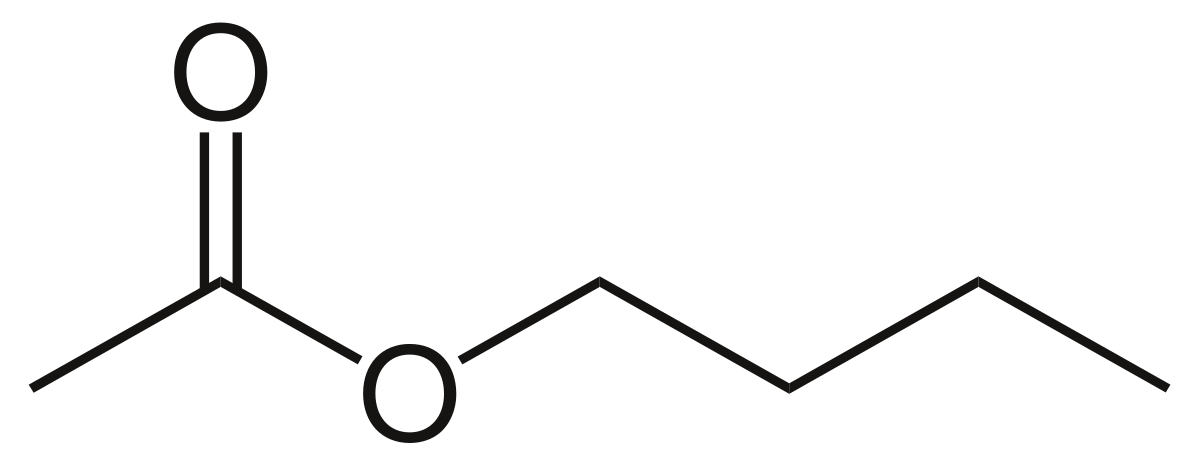
While there is a separate section in this. The compound illustrated below is called _____.
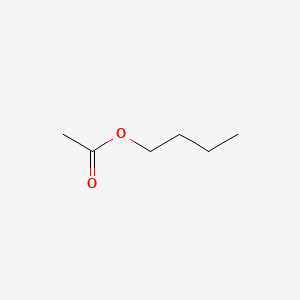
It is a urethane grade solvent and is widely used in 2K polyurethane coatings.
Butyl acetate functional group. Butyl is the largest substituent for which trivial names are commonly used for all isomers. The butyl groups carbon that is connected to the rest R of the molecule is called the R I or R-prime carbon citation neededThe prefixes sec from secondary and tert from tertiary refer to the number of additional side chains or carbons connected to the first butyl carbon. Butyl Acetate BUAC is a colourless liquid with a fruity odour.
Butyl acetate is an active solvent for film-formers such as cellulose acetate butyrate nitrocellulose polyesters epoxies alkyds vinyl copolymers and acrylic resins. It is a urethane grade solvent and is widely used in 2K polyurethane coatings. N-Propyl acetate is an ester which has the n-propyl group attached to the oxygen atom of the acetate group.
Chemical structure of propyl acetate. References This page was last edited on 12 May 2020 at 0250 UTC. Text is available under the Creative Commons.
In which R and R represent alkyl groups 1 and the functional group is the -CO-O- group. Butyl acetate butyl ethanoate water. When the reaction reaches equilibrium there is still a large amount of reactants left in the mixture resulting in a poor yield of the ester.
The yield of ester can be improved by increasing the concentration of one of the reactants either the alcohol or the. Esters are an important functional group in organic chemistry and they are generally written RCOOR or RCO 2. R where R and R are the hydrocarbon parts of the carboxylic acid and alcohol respectively.
For example butyl acetate systematically known as ethanoic acid is derived from butanol and acetic acid and would be written CH 3 CO 2 C 4 H 9. Alternative presentations are. A butyl acetate b ethyl pentanoate c propyl pentanoate d ethyl butanoate e butyl ethanoate 27.
The compound illustrated below is called _____. A acetamide b formyl acetamide c dimethyl acetate d NN-dimethylformamide e dimethylamine 28. The functional group given below is characteristic of organic _____.
A ketones b acids. Butyl diglycol is used as a high-boiling solvent to improve gloss and flow properties. On account of its high evaporation number even additions of.
In cellulose nitrate and cellulose ether lacquers even smaller amounts are effective. In emulsion paints and cold-hardening paints diethylene glycol mono-n. Esters are structurally derived from carboxylic acids by replacing the acidic hydrogen by an alkyl or aryl group.
Ethyl acetate itself is a colourless liquid at room temperature with a pleasant fruity smell bp. Ethyl acetate has many uses such as artificial fruit essences and aroma enhancers artificial flavours for confectionery ice cream and cakes as a solvent in many. The functional group of a carboxylic ester is an acyl group bonded to OR or OAr.
Large quantities of ethyl acetate and butyl acetate are commercially produced. Waxes secreted by animals and plants are esters formed from long-chain carboxylic acids and long-chain alcohols. Fats and oils are esters of long-chain carboxylic acids and glycerol.
Liquid esters of low volatility serve as. The first stage in the metabolic process appeared to be oxidation catalysed by cytochrome P-450-dependent mono-oxygenase at the omega or omega-1 position on the butyl chains. The hydroxy groups generated at the w and w-1 positions were further oxidized.
The clinical effect of buspirone in alleviating the symptoms of generalized anxiety disorders typically takes 2 to 4 weeks to achieve. 10 The delayed onset of action of buspirone suggests that the therapeutic effectiveness in generalized anxiety may involved more than its molecular mechanism of action at the 5-HT 1A receptors 9 or buspirone may induce adaptations of 5-HT 1A. The polymer of 3-methyl-1-pentene has large branched sec-butyl groups off the main chain whereas propene has relatively small methyl groups as branches.
As a result the polymer of 3-methyl-1-pentene has a more open structure. The bulkier chains cannot pack closely and the intermolecular forces between chains are smaller. The polymer of 3-methyl-1-pentene should have a lower melting point.
The way the term ionic liquid is used leads people to group them into a single class without scientific basis disregarding the fact that there is no similar common characteristics other than that they are liquids which describes them all. Industrial awareness is growing and the field of ILs is moving forward exploring new modes of applications. While there is a separate section in this.