Benzoic Acid Created by Global Safety Management Inc. Comment on the solubility of benzoic acid in water.

ɪ k is a white or colorless solid with the formula C 6 H 5 CO 2 H.
Benzoic acid melting temperature. Benzoic acid b ɛ n ˈ z oʊ. ɪ k is a white or colorless solid with the formula C 6 H 5 CO 2 H. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acidThe name is derived from gum benzoin which was for a long time its only sourceBenzoic acid occurs naturally in many plants and serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of many secondary metabolites.
Salts of benzoic acid are used as food. Comment on the solubility of benzoic acid in water. Benzoic acid is not very soluble in water.
However the solubility of this compound in water increases when the temperature is increased as is the case with most compounds. At a temperature of 0 degrees celsius the solubility of benzoic acid in water corresponds to 17 grams per litre. CHEM 2423 Recrystallization of Benzoic Acid Dr.
Pahlavan 1 EXPERIMENT 4 - Purification - Recrystallization of Benzoic acid Purpose. A To purify samples of organic compounds that are solids at room temperature b To dissociate the impure sample in the minimum amount of an appropriate hot solvent Equipment Materials. Hot plate 125-mL Erlenmeyer flask ice stirring rod spatula Büchner.
The melting point of benzoic acid is approximately 122 C 2002 Gilbert and Martin CD-Rom MSDS Data. The melting points of the recrystallized benzoic acid were 114- 122 C and 121-127 C both encompassing the expected value and allowing one to believe that the sample was close to pure which was the goal of recrystallization. Gilbert and Martin Experimental.
The actual laboratory we will do is the recrystallization of benzoic acid from water using the temperature gradient method. Benzoic acid is not very soluble in cold water but it is soluble in hot water. The purpose of this experiment is to learn the technique of recrystallization by purifying benzoic acid.
CHEM 2423 Recrystallization of Benzoic Acid Dr. Pahlavan 4 Experimental Procedures. The unknown sample may not be separated using melting points because both benzoic acid and 2-naphthol have a melting point of 123C.
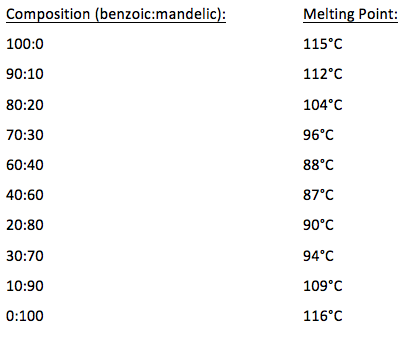
The purity of the samples will be indicated by their melting points ranges. The purer the sample the narrower the melting point range. Balmer 2 Experimental Procedure Fig1.
An unknown sample of benzoic acid 2-naphthol and naphthalene Table 1 was massed. SLOWLY heat the sample 1 C per minute and record the temperature at the very first sign of melting. Continue to watch the sample and when the sample has melted completely record the temperature again.
EVERY MELTING POINT IS REPORTED AS A RANGE. Please discard your purified benzoic acid into the container in the hood labeled. Benzoic Acid - Student Prep.
Using the solubility data you found for benzoic acid calculate the volume of water required to dissolve 10 g of benzoic acid at room temperature. Calculate the volume of boiling water needed to dissolve 10 g of benzoic acid. Explain why a Büchner or Hirsh funnel is used to isolate the final crystallized product instead of stem funnel.
The melting point of a substance the temperature at which a substance melts is a physical property that can be used for its identification. It is a measure of the amount of kinetic energy heat that must be supplied to the particles of the substance in order to overcome the intermolecular forces such as Van der Waals dipole-dipole and H-bonding that confine them to the solid state. Take a melting point and assess its purity by comparing the measured melting point with the literature value.
Reserve a small sample of your benzoic acid product crystals for TLC analysis. Transfer the ether layer into a 50 mL Erlenmeyer flask taking care not to transfer any residual water. Add 2 g of anhydrous calcium chloride to the flask and set it aside.
If you have excess water. Finally you will record the mass melting point range and infrared spectrum of your benzoic acid during the next lab period. 1Wear gloves when handling bromobenzene and benzoic acid 2.
Diethyl ether is volatile and highly flammable. Try to keep all vials and containers capped. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid also known as p-hydroxybenzoic acid PHBA is a monohydroxybenzoic acid a phenolic derivative of benzoic acidIt is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water and chloroform but more soluble in polar organic solvents such as alcohols and acetone.
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is primarily known as the basis for the preparation of its esters known as parabens. Definitions of the acid dissociation constant and pKa are given below the figures together with the definition of some classes of organic acids. In the table below pK a1 and pK a2 for water solutions at 25C are given together with boiling and melting point density and molecular weight as well as number of carbon hydrogen and oxygen atoms in each molecule.
Benzoic Acid Created by Global Safety Management Inc. 1224 deg C Solubilities. 34 gl 25C Boiling pointBoiling range.
2492C 760 mmHg Partition coefficient n-octanolwater. Not Determined Flash point closed cup. 570C Evaporation rate.
The melting point is the highest temperature at which crystallization may occur. It is also a temperature at which a solid crystal turns into a liquid. We say that such a body melts.
The melting point is specific for a given substance. For example the melting point of ice frozen water is 0 C. The melting point depends on the pressure.
A three-point calibration with benzophenone benzoic acid and caffeine is performed followed by an adjustment. The adjustment is then verified by calibration with vanillin and potassium nitrate. On-Demand Webinar Good Melting Point Practice Back to Questions.
Influence of the Heating Rate on the Melting Point Measurement. Results depend strongly on the heating rate - the higher the. O-toluic acid is a methylbenzoic acid that is benzoic acid substituted by a methyl group at position 2.
It has a role as a xenobiotic metabolite. It is a conjugate acid of an o-toluate. 1 Structures Expand this section.
2 Names and Identifiers Expand this section. 3 Chemical and Physical Properties Expand this section. 4 Spectral Information Expand this section.
Octanoate salicylate valproic acid p-octyl- p-nitro- and p-chlorobenzoic acids were effective inhibitors of benzoic acid activation to benzoyl-CoA by mitochondrial extracts. P-Aminobenzoic acid was much less effective. Of these compounds only salicylate and p-nitrobenzoic acid were not activated to their respective CoA esters.
Salicylate p-chloro- and p-nitrobenzoic acids effectively. The melting point of benzoic acid is equal to 122 degrees celsius whereas the boiling point fo benzoic acid is equal to 250 degrees celsius. Benzoic acid is not very soluble in water.
At a temperature of 25 degrees celsius the solubility of benzoic acid in water corresponds to 344 grams per litre. However it can be noted that the solubility of benzoic acid in water increases as the. Melting point is the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid.
In theory the melting point of a solid is the same as the freezing point of the liquid the point at which it turns into a solid. For example ice is a solid form of water that melts at 0 degrees Celsius32 degrees Fahrenheit and changes to its liquid form. Water freezes at the same temperature and turns into ice.
211 deg C 20 mm 3729924 C 760 mmHg Alfa Aesar 211 C 20 mm Hg 3729924 C 760 mmHg Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid 211 C 20 mmHg 3729924 C 760 mmHg OU Chemical Safety Data No longer updated More details 211 C 20 mmHg 3729924 C 760 mmHg SynQuest 211 C 20 mm 3729924 C 760 mmHg Alfa Aesar A12253. Benzoic acid 2-naphthol p-dimethoxybenzene pK a 417. Regardless of the temperature.
Rinsing of the drying agent and filter paper is performed to prevent a loss in product. All three separated compounds may be purified by recrystallization and their identities confirmed using melting point analysis. Jill Discordia Created Date.
Use a procedure that will oxidize the benzaldehyde to benzoic acid. You must use a 250-mL round bottom flask for this oxidation reaction. Perform a recrystallization on the benzoic acid you have prepared.
Remember recrystallization is when you take a solid chemical and without any chemical modification dissolve it in a solvent to. Phase at room temperature. Therefore you should obtain the melting point and weight of this compound before leaving the lab.
Allow all three products to dry in your drawer. Next week you will obtain the weights and melting points of benzoic acid and 4-chloroaniline and you can re-take the melting point naphthalene if any is left. 5 Name _____ Date _____ T.
_____ Lab period _____ Results. A pure compound will melt over a relatively narrow temperature range impurities both lower and widen the temperature range over which a compound melts. The apparatus used to measure melting points can be simple oil baths to hot-stage apparatus where the melting process is observed with the aid of a microscope.
In each case the range of temperatures at which a compound melts is recorded.