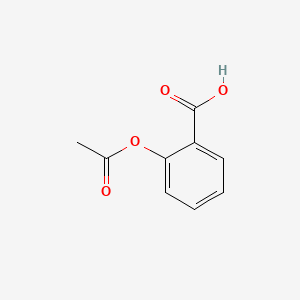
Chemical structure of aspirin. The 2D chemical structure image of aspirin is also called skeletal formula which is the standard notation for organic molecules. The carbon atoms in the chemical structure of aspirin are implied to be located at the corners and hydrogen atoms attached to carbon atoms are not indicated each carbon atom is considered to be associated with enough hydrogen atoms to provide the carbon atom. Aspirin is a salicylate drug often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains as an anti-inflammatory compound that inhibits Cox-1Target.
Cox-1Aspirin USAN also known as acetylsalicylic acid is a salicylate drug often used as ananalgesic to relieve minor aches and pains as an antipyretic to reduce fever and as an anti-inflammatory medication. The active ingredient of. Aspirin is an orally administered non-steroidal antiinflammatory agent.
Acetylsalicylic acid binds to and acetylates serine residues in cyclooxygenases resulting in decreased synthesis of prostaglandin platelet aggregation and inflammation. This agent exhibits analgesic antipyretic and anticoagulant properties. Aspirins chemical name is 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid.
Aspirin a chemical called acetylsalicylic acid ASA is widely used worldwide as an anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drug. The molecular formula for acetylsalicylic acid is C9H8O4 and the expanded formula is CH3COOC6H4COOH. Aspirin also known as acetylsalicylic acid ASA is a medication used to reduce pain fever or inflammation.
Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease pericarditis and rheumatic fever. Aspirin given shortly after a heart attack decreases the risk of death. Aspirin is also used long-term to help prevent further heart attacks ischaemic.
In the 1800s the Heyden Chemical Company was the first to mass-produce salicylic acid commercially. It was not until 1899 when a modified version named acetylsalicylic acid was registered and marketed by Bayer under the trade name aspirin. Even though it has been available since the early 1900s its real mode of action was not known until the late 1970s.
Some of the indications for aspirin. Structure properties spectra suppliers and links for. Jump to main content.
Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Light sensitiveReacts with aspirin. OU Chemical Safety Data No longer updated More details.
The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical ATC Classification System is a drug classification system that classifies the active ingredients of drugs according to the organ or system on which they act and their therapeutic pharmacological and chemical properties. Its purpose is an aid to monitor drug use and for research to improve quality medication use. It does not imply drug recommendation or.
Systematic names are more useful however because a systematic name specifies the actual structure of the compound. If the hydroxyl group is the principal functional group of a phenol the compound can be named as a substituted phenol with carbon atom 1 bearing the hydroxyl group. For example the systematic name for thymol is 5-methyl-2-isopropylphenol.
Phenols with only one other. My Library is designed to help you organize all your NSTA and personal learning resources. Resources may be sorted and further subdivided into smaller personalized collections.
In 1828 Johann Andreas Buchner Professor of Pharmacology at the University of Munich purified salicin from willow bark. A number of scientists worked on refining the process but it was Professor Hermann Kolbe at Marburg University who first worked out the chemical structure of salicylic acid and made it synthetically in 1859. The discovery of aspirin is customarily said to have resulted from Felix Hoffmanns rheumatic father encouraging his son to produce a medicine devoid of the unpleasant effects of sodium salicylate.
Hoffmann a chemist in the pharmaceutical laboratory of the German dye manufacturer Friedrich Bayer Co in Elberfeld consulted the chemical literature and came across the synthesis of. There is a limited amount of support for representing common chemical groups by an alias eg. Benzoic acid as Ph-COOH with two alias groups.
Internally in Open Babel the molecule usually has a real structure with the alias names present as only an alternative representation. For MDL MOL and SD files alias names can be read from or written to an A line. The more modern RGroup.
Willow tree bark extract oil of wintergreen and aspirin are similar in molecular structure and metabolic effect. All three belong to a group of chemicals called salicylates and are some of the oldest and most frequently used drugs. Willow trees contain salicin oil of wintergreen is methyl salicylate and aspirin is acetylsalicylic acid.
The main objective of the synthesis of aspirin lab was so produce aspirin acetylsalicylic acid through the reaction of salicylic acid and acetic anhydride. The methods used included recrystallization and scratching to produce a precipitate which was then filtered to remove any excess moisture. The results displayed a percent yield of 343 from a theoretical yield of about 197g of.
Aspirin acetylsalicylic acid is one drug that any chemist would predict based on the chemical structure alone to be relatively unstable. This is because aspirin belongs to a class of organic molecules called esters. Esters are formed when alcohols react with carboxylic acids.
A molecule of water is lost in the process. Heres a simple example Figure 1. Solutes such as aspirin dissolve in acid due to the chemical composition of the binder used in the tablet and the chemical nature of the solute.
Aspirin or acetylsalicylic acid or 2-hydroxybenzoic acid 2 carboxyphenyl ester has a benzene ring C6H6 which is hydrophobic water-hating and this portion of the molecule does not interact with water. However the molecule also has. We use cookies to help provide and enhance our service and tailor content.
To update your cookie settings please visit the Cookie Preference Center for this site. Aspirin is type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug NSAID effective in treating fever pain and inflammation in the bodyIt also prevents blood clots ie is antithrombotic. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs are used to treat pain and reduce inflammation from a variety of causes such as headaches injuries arthritis menstrual cramps and muscle aches.