
Calcium Nitrate CaOH2 Calcium Hydroxide Ca3PO32 Calcium Phosphate Ca3PO42 Tricalcium Phosphate Ca3N2 Calcium Nitride CaBr2 Calcium Bromide CaC2 Calcium Carbide CaCl2 Calcium Chloride CaCO3 Calcium Carbonate CaF2 Calcium Fluoride CaH2 Calcium Hydride CaI2 Calcium Diiodide CaO Calcium Oxide CaS Calcium Sulfide CaSO4 Calcium Sulfate CBr4. Calcium is used as a reducing agent in order to extract metals such as uranium zirconium and throium.
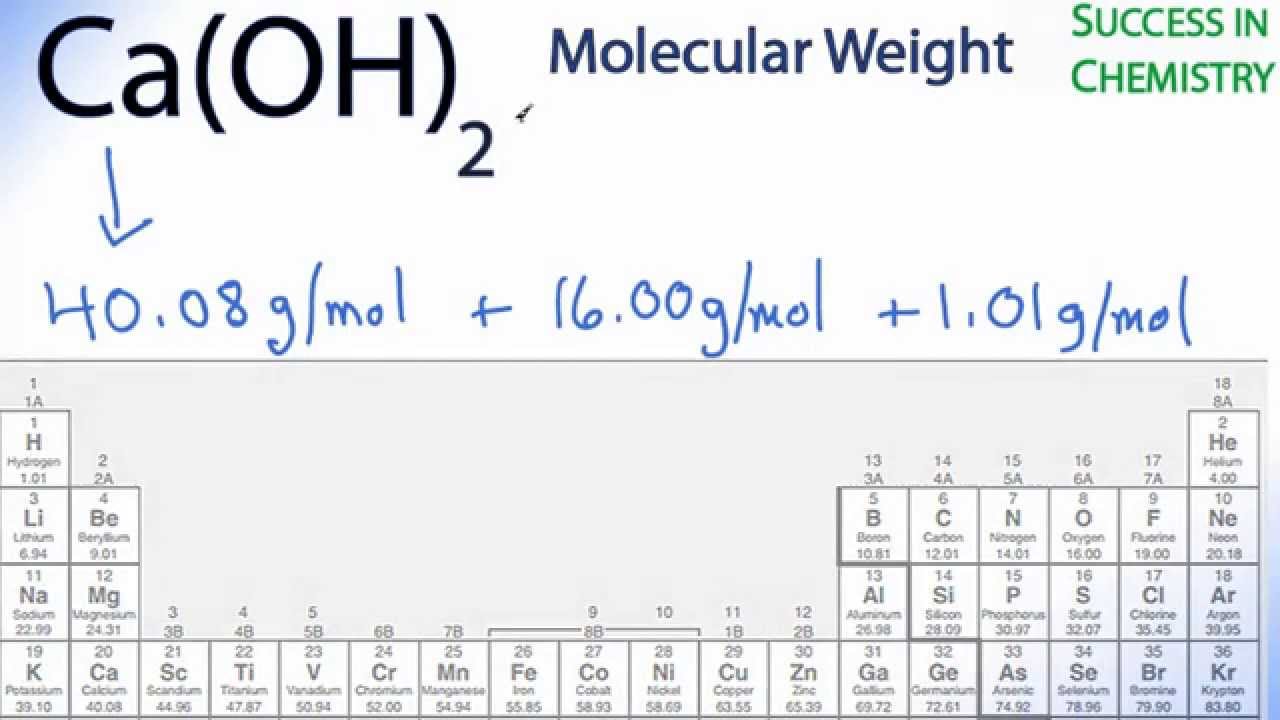
Calcium hydroxide CaOH 2 is a strong base though it is not as strong as the hydroxides of strontium.
Calcium hydroxide mass. Calcium hydroxide traditionally called slaked lime is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca 2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime calcium oxide is mixed or slaked with water. It has many names including hydrated lime caustic lime builders lime slacked lime cal and pickling lime.
Calcium hydroxide is used. 74093 grams per mole. 2211 grams per cubic centimetre.
White powder or colourless crystal. CaOH 2 has a hexagonal crystal structure. It is not very soluble in water and its solubility reduces with an increase in temperature.
For example its solubility at 0 o C is 189 gL and. Calcium hydroxide formulations are also used during treatment of root perforations root fractures and root resorption and have a role in dental traumatology for example following tooth avulsion and luxation injuries. The purpose of this paper is to review the properties and clinical applications of calcium hydroxide in endodontics and dental traumatology including its antibacterial activity.
Calcium Hydroxide CaOH 2. Also commonly referred to as slaked lime or hydrated lime. Calcium hydroxide is formed as a result of hydrating lime calcium oxide CaO.
Lime is by far the most economically favorable alkaline reagent to use for acid neutralization. Lime is significantly cheaper than caustic NaOH but is much more difficult to handle. Lime forms a Two Normal solution in water.
Calcium hydroxide CaOH 2 is a strong base though it is not as strong as the hydroxides of strontium. Amu at room temperature. Mass-dependent differences in calcium isotope composition are conventionally expressed by the ratio of two isotopes usually 44 Ca 40 Ca in a sample compared to the same ratio in a standard reference material.
44 Ca 40 Ca varies by about 1 among common. 2 moles of HCl solution reacts with one mole Calcium Hydroxide Ca OH_2 One mole of HCl has mass. 365 gmol two moles of HCl will have mass 73 g.
One mole of Ca OH_2 has mass 741 g. 73 g of HCl reacts with 741 g of Ca OH_2 1g of HCl reacts with 741g 73 of Ca OH_2 1g of HCl reacts with 1015 g of Ca OH_2. 250 mL is 25 times more than 100 mL so if 012 g calcium hydroxide dissolved in 100 mL water produces a saturated solution then 012 25 30 g calcium hydroxide dissolved in 250 mL water will produce a saturated solutution.
State your solution to the problem. The minimum mass of calcium hydroxide required is 030 g. Calcium phosphate solubility is 20 mgL and that of calcium fluoride is 16 mgL.
Calcium chromate solubility is 170 gL and at 0 o C calcium hypo chlorate solubility is 218 gL. Solubility of other calcium compounds lies between the levels of these examples for example calcium arsenate 140 mgL calcium hydroxide 13 gL and calcium sulphate 27-88 gL. Calcium Nitrate CaOH2 Calcium Hydroxide Ca3PO32 Calcium Phosphate Ca3PO42 Tricalcium Phosphate Ca3N2 Calcium Nitride CaBr2 Calcium Bromide CaC2 Calcium Carbide CaCl2 Calcium Chloride CaCO3 Calcium Carbonate CaF2 Calcium Fluoride CaH2 Calcium Hydride CaI2 Calcium Diiodide CaO Calcium Oxide CaS Calcium Sulfide CaSO4 Calcium Sulfate CBr4.
Sodium hydroxide NaOH - Sodium hydroxide is an ionic compound. The molecular weight of sodium hydroxide is 40 gmol. It is a white translucent crystalline solid and used in the manufacturing of detergents and soaps.
To learn about the structure Properties Preparation Uses Health Hazards and FAQs of Sodium hydroxide NaOH. Visit BYJUS for more information. What mass of aluminum hydroxide is formed.
T-31 13 What volume of 125 M sulfuric acid is needed to dissolve 0750 g of aluminum hydroxide. What is the molarity of the resulting solution of aluminum sulfate. Assume final solution volume volume of sulfuric acid used 14 Silver chloride is formed by mixing silver nitrate and barium chloride solutions.
What volume of 150 M barium chloride. Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and an atomic mass of 40078. Here are some of the more common uses of calcium in the world today.
Calcium is used as a reducing agent in order to extract metals such as uranium zirconium and throium. Cheese is made using calcium ions to promote the coagulation of milk. Cement and mortar important when constructing buildings.
Calcium compounds are widely used. There are vast deposits of limestone calcium carbonate used directly as a building stone and indirectly for cement. When limestone is heated in kilns it gives off carbon dioxide gas leaving behind quicklime calcium oxide.
This reacts vigorously with water to give slaked lime calcium hydroxide. Calcium can be determined by EDTA titration in solution of 01 M sodium hydroxide pH 12-13 against murexide. Just like during.
Read mass of calcium in the titrated sample in the output frame. In general this is a simple titration with no other problems then those listed as general sources of titration errors. In the presence of huge amounts of magnesium there is a risk.
Chemical Reaction Formula Atomic Mass Formula Chemical Formula Enthalpy Formula Entropy Formula Molality Formula Molar. Sulfurous acid Formula Ammonia Formula Sodium hydroxide Formula Potassium hydroxide Formula Sodium hypochlorite Formula Calcium hydroxide Formula Sodium hydride Formula Magnesium hydroxide Formula Sodium hydrogen carbonate Formula Sodium amide Formula. Calcium is an essential nutrient found in many foods such as dairy products.
The bones and teeth contain over 99 of all calcium in the human body. Bones are always breaking down and rebuilding. Conversions between mass and particles MUST go through the mole How many molecules are in 385 g of carbon dioxide.
How many oxygen atoms are in 812 g of calcium hydroxide. What is the mass of 356 x 1025 formula units of copper II sulfate. What is the number of molecules present in 5000 g of diphosphorus pentoxide.
Calcium lactate is a salt that consists of two lactate anions for each calcium cation Ca2. It is prepared commercially by the neutralization of lactic acid with calcium carbonate or calcium hydroxideApproved by the FDA as a direct food substance affirmed as generally recognized as safe calcium lactate is used as a firming agent flavoring agent leavening agent stabilizer and thickener. Calcium hydroxide CaOH 2 Magnesium carbonate MgCO 3 Sodium hydrogen carbonate NaHCO 3 Barium hydroxide BaOH 2 Chromium III oxide Cr 2 O 3.
Balancing Chemical Equations Answer Key Balance the equations below. 1 1 N 2 3 H 2 2 NH 3 2 2 KClO 3 2 KCl 3 O 2 3 2 NaCl 1 F 2 2 NaF 1 Cl 2 4 2 H 2 1 O 2 2 H 2 O 5 1 PbOH 2 2 HCl 2 H 2 O 1 PbCl 2 6 2 AlBr. The use of 26 Al as a tracer and accelerator mass spectrometry has enabled safe studies of aluminium toxicokinetics with real exposure-relevant doses in humans.
Aluminium bioavailability from occupational inhalation exposure is 2 whereas oral aluminium bioavailability from water has been reported to be 01 to 04. Oral aluminium bioavailability is increased by citrate acidic pH and. The formation of the calcium hydroxide and calcium silicate hydrate crystals provide seeds upon which more calcium silicate hydrate can form.
The calcium silicate hydrate crystals grow thicker making it more difficult for water molecules to reach the unhydrated tricalcium silicate. The speed of the reaction is now controlled by the rate at which water molecules diffuse through the calcium. Calcium carbide CaC 2 reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide CaOH 2 and acetylene gas C 2 H 2.
CaC 2 2 H 2 O C 2 H 2 CaOH 2 b. When potassium chlorate KClO 3 is heated it decomposes to form KCl and oxygen gas O 2. 2 KClO 3 2 KCl 3 O 2 c.
C 6 H 6 combusts in air. 2 C 6 H 6 15 O 2 12 CO 2 6 H 2 O d. C 5 H 12 O combusts in air.
2 C 5 H 12 O 15 O 2 10 CO 2 12 H 2. Our purpose is to solve the toughest problems in life science by collaborating with the global scientific community and through that we aim to accelerate access to better health for people everywhere.