MSDS - See attached file 4. Fragments appear due to bond cleavage next to CO alkoxy group loss -OR and hydrogen rearrangements.

Explosive range 54 to 16 vv in air.
Carboxylic acid mw. Chapter 5 Carboxylic Acids and Esters 17 Common Name Structural Formula BP C MP C Solubility g100 mL H2O Formic acid HCO2H 101 8 Infinite Acetic acid CH3CO2H 118 17 Infinite Propionic acid CH3CH2CO2H 141 -21 Infinite Butyric acid CH3CH22CO2H 164 -5 Infinite Valeric acid CH 3CH23CO2H 186 -34 5 Caproic acid CH3CH24CO2H 205 -3 1. A dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl functional groups COOH. The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as HO 2 CRCO 2 H where R can be aliphatic or aromatic.
In general dicarboxylic acids show similar chemical behavior and reactivity to monocarboxylic acidsDicarboxylic acids are also used in the preparation of copolymers. PEI 25K is a powerful trusted and cost-effective transient transfection reagent. In HEK293 and CHO expression systems PEI offers consistently high gene expression on a wide scale 96 well plates up to 100 L bioreactors.
Each year more researchers and companies turn to Polysciences PEI to gain a critical edge in their work. Relative to most other options using PEI to prepare transfection. The current experiment uses the carboxylic acid derivative acetic anhydride for ester formation.
The advantage of using acetic anhydride is that you do not produce water which can be used for hydrolysis of the newly formed ester. Concentrated sulfuric acid will be used to keep everything in the protonated state. Acetic anhydride is the preferred acid derivative to synthesize aspirin.
Carboxylic Acids Esters Amides. Carboxylic Acids M weak in aliphatic acids. 24-dimethylbenzoic acid O OH H3C CH3 MW 150 M 150 mz 77 132 M-18 133 M-17 strong M O O H C O H - H2O.
Fragmentation Esters methyl butyrate OCH3 O MW 102 M 102 71 M-31 59 M-43 74 M-28 15 M-87 OCH3 O H McLafferty CH3 α cleavage CH3CH2CH2 43 M-59 O OCH3. In short chain acids peaks due to the loss of OH molecular ion less 17 and COOH molecular ion less 45 are prominent due to cleavage of bonds next to CO. 2-Butenoic acid C 4 H 6 O 2 with MW 8609.
Fragments appear due to bond cleavage next to CO alkoxy group loss -OR and hydrogen rearrangements. Ethyl acetate C 4 H 8 O 2 with MW 8811. Product is the conjugate base of citric acid a carboxylic acid.
In a water solution sodium citrate dissociates into sodium ions and citric acid. MSDS - See attached file 4. Number of Field Applications.
Case Studies - See attached files 6. Sodium citrate is used to stabilize hydrogen peroxide. Conventional use of hydrogen peroxide involves the.
Strong base amine a weak acid phenol a strong acid carboxylic acid or a neutral substance aldehyde ketone alcohol ester. The common solvents used to determine solubility types are. Water 15M HCl concentrated H 2 SO 4 06M NaHCO 3 25M NaOH and organic solvents.
A flowchart showing the sequence of solubility tests along with the appropriate conclusions is shown in Figure 1. Butyric acid from Ancient Greek. βούτῡρον meaning butter also known under the systematic name butanoic acid is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CO 2 H.
It is an oily colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. Isobutyric acid 2-methylpropanoic acid is an isomer. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates.
Carboxylic acidreactive chemical groups Carboxylic acids COOH exist at the C-terminus of each polypeptide chain and in the side chains of aspartic acid Asp D and glutamic acid Glu E. Like primary amines carboxyls are usually on the surface of protein structure. An amphiphilic HA derivative was prepared by the amidation of the carboxylic group of the glucuronic acid called HYADD4-G HY4.
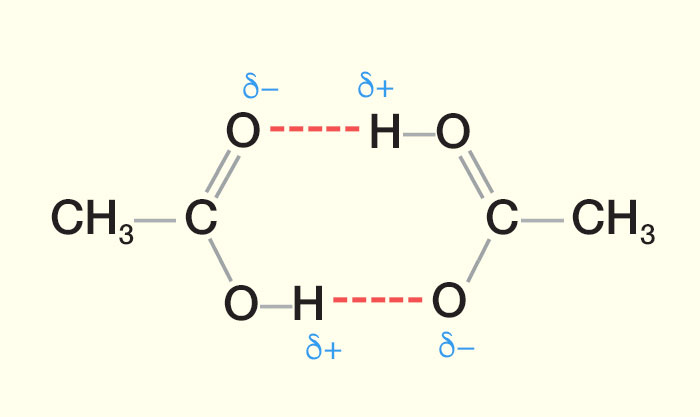
Compared viscoelastic properties of HY4 at a concentration of 5 mgmL in phosphate buffered saline with solutions of native HA having the same MW. The addition of HY4 to equine SF increased its. MW18 MW58 MW925 O MW74 bp 100 C bp -0 C bp 77 C bp 116 C C 6H 6 C 6H 6OH C 6H 6CH 3 C 6H 6CH 2OH MW78 MW94 MW92 MW108 bp 80 C bp 182 C bp 110 C bp 203 C 81 Alcohols and phenols like water can form hydrogen bonds.
Non covalent interaction between a hydrogen atom δ involved in a polar covalent bond with the lone pair of a heteroatom usually O or N which. Actually a magnesium carboxylate ie. The magnesium salt of a carboxylic acid.
In order to obtain the desired carboxylic acid this intermediate must be treated with a strong acid such as aqueous HCl during the work-up process. The addition of acid also serves to decompose any residual magnesium metal and causes the resulting magnesium salts to dissolve in the aqueous layer to facilitate. ACETIC ACID 1603 CH 3COOH MW.
1603 Issue 2 EVALUATION. 15 May 1989 Issue 2. 15 August 1994 OSHA.
STEL 15 ppm ACGIH. STEL 15 ppm 1 ppm 246 mgm3 NTP PROPERTIES. D 1049 gmL 25 C.
VP 15 kPa 114 mm Hg 20 C. Explosive range 54 to 16 vv in air. Vulcanization is a chemical process in which the rubber is heated with sulphur accelerator and activator at 140160C.
The process involves the formation of cross-links between long rubber molecules so as to achieve improved elasticity resilience tensile strength viscosity hardness and weather resistance. In short it was found that a compound with the parameters NO 8 MW 400 and acid pK a 4 was likely to be a P-gp substrate while those with parameters NO 4 MW 400 and base pK a 8 was less likely to be a substrate. 33 These guidelines are useful and enable researchers to monitor specific physicochemical properties as well as charge states to gauge P-gp susceptibility.
Phenol the cresols methylphenols and other simple alkylated phenols can be obtained from the distillation of coal tar or crude petroleum. Many phenolic compounds were discovered and used long before chemists were able to determine their structures. Therefore trivial names ie vanillin salicylic acid pyrocatechol resorcinol cresol hydroquinone and eugenol.
Firstly degradation tend to increase the number of carboxylic acid chain ends known to autocatalyze ester hydrolysis. Secondly only soluble oligomers in the surrounding aqueous medium are found to escape from the matrix. Before the completion of degradation the soluble oligomers closer to the surface can be leached out while those in the core of the matrix remain entrapped.
As the latter. These are compounds containing or derived from a bile acid or alcohol and which bears exactly two carboxylic acid groups. Kingdom Organic compounds Super Class Lipids and lipid-like molecules Class Steroids and steroid derivatives Sub Class Bile acids alcohols and derivatives Direct Parent Dihydroxy bile acids alcohols and derivatives Alternative Parents 7-alpha-hydroxysteroids 3-alpha.
2-amino- 4-hydroxypteridine-6-carboxylic acid produced by oxidn of folic acid reacts with nickel 2 to form metal complex which is extracted with isobutyl me ketone. Folic acid is determined indirectly from its nickel 2 content by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Bunseki kagaku 25 8.
509-13 1976 hazardous substances data bank hsdb ac polarograms of folic acid. EnamineStore - service for online shopping for products supplied by Enamine Ltd. It includes reagents for synthesis Building Blocks and screening compounds.
The higher the concentration of the reactants the more opportunity they have to react and the faster the reaction. According to Bahrami et al. 2001 solubility in NaOH is due to saponification.
Saponification is the hydrolysis of an ester under basic conditions to form an alcohol and the salt of a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acid-reactive chemical groups Carboxylic acids COOH exist at the C-terminus of each polypeptide chain and in the side chains of aspartic acid Asp D and glutamic acid Glu E. Like primary amines carboxyls are usually on the surface of protein structure.
Perfluorooctanoic acid PFOA is a long-chain perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acid PFCA a subset of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances PFAS that does not occur naturally in the environment. EPA has investigated PFOA because it. Is very persistent in the environment.
Is found at very low levels both in the environment and in the blood of the general US. Remains in people for a. Organic chemicals and Derivatives.
C 7 H 8 N 2 O 2. 34PNOT2-Methyl-4-NitroamilineFast Red1-amino-2-methyl-4-nitrobenzene2-amino-1-methyl-5-nitrobenzenemeisei fast red rl basemitsui red rl base.