76 Relative atomic mass. Gold is ductile as well as malleable in nature.
76 Relative atomic mass.
Chemical properties of tellurium. Tellurium is a chemical element with the symbol. Crystaline tellurium consists of parallel helical chains of Te atoms with three atoms per turn. This gray material resists oxidation by air and is not volatile.
Naturally occurring tellurium has eight isotopes. Six of those isotopes 120 Te 122 Te 123 Te 124 Te 125 Te and 126 Te are stable. The other two.
Tellurium is present in the Earths crust only in about 0001 parts per million. Tellurium minerals include calaverite sylvanite and tellurite. It is also found uncombined in nature but only very rarely.
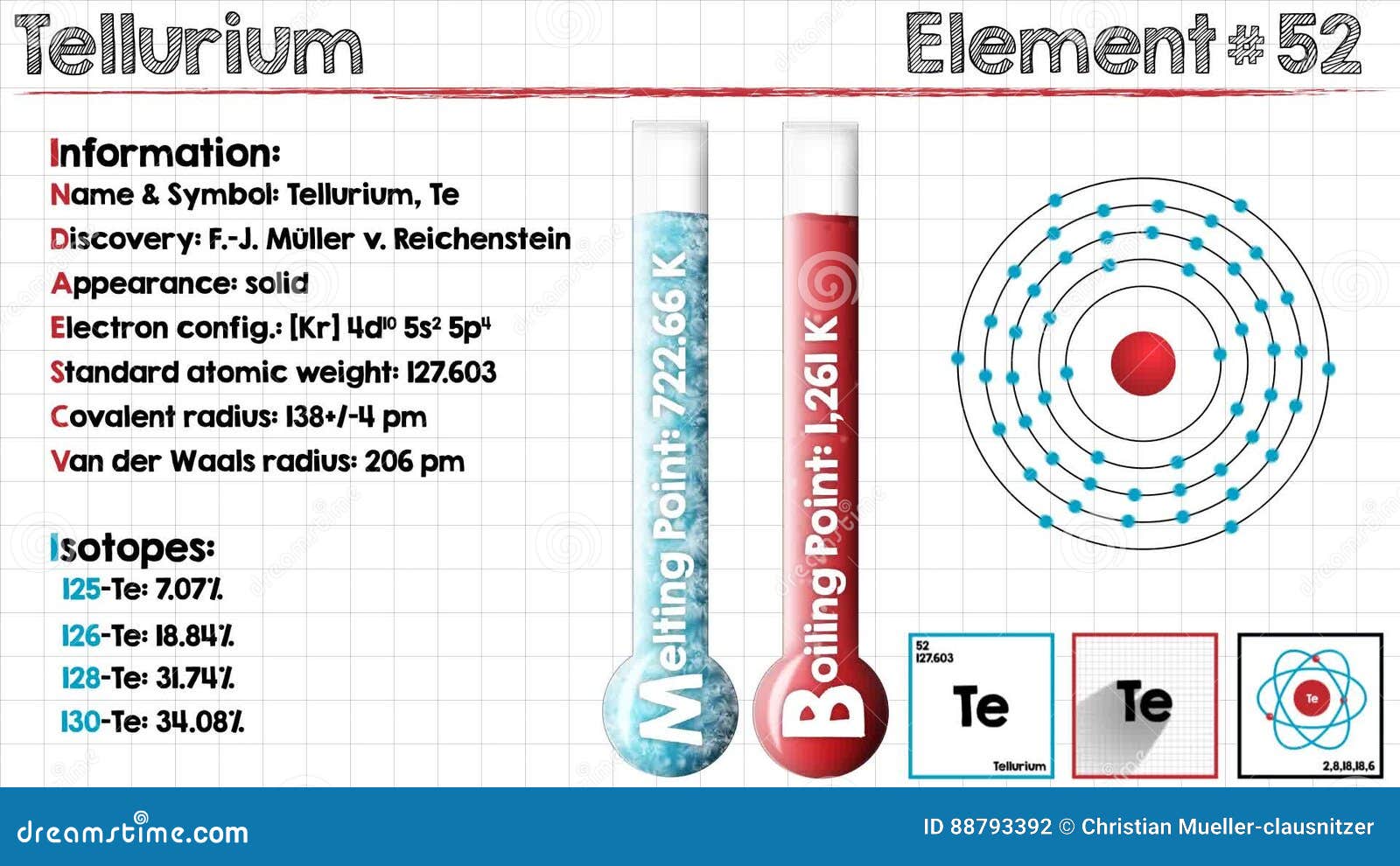
It is obtained commercially from the anode muds produced during the electrolytic refining of copper. These contain up to about 8 tellurium. Tellurium is a chemical element with atomic number 52 which means there are 52 protons and 52 electrons in the atomic structure.
The chemical symbol for Tellurium is Te. Tellurium is a brittle mildly toxic rare silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur.
It is occasionally found in native form as elemental. Tellurium is a chemical element with atomic number 52 which means there are 52 protons and 52 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Tellurium is Te.
Tellurium is a brittle mildly toxic rare silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur. It is occasionally found in native form as elemental.
Tellurium is a chemical element with atomic number 52 which means there are 52 protons and 52 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Tellurium is Te. Tellurium is a brittle mildly toxic rare silver-white metalloid.
Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur. It is occasionally found in native form as elemental. Here highly crystalline tellurium Te nanowires and two-dimensional nanosheets were synthesized by using chemical vapor deposition.
The low-dimensional Te shows high hole mobility and broadband detection. The blackbody-sensitive infrared detection of Te devices was demonstrated. A high responsivity of 6650 A W.
It also forms telluride minerals in its compound form with tellurium. Before going through the chemical properties let us have a look at the physical properties of gold. Gold is ductile as well as malleable in nature.
This means it can be drawn into wires and beaten into thin sheets. This soft metal is able to reflect heat as well as light. Gold is a metal and therefore a.
Generally elemental sodium is more reactive than lithium and it reacts with water to form a strong base sodium hydroxide NaOHIts chemistry is well explored. Reaction with air water and hydrogen. Sodium is ordinarily quite reactive with air and the reactivity is a function of the relative humidity or water-vapour content of the air.
Chemical properties of vanadium - Health effects of vanadium - Environmental effects of vanadium. Electronegativity according to Pauling. 61 gcm-3 at 20C.
0074 nm 3. Electronic shell Ar 3d 3 4s 2. In chemical activity and physical properties it resembles sulfur and tellurium.
Selenium appearsin a number of allotropic forms. The most popular are a red amorphous powder a red crystalline material and a gray crystalline metallike form called metallic selenium. This last form conducts electricity better in the light than in the dark and is used in photocells.
Selenium burns in air and is. A metalloid is a type of chemical element which has a preponderance of properties in between or that are a mixture of those of metals and nonmetalsThere is no standard definition of a metalloid and no complete agreement on which elements are metalloids. Despite the lack of specificity the term remains in use in the literature of chemistry.
The six commonly recognised metalloids are boron. The least abundant natural metalloid is tellurium. Metalloids are valuable in the electronics industry.
Silicon for example is used to make the chips found in phones and computers. Arsenic and polonium are highly toxic metalloids. Antimony and tellurium are used primarily in metal alloys to add desirable properties.
Of or relating to chemistry. Of or relating to the properties or actions of chemicals. Of or relating to chemical weapons.
A substance with a distinct molecular composition that is produced by or used in a chemical process. A drug especially an illicit or addictive one. When alloys have chemical compositions that do not fall into any of the other categories mentioned they are grouped together as special alloys.
Free machining properties are imparted upon coppe r alloys by the addition of Sulphur and Tellurium. C oppe r alloys are highly suited to recycling. The Chemical Abstracts Service registry number is a unique identifier of a particular chemical designed to prevent confusion arising from different languages and naming systems.
3033C 5491F 3306 K Period 6 Boiling point. 5008C 9046F 5281 K Block. D Density g cm 3 225872 Atomic number.
76 Relative atomic mass. 19023 State at 20C.