The reactions form new chemical bonds and create isopropyl alcohol C3H7OH. A process called hydration combines propene and water.

Dal punto di vista chimico il benzene talvolta indicato come Ph-H o φ-H è un idrocarburo aromatico monociclico avente formula bruta C 6 H 6.
Benzene alcohol structure. Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C 6 H 6The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon. Benzene is a natural constituent of crude oil and is one of the elementary petrochemicals.
Benzene is a clear colorless highly flammable and volatile liquid aromatic hydrocarbon with a gasoline-like odor. Benzene is found in crude oils and as a by-product of oil-refining processes. In industry benzene is used as a solvent as a chemical intermediate and is used in the synthesis of numerous chemicals.
Exposure to this substance. Q1 False this compound does not contain a benzene ring in its structure. Q3 No a substance that is fragrant does not imply a benzene ring is in its structure.
See camphor example figure 1 Q4 No reaction benzene requires a special catalyst to be hydrogenated due to its unusual stability given by its three conjugated pi bonds. Eventually the presently accepted structure of a regular-hexagonal. Benzene however is an extraordinary.
3 a substitution reaction the electrophilic carbonyl carbon atom bonds to the nucleophilic oxygen atom of ethyl alcohol to give an intermediate in square brackets that eliminates HCl yielding the ester ethyl acetate. In all of these examples the reactivity of the. This structure is also available as a 2d Mol file or as a computed 3d SD file The 3d structure may be viewed using Java or Javascript.
The tables and figures below show how the boiling point changes with increasing carbon number up to C 33 for different kinds of hydrocarbons alcohols and carboxylic acids. More detailed definitions and examples of molecular structures of the different groups are given below the figures. Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid.
Alkylbenzene sulfonates are a class of anionic surfactants consisting of a hydrophilic sulfonate head-group and a hydrophobic alkylbenzene tail-group. Along with sodium laureth sulfate they are one of the oldest and most widely used synthetic detergents and may be found in numerous personal-care products soaps shampoos toothpaste etc and household-care products laundry detergent. Il benzene è un composto chimico che a temperatura ambiente e pressione atmosferica si presenta sotto forma di liquido volatile incolore altamente infiammabile dallodore caratteristico.
Dal punto di vista chimico il benzene talvolta indicato come Ph-H o φ-H è un idrocarburo aromatico monociclico avente formula bruta C 6 H 6. Le distanze di legame tra gli atomi che compongono il. The third type of structure found in proteins is called tertiary protein structure.
Or an alcohol and an amine or amide. In giving the structures for various examples the backbone of the protein fragment will be represented by a short helix with only the side chain structure given as in the graphic on the left. In the prion protein tyr 128 is hydrogen bonded to asp 178 which cause one.
Systematic names are more useful however because a systematic name specifies the actual structure of the compound. If the hydroxyl group is the principal functional group of a phenol the compound can be named as a substituted phenol with carbon atom 1 bearing the hydroxyl group. For example the systematic name for thymol is 5-methyl-2-isopropylphenol.
Phenols with only one other. A one ring aromatic without any substituents is called benzene with the formula C6H6. An alkyl group is an alkane substituent missing one hydrogen with general formula C n H 2n1.
An phenyl group is a benzene substituent missing one hydrogen with general formula C 6 H 5. An organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group OH is bound to a saturated carbon. Methanol is the first and simplest member of the alcohol family in organic chemistry.
It is a one-carbon alcohol. Methanol got these names due to its historical relevance when it is first discovered to be a product that forms when cellulose the main sugar component present in wood gets fermented by any form of bacteria. A process called hydration combines propene and water.
During hydration the component substances of water which are hydrogen and oxygen H20 react with those that compose propenecarbon and hydrogen C3H6. The reactions form new chemical bonds and create isopropyl alcohol C3H7OH. There are actually two means of hydration.
One is the. 14-benzene dicarbo xylic acid. 14-Benzenedicarbox ylic acid ACDIndex Name 14-dicarboxybenzene.
YES Hydrocarbon Biodegradation BioHCwin v101. Structure incompatible with current estimation method. Sorption to aerosols 25 Dec CAEROWIN v100.
00124 Pa 93E-005 mm Hg Log Koa Koawin est. 12050 Kp particlegas partition coef. A second abbreviation single letter is used in long protein structuresConsult the table on the left for structure names and abbreviations of 20 amino acids.
There are basically four different classes of amino acids determined by different side chains. 1 non-polar and neutral 2 polar and neutral 3 acidic and polar 4 basic and polar. Solvent Other Names Structure.
Class Acetic acid Ethanoic acid CH 3 COOH Calss 3 Acetone 2-Propanone CH 3 COCH 3 Propan -2-one Calss 3. Acetonitrile CH 3 CN Calss 2. Structure of organic compounds.
The most abundant element in organic compounds are carbon covalently bonded with each other or with other elements. Carbon has four valence electrons and the electron configuration of carbon in group state is 1s 2 2s 2 2p x 1 2p y 1 2p z 0. That means it has only two unpaired electrons.
Wikimedia commons by Pumbaa And the electron. Alcohol cannot be defined as acidic or alkaline rather defined as amphiprotic because the nature of the bond between carbon and hydroxyl group is non-ionic but slightly polar in nature. Aliphatic alcohol acts as a weak acid in presence of any strong base.
Aromatic alcohols behave as weakly acidic at standard conditions because of the resonance allowing kicking off the hydrogen. Benzene LAB short-chain linear alpha olefins ethylene petrolatum paraffin waxes. Alcohol ethoxylates FAEs are the products of choice for the replacement of nonylphenol ethoxylates NPEs.
The performance properties of these nonionic surfactants can be adjusted by the alcohol selection and by the length of the hydrophilic polyethylene glycol chain. In comparison to NPEs alcohol. Oxidation Reactions of Alcohols.
Simple 1º and 2º-alcohols in the gaseous state lose hydrogen when exposed to a hot copper surface. This catalytic dehydrogenation reaction produces aldehydes as shown below and ketones and since the carbon atom bonded to the oxygen is oxidized such alcohol to carbonyl conversions are generally referred to as oxidation reactions. Protein - protein - General structure and properties of proteins.
The common property of all proteins is that they consist of long chains of α-amino alpha amino acids. The general structure of α-amino acids is shown in. The α-amino acids are so called because the α-carbon atom in the molecule carries an amino group NH2.
The α-carbon atom also carries a carboxyl group COOH. The alcohol cyclohexanol is shown for reference at the top left. It is noteworthy that the influence of a nitro substituent is over ten times stronger in the para-location than it is meta despite the fact that the latter position is closer to the hydroxyl group.
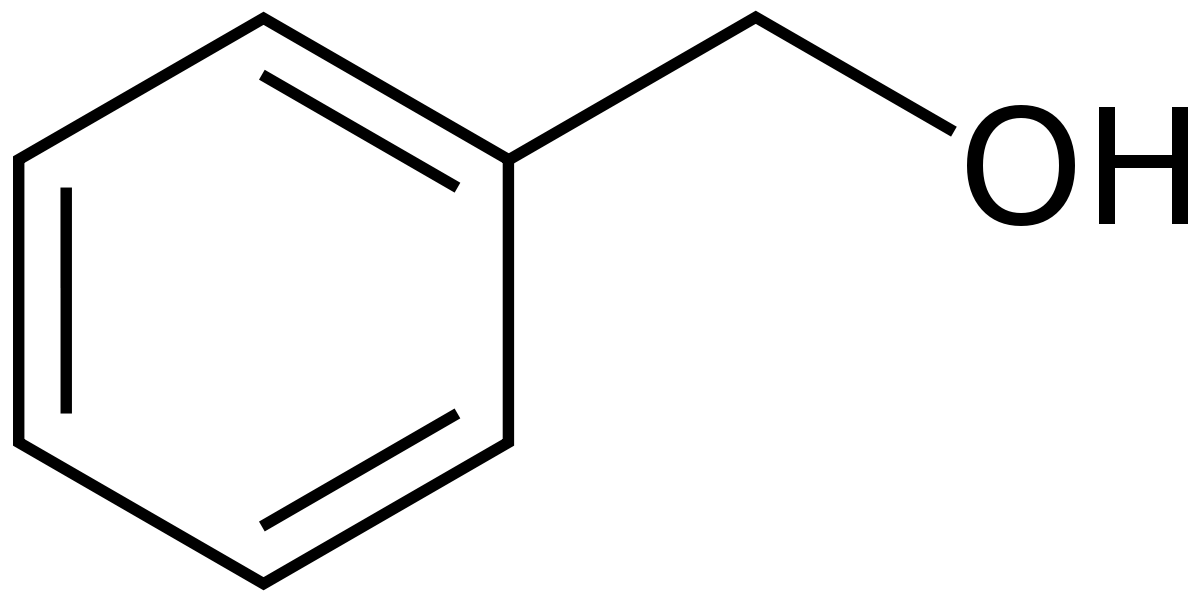
Furthermore additional nitro groups have an additive influence if they are positioned in ortho or para locations. Benzyl alcohol is an aromatic alcohol that consists of benzene bearing a single hydroxymethyl substituent. It has a role as a solvent a metabolite an antioxidant and a fragrance.
The following chemical structure represents a molecule of what molecular formula. A C 8 H 10 b C 6 H 6 c C 6 H 8 d C 8 H 12 e C 8 H 6. How many actual double bonds does the benzene ring possess.
A None carbon-carbon bonds in benzene are delocalized around the ring b 1 double bond c 2 double bonds d 3 double bonds e 4 double bonds 14. Para-xylene is the same as. A benzene and ethanol b acetonitrile and acetone c KCl and water d benzene and carbon tetrachloride.
B acetonitrile and acetone Explanation. Dipole-dipole interactions occur among the polar molecules. Polar molecules have permanent dipoles.
The positive pole of one molecule is thus attracted by the negative pole of the.