The 15 mg and 30 mg tablets contain the following inactive ingredients. Do not administer to patients with known hypersensitivity to hyaluronan sodium hyaluronate preparations.
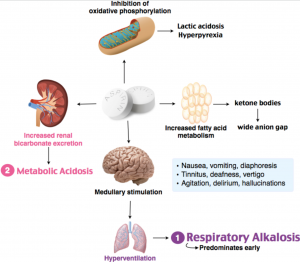
Respiratory Alkalosis is an acid-base imbalance characterized by decreased partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide and increased blood pH.
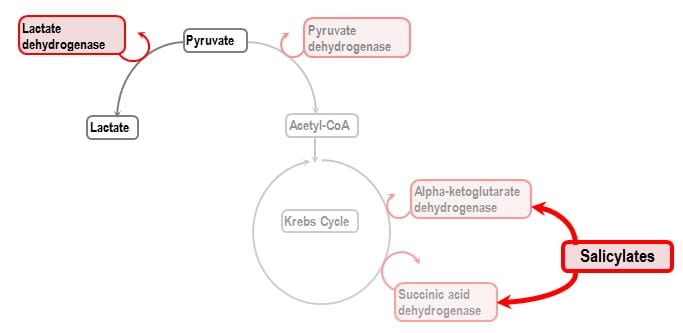
Aspirin overdose acid base. The acid-base fluid and electrolyte abnormalities observed in salicylate toxicity can be grouped into three broad phases. Sodium bicarbonate is given in a significant aspirin overdose salicylate level greater than 35 mgdl 6 hours after ingestion regardless of the serum pH as it enhances elimination of aspirin in the urine. It is given until a urine pH between 75 and 80 is achieved.
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC 6 H 4 CO 2 H. A colorless bitter-tasting solid it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin acetylsalicylic acid. It is a plant hormone.
The name is from Latin salix for willow treeIt is an ingredient in some anti-acne productsSalts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates. An overdose of aspirin causes acidosis due to the acidity of this metabolite. Metabolic acidosis can also result from uremia which is the retention of urea and uric acid.
Metabolic acidosis can also arise from diabetic ketoacidosis wherein an excess of ketones is present in the blood. Other causes of metabolic acidosis are a decrease in the excretion of hydrogen ions which inhibits the. The bicarbonate ion is the measure of a metabolic renal component of the acid-base equilibrium.
Salicylate toxicity such as aspirin overdose Liver disease. Higher-than-normal levels may be seen in. Breathing disorders compensated respiratory acidosis Cushing syndrome.
Ingestion of excessive amount of antacid diuretics and steroids. Evaluation of mixed acid-base abnormalities requires an understanding of the anion gap the relationship between the change in serum sodium and chloride concentration and the limits of compensation for the primary acid-base imbalances Saxton and Seldin 1986. Wilson and Green 1985.
Clinical findings and history are also necessary to define the factors that may contribute to the development. An overdose of aspirin causes acidosis due to the acidity of this metabolite. Metabolic acidosis can also result from uremia which is the retention of urea and uric acid.
Metabolic acidosis can also arise from diabetic ketoacidosis wherein an excess of ketones is present in the blood. Other causes of metabolic acidosis are a decrease in the excretion of hydrogen ions which inhibits the. Acetylsalicylic acid as well as the main metabolite salicylic acid are extensively bound to plasma proteins primarily albumin and distributed rapidly into all parts of the body.
Maximum plasma concentration is reached after 03 - 2 hours total salicylate. The degree of protein binding of salicylic acid is strongly dependant of both the salicylic acid and albumin concentration. Acetylsalicylic acid is rapidly metabolised to salicylic acid with a half-life of 15-30 minutes.
Salicylic acid is subsequently predominantly converted into glycine and glucuronic acid conjugates. Elimination kinetics of salicylic acid is dose-dependent because the metabolism is limited by liver enzyme capacity. Thus elimination half-time varies and is 2-3 hours after low.
Aspirin is an NSAID so taking too much of it or taking it longer than recommended can increase your risk of some serious side effects. You should always talk to your doctor first if youre not. Acidbase imbalance is an abnormality of the human bodys normal balance of acids and bases that causes the plasmapH to deviate out of the normal range 735 to 745.
Respiratory Alkalosis is an acid-base imbalance characterized by decreased partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide and increased blood pH. Approximate reference normal ranges To understand how the results of pH pCO 2 a and bicarbonate are used to classify acid-base disturbances in this way we must return to the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation pH 61 log HCO 3 H 2 CO 3. We measure pH and bicarbonate but not carbonic acid H 2 CO 3However there is a relationship between pCO 2 a and H 2 CO 3 which.
Acid-base balance in the human body is one of the most paramount physiological processes. The clinical significance of acid-base balance is one which is hard to deny. Some of the most common admissions to hospitals are due to diseases that can dangerously affect the acid-base balance.
This is why it is important for clinicians to understand basic principles which govern this portion of. Raised anion gap metabolic acidosis is recognized in acute NSAID overdose and this occurs as a result of accumulation of acidic metabolites. 30 31 Acidosis is frequently exacerbated by seizure activity tissue hypoperfusion and hypovolemia secondary to vomiting.
14 16 17 31 35 Acidosis has been reported following overdose of ibuprofen 11 14 16 30 31 39 diclofenac 29 mefenamic. Reviews 11 Uses. This medication is used on the skin to treat common skin and foot plantar warts.
Salicylic acid helps cause the wart to gradually peel off. Sodium citratecitric acid aspirin rectal. Passive renal tubular reabsorption due to increased pH.
Salicylate levels increased at moderate doses. Salicylate levels decreased at large doses dt increased renal excretion of unchanged salicylic acid. Aspirin overdose in any species can result in salicylate poisoning characterized by severe acid-base abnormalities hemorrhage seizures coma and death.
Acetaminophen paracetamol is a para-aminophenol derivative with analgesic and antipyretic effects similar to those of aspirin but it has weaker anti-inflammatory effects than does aspirin and other NSAIDs. When a person has too much acid or too little base in their blood the anion gap will be higher than normal. This is called acidosis and can be life-threatening in some situations.
C 18 H 21 NO 4 HCl MW 35182. The 5 mg ROXICODONE tablet contains inactive ingredients. Microcrystalline cellulose and stearic acid.
The 15 mg and 30 mg tablets contain the following inactive ingredients. 10 15 mg tablet. And FDC Blue No.
2 15 mg and 30 mg tablets. Aspirin overdose as the body overcompensates for the high acid levels this causes. Symptoms of blood pH changes.
If a persons blood pH moves. Dicloxacillin aspirincitric acidsodium bicarbonate. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing renal clearance.
Dicloxacillin aspirincitric acidsodium bicarbonate. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Dicloxacillin will decrease the level or effect of atogepant by affecting hepatic.
Acid-base changes due to increases or decreases in HCO 3 concentration occur more slowly than changes in CO 2 taking hours or days. Any disease or condition that affects the lungs kidneys metabolism or breathing has the potential to cause acidosis or alkalosis. The bicarbonate test gives a healthcare practitioner a rough estimate of your acid-base balance.
This is usually sufficient. May expose to potentially fatal overdose. Carbaglu carglumic acid Tablet.
Tablets should be dispersed completely in water. Carbatrol car BAMazepine Capsule. Slow-release a Cardene SR niCARdipine Capsule.
Overdose can cause excessive bleeding. What should I avoid while taking clopidogrel. It can increase your risk of stomach bleeding.
Avoid activities that may increase your risk of bleeding or injury. Use extra care to prevent bleeding while shaving or brushing your teeth. If you also take aspirin.
Ask a doctor or pharmacist before using medicines for pain fever swelling or. Do not administer to patients with known hypersensitivity to hyaluronan sodium hyaluronate preparations. Do not inject SYNVISC hylan g-f 20 in the knees of patients having knee joint infections or skin diseases or infections in the area of the injection site.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Clinical Studies.