
Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol. This page explains what acid anhydrides are and looks at their simple physical properties such as boiling points.
An ester is a chemical compound derived from an acid organic or inorganic in which at least one OH hydroxyl group is replaced by an O alkyl group as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
Chemical properties of acid anhydrides. Acid anhydride is an organic functional group consisting of 2 acyl groups combined by an oxygen atom. The non-metals oxide which are capable of reacting with water are also called Acid anhydrides. To Learn detail about Acid Anhydride Synthesis Chemical Properties Uses and FAQS Visit BYJUS for.
The pKa dissociation constant of Ethanoic Acid is 476 at 25C. Chemical Properties of Ethanoic Acid Reactions of Ethanoic Acid Esterification Reaction. When any carboxylic acid reacts with any alcohol it leads to the formation of another class of chemical compounds named esters.
This reaction which leads to the formation of esters is known as esterification reaction. Given below is an. An ester is a chemical compound derived from an acid organic or inorganic in which at least one OH hydroxyl group is replaced by an O alkyl group as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol. They are important in biology being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable. This page explains what acid anhydrides are and looks at their simple physical properties such as boiling points.
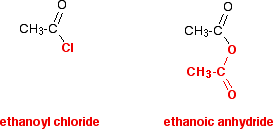
It introduces their chemical reactivity in a general way but details of specific reactions are given on separate pages - see the acid anhydrides menu link at the bottom of the page. What are acid anhydrides. The structure of acid anhydrides.
A carboxylic acid such as ethanoic. Carboxylic acid any of a class of organic compounds in which a carbon C atom is bonded to an oxygen O atom by a double bond and to a hydroxyl group OH by a single bond. A fourth bond links the carbon atom to a hydrogen H atom or to some other univalent combining group.
The carboxyl COOH group is so-named because of the carbonyl group CO and hydroxyl group. A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms with no change to the nuclei no change to the elements present and can often be described by a chemical equation.
Sorbic acid is a hexadienoic acid with double bonds at C-2 and C-4. It has four geometrical isomers of which the transtrans-form is naturally occurring. It is a hexadienoic acid a polyunsaturated fatty acid a medium-chain fatty acid and an alphabeta-unsaturated monocarboxylic acid.
It is a conjugate acid of a. Test prep MCAT Chemical processes Carboxylic acids. Carboxylic acid reactions overview.
This is the currently selected item. Carboxylic acid nomenclature and properties. Reduction of carboxylic acids.
Preparation of esters via Fischer esterification. Preparation of acyl acid chlorides. Preparation of acid anhydrides.
Hydrochloric acid solution is a colorless watery liquid with a sharp irritating odor. Consists of hydrogen chloride a gas dissolved in waterSinks and mixes with waterProduces irritating vapor. Preparation of acid anhydrides Opens a modal Preparation of amides using DCC Opens a modal Decarboxylation Opens a modal Alpha-substitution of carboxylic acids Opens a modal Practice.
Nomenclature and properties of acyl acid halides and acid anhydrides Opens a modal Nomenclature and properties of. Chemical Properties of Phosphoric Acid H 3 PO 4 Phosphoric acid is a deliquescent solid generally encountered as a viscous aqueous solution. It is weakly acidic with three possible sequential deprotonation steps forming phosphates.
Like carboxylic acids phosphoric acid can dimerize via a dehydration reaction to form phospho anhydrides. Phosphoric acid is referred to as being tribasic in. Chemical Synthesis Database.
ChemSynthesis is a freely accessible database of chemicals. This website contains substances with their synthesis references and physical properties such as melting point boiling point and density. There are currently more than 40000 compounds and more than 45000 synthesis references in the database.
A chemical waste is a hazardous waste due to corrosivity if. It is aqueous and has a pH less than or equal to 2 or greater than or equal to 125 or. It is a liquid and corrodes steel Type SAE 1020 at a rate greater than 635 mm approximately 0250 inch per year.
Polyesters are one of the most important classes of thermoplastic polymers. They can be formed from the reaction of a diacid or acid anhydride and a diol with the elimination of water or by ring-opening polymerization of cyclic di-esters. According to the composition of their main chain polyesters are classified as aliphatic semi.
The oxirane group of an epoxy monomer reacts with different curing agents such as aliphatic amines aromatic amines phenols thiols polyamides amidoamines anhydrides thiols acids and other suitable ring opening compounds. Forming rigid thermosetting products. The cured epoxies are brittle in nature due to the high degree of cross-linking and they contribute to weakening epoxy impact.