Treatment of poisoning by susceptible organophosphorous nerve agents having cholinesterase activity as well as organophosphorous or carbamate insecticides. Z7702 Contact with and suspected exposure to.
Naphthalene is a white volatile solid polycyclic hydrocarbon with a strong mothball odor.
Carbamate insecticides exposure. DO NOT use it to treat or manage an actual poison exposure. If you or someone you are with has an exposure call your local emergency number such as 911 or your local poison center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline 1-800-222-1222 from anywhere in the United States. Most household bug sprays contain plant-derived chemicals.
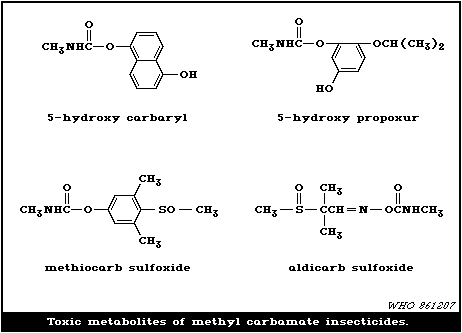
Exposures may be episodic eg pulsed deliveries of insecticides with stormwater runoff or sustained eg long-term exposure to insecticide-contaminated sediments and the bioavailability uptake and toxicity of insecticides during these exposures will. Carbamate pesticides such as aldicarb carbofuran and ziram are another class of chemical pesticides that have been associated with endocrine-disrupting activity 10 93 possible reproductive disorders 63 93 and effects on cellular metabolic mechanisms and mitochondrial function Moreover in vitro studies have revealed the ability of carbamate pesticides to. The carbamate insecticides are derivatives of carbamic acid as the OPs are derivatives of phosphoric acid.
And like the OPs. Visible activity such as feeding and egg laying stops shortly after exposure though death may not occur for several days. The fumigants are small volatile organic molecules that become gases at temperatures above 40F.
They are usually heavier than. Carbamate insecticides have similar mechanisms to organophosphates but have a much shorter duration of action and are somewhat less toxic. Pyrethroid pesticides mimic the insecticidal activity of the natural compound pyrethrin the biopesticide found in Pyrethrum Now Chrysanthemum and Tanacetum species.
These compounds are nonpersistent sodium channel. Organophosphate and carbamate insecticides eg. Malathion and bendiocarb respectively are more expensive than DDT per kilogram and are applied at roughly the same dosage.
Pyrethroids such as deltamethrin are also more expensive than DDT but are applied more sparingly 00203 gm 2 vs 12 gm 2 so the net cost per house per treatment is about the same. Symptoms observed as a result of human exposure to these toxins are vomiting dermatitis cough and rhinitis. Ochratoxin A OTA is a toxic metabolite formed by Aspergillus ochraceus Penicillium verrucosum and other mould species.
It is one of the most commonly occurring mycotoxins in improperly stored food. OTA has been found in corn peanuts and decaying vegetation. Prohibited in areas where application may result in exposure to endangered species.
Group 3A REI 12h Brigadier. A broad-spectrum carbamate insecticide with translaminar activity. Works on contact and short-term via ingestion of treated foliage on all pest life stages.
Registered as a foliar spray on a variety of crops for control of aphids caterpillars and beetles including brown. Among agriculturalists of developing countries pesticide exposure is the primary occupational hazard Wasseling et al 2001. The functional group present in carbamate insecticides are carbamate esters.
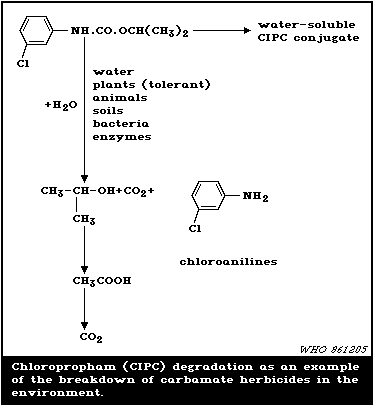
Their mechanism of action is by reversible inactivation of the enzyme acteylcholinesterase. Carbamates break down in the environment within weeks or months Goel. Insecticides cause the greatest number of pesticide poisonings in the United States.
The most serious pesticide poisonings usually result from acute exposure to organophosphate and carbamate insecticides. Organophosphate insecticides include chlorpyrifos diazinon dimethoate disulfoton malathion methyl parathion and ethyl. Chronic exposure to disulfoton may result in tolerance to toxicity.
Ethyl 4-Nitrophenyl Phenylphosphonothioate EPN. EPN is a nonsystemic insecticide and acaricide structurally related to parathion. The acute oral LD 50 in rats is 836 mgkg.
EPN at a dosage of 10 mgkg was found to be nontoxic to adult cattle and sheep. The minimum oral toxic dose of EPN is 25 mgkg in calves and 25. Most pesticide poisoning cases involve either organophosphate or carbamate insecticides.
Both chemical groups affect humans by inhibiting acetyl cholinesterase an enzyme essential to proper functioning of the nervous system. Some organophosphate and carbamate insecticides commonly used in Nebraska are listed in Table II. Poison - poison - Types of poison.
In regard to poisoning chemicals can be divided into three broad groups. Agricultural and industrial chemicals drugs and health care products and biological poisonsie plant and animal sources. These three groups along with a fourth category radiation are discussed below.
The majority of agricultural chemicals are pesticides which include. Malathion is toxic via skin contact ingestion and inhalation exposure. Malathion and other organophosphate insecticides bind to the enzyme acetylcholinesterase AChE at nerve endings throughout the bodies of insects and other organisms.
9 Under normal circumstances AChE binds to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine ACh at the nerve junction effectively ending the stimulation of the. Z770 Contact with and suspected exposure to haza. Z7701 Contact with and suspected exposure to haza.
Z77010 Contact with and suspected exposure to arse. Z77011 Contact with and suspected exposure to lead. Z77012 Contact with and suspected exposure to uran.
Z77018 Contact with and suspected exposure to othe. Z7702 Contact with and suspected exposure to. The Recognition and Management of Pesticide Poisonings.
6 th Edition manual gives healthcare providers a quick reference resource for the best toxicology and treatment information for patients with pesticide exposures. This manual also guides clinicians on how to. Conduct environmental and occupational exposure screening on patients.
Report of exposure incidents. Some organophosphate insecticides such as acephate azinphos methyl chlorpyrifos ethoprophos ethyl- parathion and phorate are very toxic to earthworms. The other organophosphate insecticides listed are nontoxic to moderately toxic to earthworms.
Carbamate insecticides and fungicides are very toxic to earthworms. Carbaryl and carbofuran both commonly used in field crop. Treatment of poisoning by susceptible organophosphorous nerve agents having cholinesterase activity as well as organophosphorous or carbamate insecticides.
Usual Pediatric Dose for Nerve Agent Poisoning. Children weighing over 90 pounds. 2 mg dose 40 to 90 pounds.
1 mg dose 15 to 40 pounds. The routes of exposure involve ingested gastric toxins contact exposure expectorant and evaporators. Animals or plants when treated with systemic pesticides the chemicals move to untreated parts of the organism.
Systemic herbicides travel through plants and can reach untreated parts of roots leaves or stems. They are effective in killing weeds with an incomplete spray cap. A general introduction EHC 64 1986 Carbaryl EHC 153 1994.
Dermal exposure EHC 242 2014 Di-n-butyl phthalate EHC 189 1997 Diaminotoluenes EHC 74 1987 Diazinon EHC 198 1998 Dibromoethane 12- EHC 177 1996 Dichloroethane 12- EHC 176 1995 2nd edition Dichloroethane 12- EHC 62 1987 1st edition Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid 24- 24-D EHC. The purpose of this document is to enable health care workers and public health officials to recognize an unknown or suspected exposure to a nerve agent or an organophosphate OP pesticide. Nerve agents are chemical warfare agents that have the same mechanism of action as OP organophosphate pesticides insecticides.
They are potent inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. The nicotine-based neonicotinoids were developed in the mid-1990s in large part because they showed reduced toxicity to wildlife compared with previously used organophosphate and carbamate insecticides. The scientific data about the impact of pesticides and neonicotinoids in particular at environmentally and agriculturally realistic levels is.
Propoxur is a carbamate insecticide that is extremely toxic to these bugs. The Environmental Protection Agency in the United States is reluctant to approve this insecticide for use indoors. If children have chronic exposure to the chemical it could be toxic to them.
However this does not mean that a harsh pesticide is necessary for eradication. Today there a several pesticides that is. Some of these agents may lead to cancer after only a very small exposure while others might require intense exposure over many years.
Again refer to the agencies reports for specifics. Even if a substance or exposure is known or suspected to cause cancer this does not necessarily mean that it can or should be avoided at all costs. For example sunlight is a major source of ultraviolet.
Naphthalene is a white volatile solid polycyclic hydrocarbon with a strong mothball odor. Naphthalene is obtained from either coal tar or petroleum distillation and is primarily used to manufacture phthalic anhydride but is also used in moth repellentsExposure to naphthalene is associated with hemolytic anemia damage to the liver and neurological system cataracts and retinal hemorrhage.