
About the Societies. Aspirin given shortly after a heart attack decreases the risk of death.
Within the pain pathway there are 3 orders of neurones that carry action potentials signalling pain.
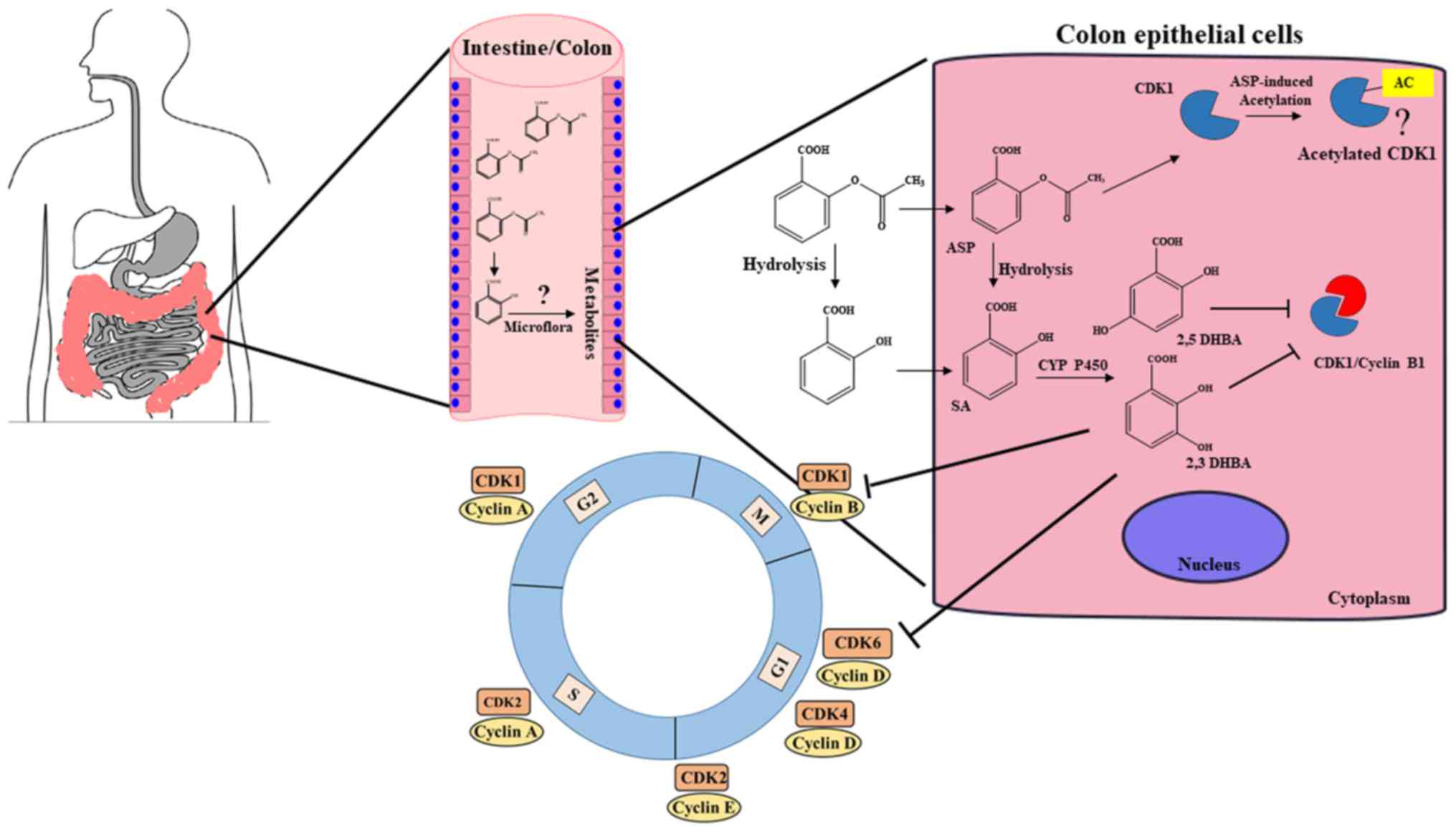
Aspirin metabolism pathway. Therefore aspirin has a very short half-life. Salicylate in turn is mainly metabolized by the liver. This metabolism occurs primarily by hepatic conjugation with glycin or glucuronic acid each involving different metabolic pathways.
The predominant pathway is the conjugation with glycin which is saturable. With low doses of aspirin. Aspirin also known as acetylsalicylic acid ASA is a medication used to reduce pain fever or inflammation.
Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease pericarditis and rheumatic fever. Aspirin given shortly after a heart attack decreases the risk of death. Aspirin is also used long-term to help prevent further heart attacks ischaemic.
Acetylsalicylic acid is hydrolyzed in the plasma to salicylic acid. Plasma concentrations of aspirin following after administration of the extended-release form are mostly undetectable 4-8 hours after ingestion of a single dose. Salicylic acid was measured at 24 hours following a single dose of extended-release acetylsalicylic acid 21.
Fatty acid sources Eicosanoid eicosa- Greek for twenty. See icosahedron is the collective term for straight-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids PUFAs of 20 carbon units in length that have been metabolized or otherwise converted to oxygen-containing productsThe PUFA precursors to the eicosanoids include. Arachidonic acid AA ie.
5Z 8Z11Z14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid is ω-6 fatty. Researchers hypothesize that due to the blocking of the COX pathway the arachidonic acids are shuttled into the lipoxygenase pathway. The production of anti-inflammatory lipoxins results from modifying prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase PTGS2 also called COX-2 that results in the production of lipoxins most of which are anti-inflammatory.
These compounds are called aspirin. Hydrolyzed to salicylate active by esterases in GI mucosa red blood cells synovial fluid and blood. Metabolism of salicylate occurs primarily by hepatic conjugation.
Metabolic pathways are saturable. Urine 75 as salicyluric acid 10 as salicylic acid Onset of Action. 3 to 4.
Aspirin is an orally administered non-steroidal antiinflammatory agent. Acetylsalicylic acid binds to and acetylates serine residues in cyclooxygenases resulting in decreased synthesis of prostaglandin platelet aggregation and inflammation. This agent exhibits analgesic antipyretic and anticoagulant properties.
Extent of first pass metabolism differs in different drugs Extent of first pass metabolism of important drugs 27 First pass Metabolism Low Intermediate High not given orally High oral dose Phenobarbitone Aspirin Isoprenaline propranolol Phenylbutazone Quinidine Lignocaine Alprenolol Tolbutamide Desipramine Hydrocortisone Verapamil Pindolol Nortriptyline Testosterone Salbutamol. Metabolism and transport of acetaminophen in the liver at therapeutic doses. Glucuronidation is the main pathway of acetaminophen metabolism followed by sulfation and a minor contribution from the oxidation route.
Oxidation by CYP isozymes yields a reactive metabolite NAPQI that is detoxified by the glutathione pathway. A metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions that takes a starting molecule and modifies it step-by-step through a series of metabolic intermediates eventually yielding a final product. In the example of sugar metabolism the first metabolic pathway synthesized sugar from smaller molecules and the other pathway broke sugar down into smaller molecules.
These two opposite processes. This pathway of cholesterol metabolism in the brain is a part of the reverse cholesterol transport process and serves as a major route of cholesterol turnover in the brain. 24S-hydroxycholesterol is a known potent activator of LXR and as such serves as an activator of the expression of LXR target genes and thus can effect regulation of overall cholesterol metabolism not only in the brain but.
Variables that were believed to be in the causal pathway or occurred after aspirin use began were not adjusted for. Because aspirin as a cyclooxygenase-1 COX-1 inhibitor modifies inflammatory and coagulation responses these variables were considered to be in the causal pathway and were not adjusted for. The proportional hazards assumption was tested graphically by plotting scaled.
A small-molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway SM04690 as a potential disease modifying agent for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Vol26 No1 p18-27. Osteoarthritis and stem cell therapy in humans.
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Vol26 No6 p711-729. The General Pain Pathway. Within the pain pathway there are 3 orders of neurones that carry action potentials signalling pain.
First-order neurones These are pseudounipolar neurones which have cells bodies within the dorsal root ganglion. They have one axon which splits into two branches a peripheral branch which extends towards the peripheries and a central branch which extends. Salicylate-curcumin mimics were prepared in a facile pathway.
Synthesis of aspirin-piperidone conjugates 5a-p general procedure The appropriate acid chloride of aspirin 3ab 25 mmol in DMF 5 ml was added dropwise within 10 min to a stirring solution of the corresponding piperidone 4ai 25 mmol in DMF 15 ml containing triethylamine 3 mmol in an ice-cold water bath. However due to first-pass metabolism only about 50 of the absorbed dose is systemically available see Table 1. When diclofenac sodium extended-release tablets are taken with food there is a delay of 1 to 2 hours in the T max and a 2-fold increase in C max values.
The extent of absorption of diclofenac however is not significantly affected by food intake. Aspirin is well established for secondary prevention of ASCVD and is widely recommended for this indication but recent studies have shown that in the modern era aspirin should not be used in the routine primary prevention of ASCVD due to lack of net benefit. Most important is to avoid aspirin in persons with increased risk of bleeding including a history of GI bleeding or peptic ulcer.
The mechanisms of this adverse interaction are antiplatelet effects gastric mucosal damage and a hypothrombinemic response to warfarin with an aspirin dosage of 2. The need for simultaneous use of low-dose aspirin 100 mgday with anticoagulants are common for patients with cardiovascular disease but may result in increased bleeding. Promptly evaluate any signs or symptoms of blood loss if treated concomitantly with low-dose aspiriin.
Avoid coadministration with chronic use of higher dose aspirin. In 1 trial APPRAISE-2 therapy was. Patients with stable coronary disease receiving aspirin andor clopidogrel and statins.
Activation of the JAKSTAT pathway also plays a pivotal pathogenetic in chronic Philadelphia-chromosome-negative MPNs through the presence of mutated constitutively activated tyrosine kinases such as JAK2 the thrombopoietin receptor monophosphoryl lipid A and calreticulin. About the Societies. The Association for Academic Surgery is widely recognized as an inclusive surgical organization.
The impetus of the membership remains research-based academic surgery and to promote the shared vision of research and academic pursuits through the exchange of ideas between senior surgical residents junior faculty and established academic surgical professors. A feedback system uses one of the products of a pathway usually the end product to control the activity of the pathway and to regulate the amount of that product. Feedback control may be positive or negative.
To understand negative feedback think of how the thermostat in your house controls the temperature. Lets say that the thermostat is set at 70 degrees F the end product concentration. Cowburn AS Sladek K Soja J et al.
Overexpression of leukotriene C4 synthase in bronchial biopsies from patients with aspirin-intolerant asthma. J Clin Invest. Researchers have made an important discovery that partially answers the long-standing question of why a mothers immune system does not reject a developing fetus as foreign tissue.
Aspirin is an NSAID medicine but it does not increase the chance of a heart attack. Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain stomach and intestines. Aspirin can also cause ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
Some NSAIDs are sold in lower doses without a prescription over-the- counter. Talk to your healthcare provider before using over-the.