
It is a plant hormone. Complications can include swelling of the brain or lungs seizures low blood sugar or cardiac arrest.
In general an acid and a base react to produce a salt and water by transferring a proton H.
Aspirin acid or base. Aspirin or acetylsalicylic acid is perhaps the most commonly used analgesic and antipyretic medication worldwide having been in clinical use for over 100 years. Aspirin can cause several forms of liver injury. In high doses aspirin can cause moderate to marked serum aminotransferase elevations occasionally with jaundice or signs of liver dysfunction and in lower doses in susceptible.
Treatment for salicylate toxicity is based on salicylate concentration acid-base status volume status electrolytes GI decontamination airway protection and respiratory status and enhanced elimination. The acuity of exposure type of formulations co-ingestions comorbidities and clinical status of the patient can affect salicylate levels in serum. Of all of these particularly acid-base.
Aspirin is a salicylate drug often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains as an anti-inflammatory compound that inhibits Cox-1Target. Cox-1Aspirin USAN also known as acetylsalicylic acid is a salicylate drug often used as ananalgesic to relieve minor aches and pains as an antipyretic to reduce fever and as an anti-inflammatory medication. The active ingredient of.
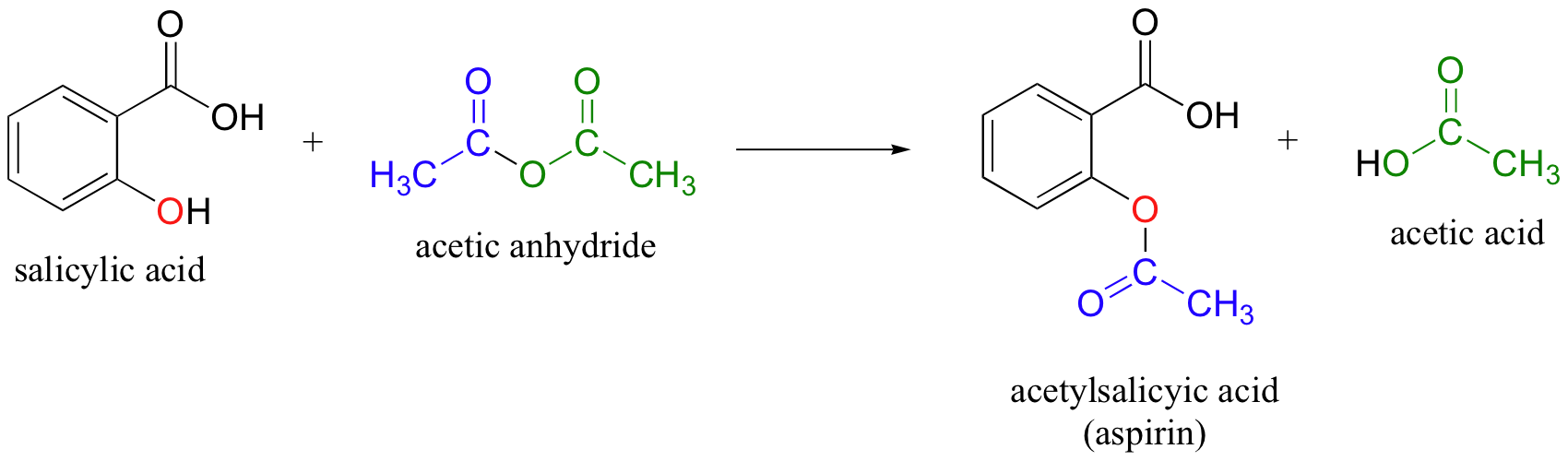
Aspirin acetylsalicylic acid is an aromatic compound containing both a carboxylic acid functional group and an ester functional group. Aspirin is a weak acid that is only slightly soluble in water. Aspirin can be prepared by reacting salicylic acid and acetic anhydride in the presence of an acid catalyst.
Structure of Aspirin acetylsalicylic. Aspirin is a weak acid that also undergoes slow hydrolysis. Ie each aspirin molecule reacts with two hydroxide ions.
To overcome this problem a known excess amount of base is added to the sample solution and an HCl titration is carried out to determine the amount of unreacted base. This is subtracted from the initial amount of base to find the amount of base that actually reacted with the. An acid-base indicator is used to indicate the endpoint of the reaction.
These indicators change the color of the solution at the endpoint. In modern labs instead of indicators pH meters are used to detect the endpoint. 5 Types of Acid Base Titration.
Acid-base titration can be done in both aqueous and nonaqueous media. Aqueous acid base. Salicylate poisoning also known as aspirin poisoning is the acute or chronic poisoning with a salicylate such as aspirin.
The classic symptoms are ringing in the ears nausea abdominal pain and a fast breathing rate. Early on these may be subtle while larger doses may result in fever. Complications can include swelling of the brain or lungs seizures low blood sugar or cardiac arrest.
Acetylsalicylic acid or Aspirin by the German company Bayer in 1899. The name aspirin is derived from acetylated spiraeic acid the old name for salicylic acid. Aspirin is an ester of salicylic acid which passes through the stomach unchanged before being hydrolysed by the basic medium of the intestine to form the active compound.
Aspirin acts to inhibit the production of. This is called the acid-base balance. Your kidneys and lungs work to maintain the acid-base balance.
Even slight variations from the normal range. Aspirin is a weak acid that also undergoes slow hydrolysis. Ie each aspirin molecule reacts with two hydroxide ions.
To overcome this problem a known excess amount of base is added to the sample solution and an HCl titration is carried out to determine the amount of unreacted base. This is subtracted from the initial amount of base to find the amount of base that actually reacted with the. Acetylsalicylic acid aspirin C9 8O4 OH O OH.
43 In this experiment the salicylic acid is the limiting reactant and the acetic anhydride is in excess. After the reaction heating period is over the excess unreacted acetic anhydride will be destroyed by the addition of water to the mixture. Water reacts with acetic anhydride to form 2 molecules of acetic acid according to the reaction shown.
Acetylsalicylic acid Commonly known or available as Aspirin DrugBank Accession Number DB00945 Background. Also known as Aspirin acetylsalicylic acid ASA is a commonly used drug for the treatment of pain and fever due to various causes. Acetylsalicylic acid has both anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects.
This drug also inhibits platelet aggregation and is used in the prevention of blood. Evaluation of mixed acid-base abnormalities requires an understanding of the anion gap the relationship between the change in serum sodium and chloride concentration and the limits of compensation for the primary acid-base imbalances Saxton and Seldin 1986. Wilson and Green 1985.
Clinical findings and history are also necessary to define the factors that may contribute to the development. Routinely determined using the acidbase titration method described in the British Pharmacopoeia 2 but a large number of alternative instrumental methods are also described in literature. This application note will compare two such spectrophotometric methods.
Acetylsalicylic acid is readily hydrolysed in basic medium to yield the salicylate dianion. Aspirin Acetylsalicylic acid Salicylate. Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC 6 H 4 CO 2 H.
A colorless bitter-tasting solid it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin acetylsalicylic acid. It is a plant hormone. The name is from Latin salix for willow treeIt is an ingredient in some anti-acne productsSalts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates.
The active form of aspirin is its metabolite sulfasalicylic acid. An overdose of aspirin causes acidosis due to the acidity of this metabolite. Metabolic acidosis can also result from uremia which is the retention of urea and uric acid.
Metabolic acidosis can also arise from diabetic ketoacidosis wherein an excess of ketones is present in the blood. Other causes of metabolic acidosis are a. In general an acid and a base react to produce a salt and water by transferring a proton H.
HA aq NaOH aq H2O l NaA aq 1 acid base salt The active ingredient in aspirin and the chemical for which aspirin is the common name is acetylsalicylic acid. To determine the amount of aspirin acetylsalicylic acid in a sample the precise volume and concentration. Acid-base status is the balance of acid and base in the blood.
Aspirin may change this balance quickly so the doctor will monitor this to guide treatment. Aspirin Poisoning Treatment - Self-Care. Aspirin is an acid because of the carboxylic acid group which gives the molecule a relatively stable anion negatively charged form which means that it can readily donate a proton.
The Bronstead-Lowry theory states that an acid is a proton donor while a base is a proton acceptor Therefore since aspirin donates a proton H it can be classed as an acid. Understanding acid-base balance is a core concept that can help you think critically about your patients and recognize how imbalances can impact their overall wellbeing. As you recall from your anatomy and physiology course having a proper balance between acid and base in the body is critical to maintaining homeostasis and optimal cellular function.
Recall that the normal range for a serum pH. Acidbase reactions are essential in both biochemistry and industrial chemistry. Moreover many of the substances we encounter in our homes the supermarket and the pharmacy are acids or bases.
For example aspirin is an acid acetylsalicylic acid and antacids are bases. In fact every amateur chef who has prepared mayonnaise or squeezed a. As has been the case since the introduction of Aspirin acetylsalicylic acid ASA its active ingredient continues to be used as the benchmark in pain relief and CV event prevention.
At over-the-counter OTC doses Aspirin offers the same pain-relieving properties as many molecules discovered decades later. It has been the most utilized pain reliever in history. As such its efficacy.
The four principal acid-base imbalances are illustrated in Table 1. As well as possible causes for each condition. The H ion concentration is reflected in the serum pH value.
Normal pH levels range from 735 to 745 and are slightly alkaline. Elevated levels indicate alkalosis decreased H ion concentration caused by excess alkaline agents or a reduced amount of acidic components while. Acetylsalicylic acid as well as the main metabolite salicylic acid are extensively bound to plasma proteins primarily albumin and distributed rapidly into all parts of the body.
Maximum plasma concentration is reached after 03 - 2 hours total salicylate. The degree of protein binding of salicylic acid is strongly dependant of both the salicylic acid and albumin concentration. Our doctors define difficult medical language in easy-to-understand explanations of over 19000 medical terms.