Silvery white tough and harder than iron nickel is widely familiar because of its use in coinage but is more important as the pure metal or in the form of alloys. Nickel chemical element ferromagnetic metal of Group 10 VIIIb of the periodic table markedly resistant to oxidation and corrosion.

Pure cobalt is obtained through smelting process which is hard and lustrous and release vapors of arsenic.
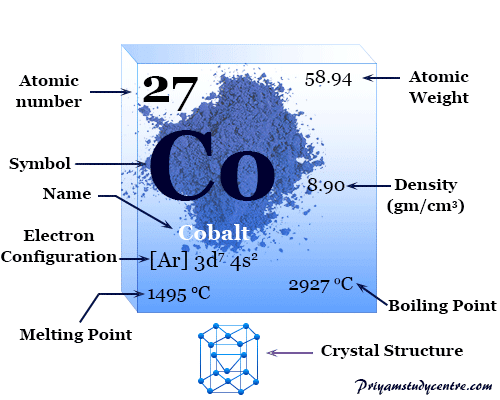
Chemical properties of cobalt. Chemical Properties Of Cobalt. 1495C 2723F 1768 K. 2927C 5301F 3200 K.
Density g cm3 886. Electron configuration Ar 3d 7 4s 2. ChemSpider is a free chemical structure database.
Cobalt metallic chemical element one of the transition elements atomic number 27. The metal is used especially for heat-resistant and magnetic alloys. A relatively large percentage of the worlds production goes into magnetic alloys such as the Alnicos for permanent magnets.
Cobalt is used in many alloys superalloys for parts in gas turbine aircrafr engines corrosion resistant alloys high-speed steels cemented carbides in magents and magnetic recording media as catalysts for the petroleum and chemical industries as drying agents for paints and inks. Cobalt blue is an important part of artists palette and is used bu craft workers in porcelain pottery. Chemical properties can only be established by changing a substances chemical.
Beryllium carbon calcium cobalt zinc and iron. Chemical stability - This chemical property in a given environment also referred to as thermodynamic stability of a chemical system refers to the stability that takes place when a chemical system is in its lowest energy state a state of chemical. Cobalt is a naturally occurring element found in rocks soil water plants and animals.
Cobalt is used to produce alloys used in the manufacture of aircraft engines magnets grinding and cutting tools artificial hip and knee joints. Cobalt compounds are also used to color glass ceramics and paints and used as a drier for porcelain enamel and paintsRadioactive cobalt is used for. Because of its impressive properties cobalt is an important component in wear resistant and corrosive resistant alloys.
And cobalt alloys and coatings are seen everywhere from drills to saws from aircraft turbines to prosthetic bone replacements. The fact that cobalt is magnetic has also been exploited with the Japanese invention of cobalt magnetic steel where adding cobalt to steel vastly. Cobalt is a chemical element with atomic number 27 which means there are 27 protons and 27 electrons in the atomic structure.
The chemical symbol for Cobalt is Co. Cobalt is found in the Earths crust only in chemically combined form save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element produced by reductive.
Its physical properties resemble iron and nickel. Cobalt is a ferromagnetic strongest magnet up to 1121 0 C. Its specific gravity is 89.
Pure cobalt is obtained through smelting process which is hard and lustrous and release vapors of arsenic. Cobalt is a is transition metal. It melts at 1495 o C and its boiling temperature is 2927 o C 2.
Cobalt is not very. Cobalt is a chemical element with atomic number 27 which means there are 27 protons and 27 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Cobalt is Co.
Cobalt is found in the Earths crust only in chemically combined form save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element produced by reductive. Introduction Chemical Properties Mechanical Properties Manufacturing Process Applications References.
Introduction to Stellite Alloys. Stellite alloys are a group of cobalt-chromium super-alloys consisting of complex carbides in an alloy matrix predominantly designed for high wear resistance and superior chemical and corrosion performance in hostile environments. Cobalt is found in cobaltite erythrite glaucodot and skutterudite ores.
Cobalt produces brilliant blue pigments which have been used since ancient times to color paint and glass. Cobalt is a ferromagnetic metal and is used primarily in the production of magnetic and high-strength superalloys. Co-60 a commercially important radioisotope is.
Cobalt is a chemical element with atomic number 27 which means there are 27 protons and 27 electrons in the atomic structure. These have similar chemical properties but palladium has the lowest melting point and is the least dense of them. Silver is a chemical element with atomic.
Cobalt is a chemical element with atomic number 27 which means there are 27 protons and 27 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical properties of this silvery gray crystalline transition metal are intermediate between rhenium and manganese. Ruthenium is a.
Cobaltous Sulfate is a reddish toxic metallic salt. Cobalt sulfate is used in the electrochemical industries as a drier in paints and inks as a coloring agent in storage batteries and as a supplement for Vitamin B12 deficiency. Exposure to cobalt sulfate results in irritation of the skin eyes and respiratory tract and affects the thyroid lungs heart and kidneys.
Physical Chemical Properties of Tungsten. Tungsten is one of the important strategic resources. Due to its excellent physical and chemical properties tungsten and its alloys are used to manufacture key armor-piercing components that attack various types of armored targets gyro inertial components for satellites and high-temperature anti-ablation components such as rockets combustion.
Here in this post we sort out and list 21 chemical elements and effects on steel properties. 21 Chemical Elements and Effects on Steel Mechanical Properties. Steel in general is an alloy of.
Chemical properties are all those properties that are visible only when any reaction is taking place between sodium and any other chemical substance. As per the periodic table sodium is more reactive than lithium and less reactive than potassium. Sodium readily reacts with oxygen to form sodium oxide.
When pure form of sodium comes in contact with air it forms sodium oxide instantly. Chemical properties of vanadium - Health effects of vanadium - Environmental effects of vanadium. Electronegativity according to Pauling.
61 gcm-3 at 20C. 0074 nm 3. Electronic shell Ar 3d 3 4s 2.
Nickel chemical element ferromagnetic metal of Group 10 VIIIb of the periodic table markedly resistant to oxidation and corrosion. Silvery white tough and harder than iron nickel is widely familiar because of its use in coinage but is more important as the pure metal or in the form of alloys. Properties Titanium has a melting point of 1660 - 10C boiling point of 3287C specific gravity of 454 with a valence of 2 3 or 4.
Pure titanium is a lustrous white metal with low density high strength and high corrosion resistance. Chemical Properties Of Iron. Density g cm 3 78 gcm-3 at 20C.
State at 20C. Electron configuration Ar 3d 6 4s 2. ChemSpider is a free chemical structure database.
What is iron. Aims scope Criteria for publication in Chemical Physics are novelty quality and general interest in experimental and theoretical chemical physics and physical chemistryArticles are welcome that deal with problems of electronic and structural dynamics reaction mechanisms fundamental aspects of catalysis solar energy conversion and chemical reactions in general involving atoms molecules. Dicobalt octacarbonyl is a white solid when of high purity but more typically is an orange-colored pyrophoric solid that is thermally unstable.
It is synthesised by the high pressure carbonylation of cobaltII saltsIn the method patented by James Eli Knap cobaltII acetate is heated to between 150 and 200 C and exposed to hydrogen and carbon monoxide. Knowledge of the physicochemical properties of potential chemical alternatives is a requirement of the alternatives assessment process for two reasons. First the inherent hazard of a chemical such as its capacity to interfere with normal biological processes and its physical hazards and environmental fate degradation persistence are determined by its intrinsic physicochemical properties.
This is the reason why they often exhibit several common oxidation states. There are three noteworthy elements in the transition metals family. These elements are iron cobalt and nickel and they are the only elements known to produce a magnetic field.
The Transition Metals are.