What is the molar mass of sodium carbonate Na2CO3. Mass percent of substance 1 is 100 w 1.
The molar mass calculated is approximately 85 percent right and 15 percent wrong.
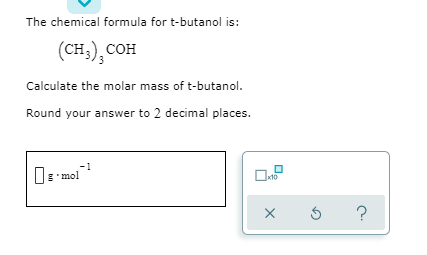
Butanol molar mass. Tert-Butyl alcohol is the simplest tertiary alcohol with a formula of CH 3 3 COH sometimes represented as t-BuOHIt is one of the four isomers of butanol. Tert-Butyl alcohol is a colorless solid which melts near room temperature and has a camphor-like odorIt is miscible with water ethanol and diethyl ether. Isoamyl alcohol is a colorless liquid with the formula C 5 H 12 O specifically H 3 C 2 CHCH 2 CH 2 OH.
It is one of several isomers of amyl alcohol pentanol. It is also known as isopentyl alcohol isopentanol or in the IUPAC recommended nomenclature 3-methyl-butan-1-olAn obsolete name for it was isobutyl carbinol. Isoamyl alcohol is an ingredient in the production of.
What is the molar mass of sodium carbonate Na2CO3. Since sodium carbonate contains one carbon atom two sodium atoms and three oxygen atoms the molecular weight is. 230 x 2 46.
120 x 1 12. 16 x 3 48. If molecular formula calculator add up the total value which is 12 46 48 106.
Therefore the molar mass of Na2CO3 is 106 gmol. In the NaOH. Molecular mass or molar mass are used in stoichiometry calculations in chemistry.
In related terms another unit of mass often used is Dalton Da or unified atomic mass unit u when describing atomic masses and molecular masses. It is defined to be 112 of the mass of one atom of carbon-12 and in older works is also abbreviated as amu. Also important in this field is Avogadros number N.
The molar mass calculated is approximately 85 percent right and 15 percent wrong. The accuracy and certainty of these results can be improved in the future by eliminating the sources of errors during the experiment. The freezing point depression aspectcan also be applied in daily life for example in raising the boiling point of the water that cools cars.
Antifreeze decreases the freezing. Except where noted spectra from this collection were measured on dispersive instruments often in carefully selected solvents and hence may differ in detail from measurements on FTIR instruments or in other chemical environments. More information on the manner in which spectra in this collection were collected can be found here.
Concentration information is not available for. C 4 H 9 OH l 6O 2g 4CO 2g 5H 2 O l ΔH -2671. From the table we see that 1 mole of methane gas CH 4g undergoes complete combustion in excess oxygen gas releasing 890 kJ of heat.
The molar heat of combustion of methane gas is given in the table as a positive value 890 kJ mol-1. The enthalpy change for the combustion of methane gas is given in the table. I would find this using n massmolar mass.
To convert from kJmol to kJL do I multiply by molL ie. The number of moles in 1L. If so how do I find that value.
I have to do this for ethanol 1-propanol 1-butanol 1-hexanol 1-heptanol and 1-octanol. The concentration of n-butanol in mgL when TIE-1 was cultured with ammonium NH 4 red or dinitrogen gas N 2 blue and a acetate photoheterotrophy b 3-hydroxybutyrate photoheterotrophy c. Molar Mass ¼ Molecular Weight M gmol v T cK P c bar z c Methane 16043 0012 1906 4599 0286 Ethane 3007 01 3053 4872 0279 Propane 44097 0152 3698 4248 0276 n-Butane 58123 02 4251 3796 0274 n-Pentane 7215 0252 4697 337 027 n-Hexane 86177 0301 5076 3025 0266 n-Heptane 100204 035 5402 274 0261 n-Octane 114231 04 5687 249 0256 n-Nonane 128258.
Mass fraction of substance 1 w 1 or w1. Where gs is the mass of substance s. Mass percent of substance 1 is 100 w 1.
The equivalent terms weight fraction weight percent and g 1100g solution are no longer used. Molality of solute 1 in a solvent 2 m 1. Here M 2 is the molar mass of the solvent.
Chemical Reaction Formula Atomic Mass Formula Chemical Formula Enthalpy Formula Entropy Formula Molality Formula Molar Mass Formula Molarity Formula Structural Formula Molecular Formula Chemical Compound Formula Chemical Equilibrium Formula Normality Formula Photosynthesis Formula Grams to Moles Conversion Formula Moles to Grams Conversion. As an example n-butanol will react with the methylol urea as shown in Figure 244. The mixture is boiled under reflux typically for about 15 min to give dimethylol urea and other low molar mass products.
The resins is then acidified to pH 4 with formic acid and reacted for a further 520 min. The resulting resin is then stabilized by neutralizing to a pH 75 to give a water-soluble. The difference in the R-2-butanol and the S-2-butanol has to do with the.
Latest answer posted January 21 2016 1207 am UTC. The molar mass of. 20775 NISTEPAMSDC Mass Spectral Database 1990 version.
605 Atlas of Mass Spectral Data John Wiley. The n-alkanols exhibited an increased molar inhibition of the ATPase activity with an increase in the carbon chain length up to 1-octanol. 1-octanol and 1-decanol caused a biphasic effect on the ATPase activity depending on the alkanol concentration whereas 1-dodecanol caused a.