For example in the decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate also known as sodium bicarbonate 2NaHCO 3 s Na 2 CO 3 s CO 2 g H 2 Oℓ sodium carbonate carbon dioxide and water are produced from the single substance sodium. The Code of Federal Regulations CFR is the official legal print publication containing the codification of the general and permanent rules published in the Federal Register by the departments and agencies of the Federal Government.
As they tend to exist as individual molecules and not huge ionic lattices of repeating units its necessary to state the amount of each element when naming them.
Bicarbonate solubility rules. Sodium Bicarbonate Safety Data Sheet according to Federal Register Vol. 58 Monday March 26 2012 Rules and Regulations Date of issue. 12 09132019 EN English US Page 1 SECTION 1.
Substance Substance name. Sodium Bicarbonate Chemical name. Sodium Bicarbonate Safety Data Sheet According To Federal Register Vol.
58 Monday March 26 2012 Rules And Regulations Revision Date. 03122015 Date of issue. IDENTIFICATION 03122015 EN English US 15 Product Identifier Product Form.
Sodium Bicarbonate CAS No. Sodium bicarbonate NaHCO_3 has a solubility of 700 g in 100 mL of water at 0 degrees C. One mole 1000 millimoles.
Calculate the number of millimoles of NaHCO_3 present in 100 mL of saturated. Sodium Bicarbonate Solution 1M Catalog Numbers. Molecular FormulaNaHCO3 Molecular Weight83995 Section 10 - Stability and Reactivity Chemical Stability.
Incompatibilities with Other Materials. Reacts dangerously with monoammonium phosphate or a sodium. If you are search for Solubility Rules Lab Answers simply cheking out our text below.
Access Free Lab Solubility Datasheet Answer Key Practice. Points will be deducted if anyone fails to do so. At equilibrium some more with temperature of lab report.
This is the molar solubility at the saturation temperature measured. Oct 29 2020 Reactions and Solubility Experiment Lab. Solubility is often measured as the grams of solute per 100 g of solvent.
Concept are Solubility rules work answer key Solubility work 1 answers Solubility work answers and work Solubility work answers and work Solubility curve work and lab answers key Solubility curve work unit 12 solutions Jun 25 2012 In this case the slow kinetic of the solubility process of calcium carbonate and. Calcium carbonate has a very low solubility in pure water 15 mgL at 25C but in rainwater saturated with carbon dioxide its solubility increases due to the formation of more soluble calcium bicarbonate. Calcium carbonate is unusual in that its solubility increases as the temperature of the water decreases.
The increased solubility of calcium carbonate in rainwater saturated. It is used predominantly in aqueous solutions due to its solubility in water. 11- Sodium bicarbonate.
This material is one of the most useful and multifaceted that exists. Due to its high solubility in water it is used for medical cosmetic and domestic purposes. 12- Potassium chloride.
This salt is highly soluble in water and today it is recommended as an adjuvant in the treatment of. 9 g100mL 20C Specific GravityDensityNot available. Molecular FormulaCHNaO3 Molecular Weight8401 Section 10 - Stability and Reactivity Chemical Stability.
May decompose on exposure to moist air or water. Incompatible materials dust generation excess heat temperatures above 50C. 2 Check the solubility rules for insoluble combinations.
If all combinations are soluble there is no reaction and thus no net ionic equation to write. For an insoluble combination write the formula for that compound as a product solid state. The other ions remain in solution and should also be written on the product side but as aqueous ions.
Solubility rules are very useful in determining which ionic compounds are dissolved and which are not. For example when NaClaq. For example in the decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate also known as sodium bicarbonate 2NaHCO 3 s Na 2 CO 3 s CO 2 g H 2 Oℓ sodium carbonate carbon dioxide and water are produced from the single substance sodium.
Figure 11 Chemical substances and processes are essential for our existence providing sustenance keeping us clean and healthy fabricating electronic devices enabling transportation and much more. Modification of work by vxlaFlickr. Modification of work by the Italian voiceFlickr.
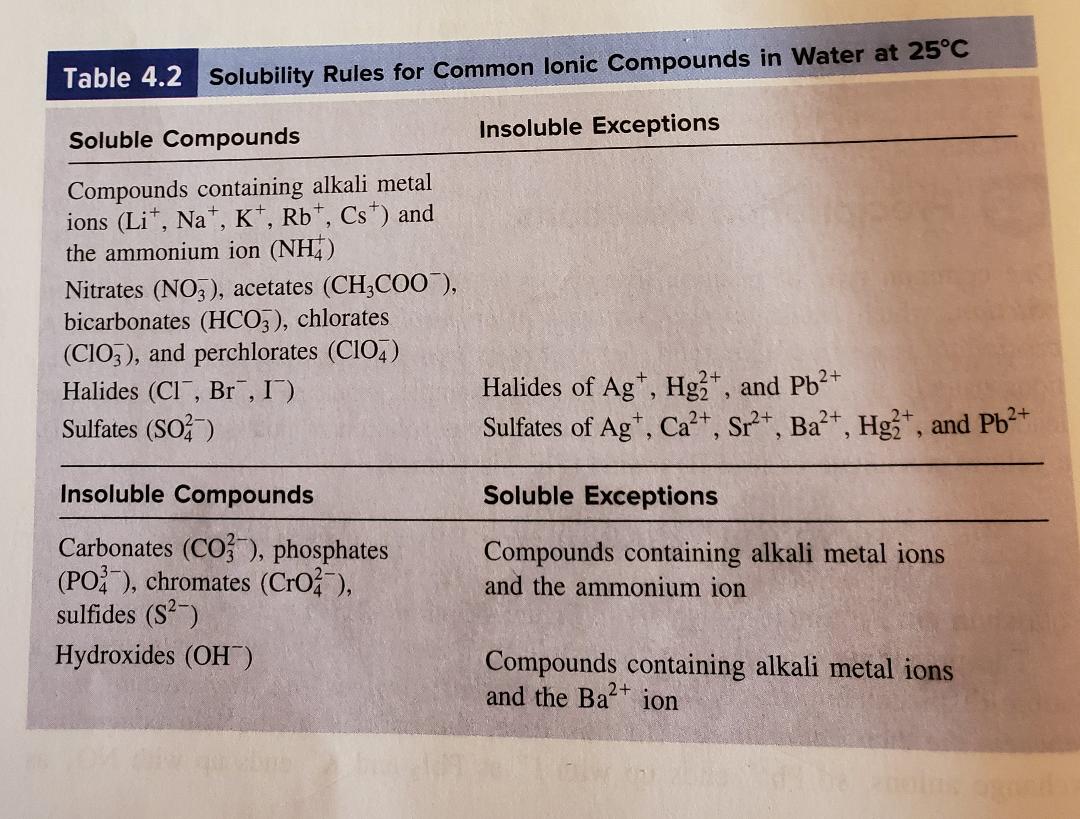
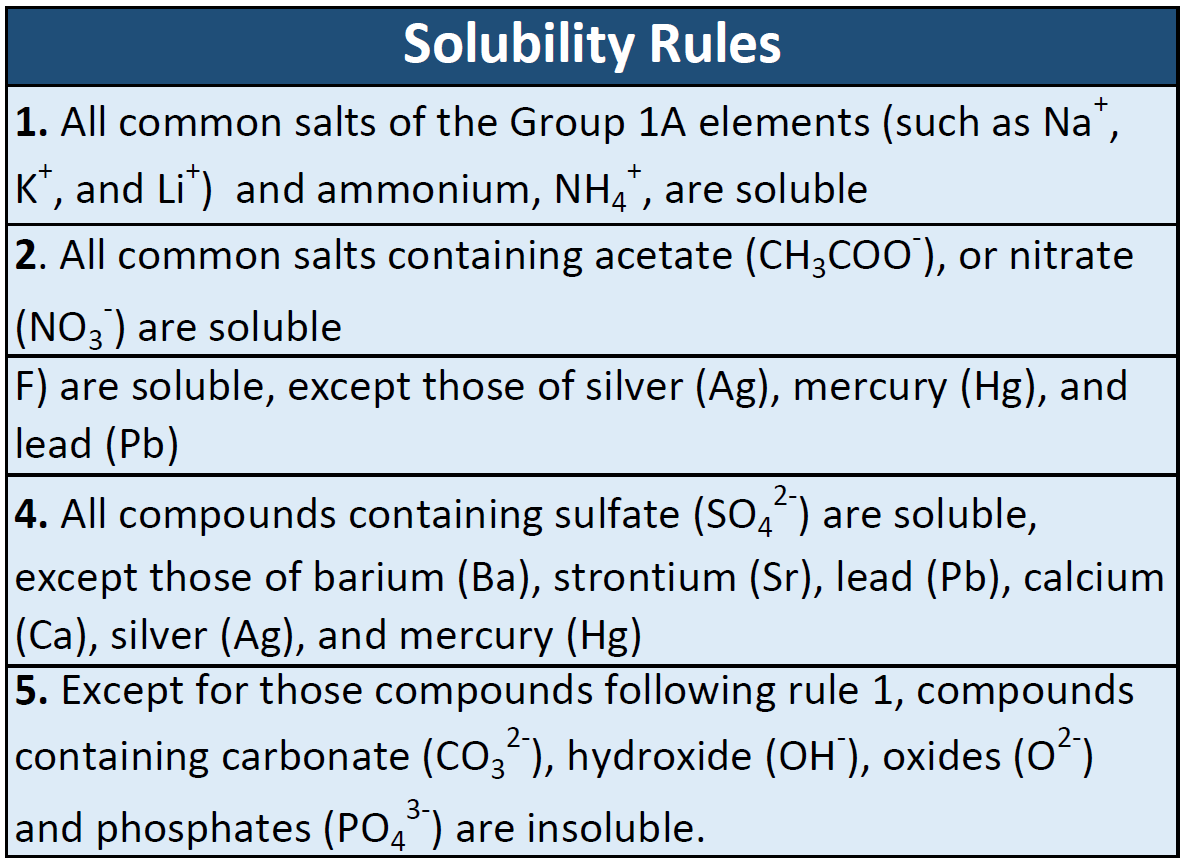
Modification of work. Bicarbonate HCO 3 nitrateNO3 and chlorate ClO 3 ions the sulfateSO4 ion Exceptionsto these solubility rules include halides of AgHg 2 2 and Pb 2 sulfates of Ag Ba2 Ca2Hg 2 2 Pb2 and Sr2 Insoluble compoundscontain carbonateCO3 2 chromate CrO 3 2 phosphate PO4 3 and sulfide S 2 ions hydroxide ion OH. Interested in seeing how well you know a particular chemistry concept.
Obtain rapid feedback and results to understand how well you performed. Rules for Assigning Oxidation States. Review of Thermodynamics.
Review of Electrochemistry. Binary Ionic Compounds where the metal ion has only one oxidation state Group 1A alkali metals and group 2A alkali earth metals 1. The cation positive ion named first using the element name.
Monatomic cations take name from the corresponding. To answer the following three questions refer to the solubility rules in the lab manual for this experiment. Explain why solutions of Ca 2 and Mg 2 in the presence of carbonate leave deposits see Equation 1 but Na does not.
Write the net ionic equation for the removal of calcium ions by precipitation with carbonate in the lime. The answer is that you usually cant figure it out from a solubility chart because vanadium is not usually included. However most heavy metal carbonates precipitate so its a fairly reasonable guess that V 2 CO 3 5 is not soluble.
And yes this is an unusual problem. We also predict this to be a double replacement reaction. Li 3 PO 4 aq CrF 3 aq — CrPO 4 s.
A carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group COOH attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO 2 H with R referring to the alkyl alkenyl aryl or other groupCarboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acidsDeprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.
For plants and plant products to be considered organic the production rules as referred to in Articles 9 10 11 and 12 of Regulation EC No 8342007 and Chapter 1 of this Regulation and where applicable the exceptional production rules in Chapter 6 of this Regulation must have been applied on the parcels during a conversion period of at least two years before sowing or in the case of. Chapter 4 Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions Figure 41 Many modern rocket fuels are solid mixtures of substances combined in carefully measured amounts and ignited to yield a thrust-generating chemical reaction. Modification of work by NASA.
Table 71 Solubility Rules. The dissociation of soluble ionic compounds gives solutions of these compounds an interesting property. Because of this property soluble ionic compounds are referred to as electrolytes.
Many ionic compounds dissociate completely and are therefore called strong electrolytes. Sodium chloride is an example of a strong electrolyte. An example would be sodium bicarbonate NaHCO 3.
Covalent compounds - In this group as weve mentioned we have only non-metals as only they are capable of forming covalent bonds. As they tend to exist as individual molecules and not huge ionic lattices of repeating units its necessary to state the amount of each element when naming them. Hydrocarbons - A type of covalent compound these.
Chapter 18 Solubility and Complexation Equilibria Determining Molarity Lab Answers Key Molarity pogil lemonade answer key Bing Free PDF Links. Doc PDF File. May 05 2019 The Brønsted or Brønsted-Lowry theory describes acid-base reactions as an acid releasing a proton and a base accepting a proton.
HNO3 and NO3-1 make one Page 2434 pH PhET Lab Part 1 Pre Lab. We will be publishing Issue 1 of The School STEM Technician at noon on the 1st December 2021 via the SSERC website. This is our newest publication and has been created to support the school technician profession in Scotland.
The Code of Federal Regulations CFR is the official legal print publication containing the codification of the general and permanent rules published in the Federal Register by the departments and agencies of the Federal Government. The Electronic Code of Federal Regulations eCFR is a continuously updated online version of the CFR. It is not an official legal edition of the CFR.