
Once the ice is totally melted the temperature can now begin to rise again. 153 gL 0 C 181 gL 9 C.
Benzene and toluene form very nearly ideal solutions so we shall regard the solution as ideal.
Benzene boiling temperature. 801 C 1762 F. 3532 K Solubility in water. 153 gL 0 C 181 gL 9 C.
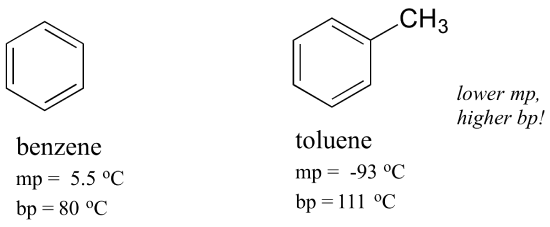
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C 6 H 6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon.
Boiling point - the temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas For hydrocarbons with the same carbon number the boiling point increases in the following order. Multisubstituted alkane singelsubstituted alkane singelsubstituted alkene normal alkene normal alkane alkyl cyclohexane alkylbenzene cycloalkene cycloalkane 2- 4- and 3-alkanol 1-alkylnaphthalene 1-alkanol. Benzene is a liquid at standard conditions.
However if heated it becomes a gas and when cooled it becomes a solid. The phase diagram for benzene shows the phase behavior with changes in temperature and pressure. The curve between the critical point and the triple point shows the benzene boiling point with changes in pressure.
It also shows. Benzene is widely used in the United States. It ranks in the top 20 chemicals for production volume.
Some industries use benzene to make other chemicals which are used to make plastics resins and nylon and synthetic fibers. Benzene is also used to make some types of rubbers lubricants dyes detergents drugs and pesticides. Natural sources of benzene include volcanoes and forest fires.
BENZENE reacts vigorously with allyl chloride or other alkyl halides even at -70 C in the presence of ethyl aluminum dichloride or ethyl aluminum sesquichloride. Explosions have been reported NFPA 491M 1991. Ignites in contact with powdered chromic anhydride Mellor 11235 1946-47.
Incompatible with oxidizing agents such as nitric acid. Mixtures with bromine trifluoride bromine. Benzene melts at a temperature of 55 C boils at 801C.
Benzene and its derivatives are part of an essential chemical community known as aromatic compounds. Benzene is a precursor in the production of medicines plastics oil synthetic rubber and dyes. As a result the hydrogenation of benzene happens much more slowly than the hydrogenation of other organic compounds containing carbon.
Nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C 6 H 5 NO 2It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odorIt freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor to anilineIn the laboratory it is occasionally used as a solvent especially for electrophilic reagents. You can now roughly evaluate its boiling point.
Take water for example. Enter 760 millimeters of mercury or 1013 hPa – units do not matter as the pressure value and 100 as the boiling point. Now you can calculate its boiling point under any pressure.
Type 15 in the second left field and 18 will appear in the second right field. This is the answer. Water boils at 18C under 15 millimeters.
Consider a solution of two liquids say benzene and toluene held at a constant temperature. Benzene and toluene form very nearly ideal solutions so we shall regard the solution as ideal. We know that an ideal solution obeys Raoults law so for each component we must have 1 p i i i X i i p i i If we now hold temperature constant and plot the vapor pressure of a benzene-toluene solution as.
Benzene react with chlorine in the presence of aluminum chloride or iron to prepare chlorobenzene. C 6 H 6 Cl 2 C 6 H 5 Cl HCl. Benzene react with bromine in the presence of aluminum bromide or iron to produce bromobenzene.
Iron is used because it is readily available and cheaper. C 6 H 6 Br 2 C 6 H 5 Br HBr. At an atmospheric pressure of exactly 760mm Hg 1 atm the temperature at which a liquid boils is called the normal boiling point of the liquid.
For water the vapour pressure reaches the standard atmospheric pressure of 1 atmosphere at 100C. So the normal boiling point of water is 100C 212F or 373KThe boiling point of pure water increases on the addition of soluble substances such. Temperature is the property of matter which reflects the quantity of energy of motion of the component particles.
It is a comparative measure of how hot or cold a material is. The coldest theoretical temperature is called absolute zero. It is the temperature where the thermal motion of particles is at its minimum not the same as motionless.
Absolute zero is 0 K on the Kelvin scale 27315. Notice that the change in freezing or boiling temperature depends solely on the nature of the solvent not on the identity of the solute. One valuable use of these relationships is to determine the molecular mass of various dissolved substances.
As an example perform such a calculation to find the molecular mass of the organic compound santonic acid which dissolves in benzene or chloroform. Clear colorless to light yellow liquid at room temperatureBenzene is a solid below 42F 56C. Benzene is used to make chemicals used in the manufacture of industrial products such as dyes detergents explosives pesticides synthetic rubber plastics and pharmaceuticalsBenzene is found in gasoline and trace amounts are found in cigarette smoke.
To determine the boiling point of organic compounds like Benzene and Benzaldehyde. Benzene Benzaldehyde the aluminum block fusion tube stand with clamp capillary tube tripod thermometer and kerosene burner. If we know the boiling point of the substance at some specific pressure tables usually give the value under the so-called normal pressure ie.
101325 hPa and enthalpy of vaporization molar heat of evaporation then we can estimate the boiling point under another selected pressure. The relationship between pressure change and temperature change during evaporation in general. The boiling point of a solution then will be greater than the boiling point of the pure solvent because the solution which has a lower vapor pressure will need to be heated to a higher temperature in order for the vapor pressure to become equal to the external pressure ie the boiling point.
When the temperature of a liquid is below its boiling point we can assume that the only molecules that can escape from the liquid to form a gas are those that lie near the surface of the liquid. When a solute is added to the solvent some of the solute molecules occupy the space near the surface of the liquid as shown in the figure below. When a solute is dissolved in a solvent the number.
The definition of boiling point states that it is the temperature when the vapor pressure of the compound equals to the atmospheric pressure. In other words we can say it is the temperature at which there is so much of the compound evaporated that it creates a pressure equal to the external pressure. In a simpler perspective lets say that it is the temperature when the liquid turns into a.
What temperature should you set your vaporizer as a medical user. As a medical user the optimal vaping temperature should be at around 392F200C. The boiling point of CBD is 320F 160C 356F180C.
The boiling point of THC is 315F157C. So you would think just go for a minimum temperature of 356F180C. This means that for the sake of determining freezing point depression or boiling point elevation the vapor pressure does not effect the change in temperature.
Also remember that a pure solvent is a solution that has had nothing extra added to it or dissolved in it. We will be comparing the properties of that pure solvent with its new properties when added to a solution. Liquid water rises in temperature.
Once the ice is totally melted the temperature can now begin to rise again. It continues to go up until it reaches its normal boiling point of 1000 C. Since the temperature went from zero to 100 the Δt is 100.
Approximate values only may vary with pH concen-tration and temperature. Melting and boiling points are those of the corre-sponding unlabeled compound except for D 2O. These temperature limits can be used as a guide to determine the useful liquid range of the solvents.
Information gathered from the Merck Index Fourteenth Edition. HOD Peaks - NMR spectra of neat.