57 - 218 - 221. It has a flashpoint of 482 F.

Aspirin or acetylsalicylic acid is perhaps the most commonly used analgesic and antipyretic medication worldwide having been in clinical use for over 100 years.
Chemical formula for acetylsalicylic acid. Acetylsalicylic acid commonly known as Aspirin is a prototypical analgesic with a chemical formula C 9 H 8 O 4. It is also known as aspirin or 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid. It appears as a crystalline powder which is colourless to white.
Generally it has no smell but when in moist air it acquires a smell of acetic acid. It has a flashpoint of 482 F. It is most widely used in medication to treat.
Acetylsalicylic acid was first produced by Alsatian Chemist Charles Frederic Gerhardt in 1853 from sodium salicylate and acetyl chloride. Soon the drug became famous and Bayer a drug and dye firm started producing it at large scale. Bayer named it Aspirin.
It was Bayers brand name for the drug. Its popularity declined in 1962 after the synthesis of drugs like paracetamol and ibuprofen. Aspirin is a salicylate drug often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains as an anti-inflammatory compound that inhibits Cox-1Target.
Cox-1Aspirin USAN also known as acetylsalicylic acid is a salicylate drug often used as ananalgesic to relieve minor aches and pains as an antipyretic to reduce fever and as an anti-inflammatory medication. The active ingredient of. Aspirin or acetylsalicylic acid is perhaps the most commonly used analgesic and antipyretic medication worldwide having been in clinical use for over 100 years.
Aspirin can cause several forms of liver injury. In high doses aspirin can cause moderate to marked serum aminotransferase elevations occasionally with jaundice or signs of liver dysfunction and in lower doses in susceptible. In some countries this medicine may only be approved for veterinary use.
In the US Acetylsalicylic Acid is a member of the following drug classes. Platelet aggregation inhibitors salicylates and is used to treat Angina Angina Pectoris Prophylaxis Ankylosing Spondylitis Antiphospholipid Syndrome Aseptic Necrosis Back Pain Fever Heart Attack Ischemic Stroke. Aspirin also known as acetylsalicylic acid ASA is a medication used to reduce pain fever or inflammation.
Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease pericarditis and rheumatic fever. Aspirin given shortly after a heart attack decreases the risk of death. Aspirin is also used long-term to help prevent further heart attacks ischaemic.
Acetylsalicylic acid Commonly known or available as Aspirin DrugBank Accession Number DB00945 Background. Also known as Aspirin acetylsalicylic acid ASA is a commonly used drug for the treatment of pain and fever due to various causes. Acetylsalicylic acid has both anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects.
This drug also inhibits platelet aggregation and is used in the prevention of blood. 50-78-2 HC 12 H 17 ON 4 SCl 2. Thiamine hydrochloride vitamin B 1 hydrochloride.
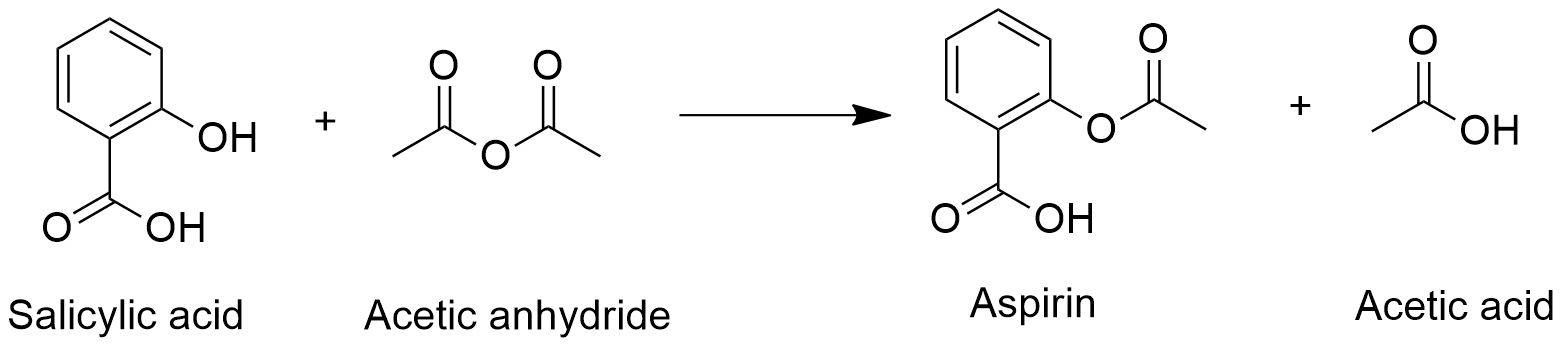
Hydrochloric acid hydrogen chloride. Aspirin is prepared from the reaction of salicylic acid C 7 H 6 O 3 and acetic anhydride C 4 H 6 O 3 to produce aspirin C 9 H 8 O 4 and acetic acid HC 2 H 3 O 2. The formula for this reaction is C 7 H 6 O 3 C 4 H 6 O 3 C 9 H 8 O 4 HC 2 H 3 O 2.
How many grams of salicylic acid are needed to make 1000 1-gram tablets of aspirin. Assume 100 percent yield Solution. For example in an experiment in which you prepare acetylsalicylic acid aspirin from salicylic acid you know from the balanced equation for aspirin synthesis that the mole ratio between the limiting reactant salicylic acid and the product acetylsalicylic acid is 11.
Acid anhydrides are the molecules that are capable of forming acidic solutions in water. The meaning of anhydride is the removal of water. Acid anhydride is an organic functional group consisting of 2 acyl groups combined by an oxygen atom.
The non-metals oxide which are capable of reacting with water are also called Acid anhydrides. To Learn detail about Acid Anhydride Synthesis Chemical. BSYNRYMUTXBXSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copy CAS Registry Number.
This structure is also available as a 2d Mol file or as a computed 3d SD file The 3d structure may be viewed using Java or Javascript. Arachidonic acid is a long-chain fatty acid that is a C20 polyunsaturated fatty acid having four Z-double bonds at positions 5 8 11 and 14. It has a role as a human metabolite an EC 3111 carboxylesterase inhibitor a Daphnia galeata metabolite and a mouse metabolite.
C9H8O4 Acetylsalicylic acid Aspirin is one of the most common medicines we have heard since childhood. It is used to treat pain fever and inflammations. Acetylsalicylic acid is the major component of aspirin and many other medicines.
List the common names together with the chemical names and formulae of 20 household chemicals. Identify 20 chemicals in everyday household items which is a hint to read the ingredients labels on packets of cleaning materials paints and other containers of substances in your home. Or other similar questions which may ask for more or fewer examples.
Chemical Name Trivial Name Formula Melting Point o C Equivalent Weight geq Amide Melting Point o C Diamide Melting Point o C pka 1 pka 2. 2-butynedioic acid acetylenedicarboxylic acid HOOCCCCOOH. 57 - 218 - 221.
2-acetoxybenzoic acid acetylsalicylic acid CH 3 COOC 6 H 4 COOH. 144 - 145 - 355. 4-acetylbenzoic acid—-CH 3 COC 6 H 4 COOH.
The information below refers to products available in the United States that contain aspirin. Acetylsalicylic Acid Ecotrin Aspir 81 Bayer Aspirin Drug classes. Platelet aggregation inhibitors salicylates Aspirin systemic is used in the treatment of.
Chemical Formula C 24 H 40 O 4 Synonyms 3alpha5beta7beta-37-dihydroxycholan-24-oic acid 3α5β7β-37-dihydroxycholan-24-oic acid. The drug decreases the. Felix Hoffmann a German chemist produced a stable form of acetylsalicylic acid more commonly known as aspirin.
Aspirin is a derivative of salicylic acid that is a mild nonnarcotic analgesic useful in the relief of headache and muscle and joint aches. Esterification is a chemical reaction used for making esters. The reaction in which a Carboxylic acid combines with an alcohol in.