
This aromatic compounds are cyclic in nature but they are unsaturated and have scent of their own for example Benzede which is used as a solvent. The journey has been long and filled with unexpected twists and turns.
41 Other N-centered nucleophiles 10 S- and Se-Nucleophiles 33 P-Nucleophiles 18.
Aromatic conjugated ketones. Conjugated microporous polymers CMPs are porous organic materials that display semiconducting behavior due to their highly π-conjugated structures. As such they are promising next-generation materials for applications requiring both conductivity and porosity such as supercapacitive energy storage and electrochemical sensing. However most CMPs and related porous aromatic frameworks.
Aromatic compounds also known as arenes or aromatics are chemical compounds that contain conjugated planar ring systems with delocalized pi electron clouds instead of discrete alternating single and double bondsTypical aromatic compounds are benzene and tolueneThey should satisfy Hückels rule. Contrast CategoryAntiaromatic compounds see antiaromaticity. Aromatic Compounds sp2 C-H stretch 3100-3020 cm-1 3000 CC stretch 1585 cm-1.
Ketones CO stretch 1750-1710 cm-1 1715 is typical for aliphatic ketones 1685-1665 cm-1 conjugated Carboxylic acids O-H of CO2H 3600-2500 cm-1 centered at 3000 CO stretch 1720-1710 cm-1 aliphatic 1700-1680 cm-1 conjugated Esters CO stretch 1750-1735 cm-1 aliphatic 1720-1715 cm-1. A list of alcohols aldehydes and ketones along with the MP of a solid derivative of each compound is. This most often means that the carbonyl group in the unknown is non-conjugated.
A reddish-orange color most likely means that the carbonyl group is conjugated. There are exceptions to this so care should be taken when interpret ing this observation. In a few cases compounds in which.
Interactive problems to aid students of organic chemistry. The practice problems offered here are chiefly interactive and should provide a useful assessment of understanding at various stages in the development of the subject. Aromatic vs Antiaromatic vs Non Aromatic Practice Exercises.
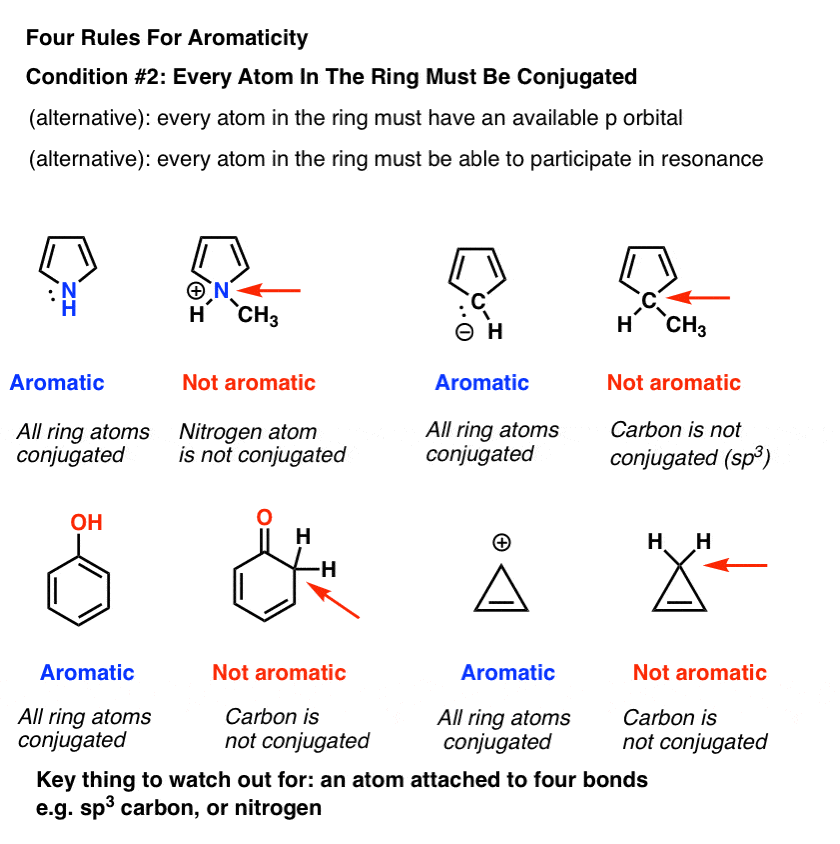
Our last post in this series on aromaticity went through the 4 conditions a molecule must fulfill in order to be aromatic. First it must be cyclic Second every atom around the ring must have an available p-orbital. Third the number of electrons in the pi system must be 2 6 10 14 18 or a higher number in the set that.
Aromatic Compounds 1999. Substitution and Elimination Reactions 1999. Enols and Enolates 1999.
Aldehydes and Ketones 1999. Over the years of teaching organic chemistry Ive developed a huge and constantly growing collection of organic chemistry study notes and cheat sheets. Currently I have over.
The benzylic position is quite reactive and presents a useful synthetic tool for preparing many aromatic compoundsThe reason for this reactivity is the resonance stabilization of the benzylic carbon regardless if the reaction goes through an ionic or radical mechanism. We will discuss each of these in the next sections. Substitution and Elimination Reactions at the Benzylic Position.
Heterocyclic aromatic compounds contain in their molecules at least one heteroatom and one carbon. For these systems the possibility of semi-conjugated HMBs does not arise. HMBs with only one 2π heteroatom are either conjugated cross-conjugated or pseudo-cross-conjugated.
The classification of heterocyclic mesomeric betaines with a single 2π heteroatom. Conjugated ring systems having 4n π-electrons eg. 4 8 12 etc.
Electrons not only fail to show any aromatic properties but appear to be less stable and more reactive than expected. As noted above 1357-cyclooctatetraene is non-planar and adopts a tub-shaped conformation. The compound is readily prepared and undergoes addition reactions typical of alkenes.
Catalytic hydrogenation of. Resonance and Conjugated Dienes. 12 and 14 Electrophilic Addition to Dienes.
Kinetic vs Thermodynamic Control of Electrophilic Addition to Dienes. Predict the Products of the Diels-Alder Reaction with Practice Problems. Endo and Exo products of Diels-Alder Reaction with Practice.
In short the roles of the aromatic ring and attacking species are reversed. The attacking species CH 3 O is the nucleophile and the ring is the electrophile. Since the nucleophile is the attacking species this type of reaction has come to be known as nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
The Effect Of Substituents On The Ring. A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon PAH is a hydrocarbona chemical compound containing only carbon and hydrogenthat is composed of multiple aromatic ringsThe group is a major subset of the aromatic hydrocarbonsThe simplest of such chemicals are naphthalene having two aromatic rings and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthreneThe terms polyaromatic hydrocarbon or. Aldehydes and ketones of low molecular weights are volatile compounds.
Identification of aldehydes and ketones is based on two types of reactions addition reaction to the double bond and oxidation reaction. In aldehydes the carbonyl group is attached to a hydrogen atom and an aliphatic or aromatic radical. Formaldehyde is an exceptional case.
Ketones in the presence of dilute base yields a molecule having both alcohol and aldehyde functional groups. An example of the type of base-catalyzed aldol condensation that you will perform is shown below. O 2 O - 2 H 2 O.
Benzaldehyde Acetone Dibenzalacetone 15-diphenyl-14-pentadien-3-one 1 These products are a β-hydroxyaldehyde or a β-hydroxyketone. This reaction is used. Carbon can form covalent bonds with itself and other elements to create a mind-boggling array of structures.
In organic chemistry we will learn about the reactions chemists use to synthesize crazy carbon based structures as well as the analytical methods to characterize them. 14 - Aromatic Compounds and Aromaticity 15 - Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution EAS 16 - Reactions and Synthesis of Alcohols 17 - Ethers Epoxides and Sulfides 18 - Aldehydes and Ketones. Aromatic amines 7 Amide anions N reactivity 21 Amidines and Imines 10 Amino acids 20 Azoles and Azole Anions 33 Guanidines 8 Hydrazines Hydroxylamines etc.
21 Imidazolines and related compounds 10 Isothioureas 11 Nucleobases and Their Subunits 15 Pyridines Quinolines etc. 41 Other N-centered nucleophiles 10 S- and Se-Nucleophiles 33 P-Nucleophiles 18. A simple and efficient enantioselective epoxidation of αβ-unsaturated ketones is catalyzed by rare-earth metal amides in the.
Methylene blue as photoredox catalyst and persulfate as oxidant deliver ketones and epoxyketones from a range of aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes as well as conjugated and nonconjugated olefins as abundant and inexpensive chemical feedstocks. De Souza J. The Nazarov Cyclization allows the synthesis of cyclopentenones from divinyl ketones.
Mechanism of the Nazarov Cyclization. The reaction is catalyzed by strong Lewis or Brønstedt acids and one or more equivalents of the Lewis acid are normally necessary. The regioselectivity of the cyclization is quite low if the side chains have a similar degree of substitution.
Nazarov reactions with more. Organic Chemistry Textbook by Robert Neuman I began writing an organic chemistry textbook in 1992. The journey has been long and filled with unexpected twists and turns.
I had hoped that I might some day see the book on shelves of campus bookstores but I realized several years ago that this was unlikely. In aromatic compounds each band in the spectrum can be assigned. CH stretch from 3100-3000 cm-1.
Overtones weak from 2000-1665 cm-1. CC stretch in-ring from 1600-1585 cm-1. CC stretch in-ring from 1500-1400 cm-1.
CH oop from 900-675 cm-1. Note that this is at slightly higher frequency than is the CH stretch in alkanes. Other chemical classes of concern include other metals N-nitrosamines and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons PAHs.
Carbonyl compounds include the ketones and aldehydes. These compounds are studied because of their reactivity and levels which approach 1 mg generated per cigarette. The most prevalent aldehydes in mainstream smoke from cigarettes generated using the.
Amines are organic derivatives of ammonia in which one two or all three of the hydrogens of ammonia are replaced by organic groups. Compounds RNH 2 are called primary amines R 2 NH secondary amines and R 3 N are tertiary amines. The designation of amines as primary secondary and tertiary is different from the usage of these terms in.
Aromatic compound is also example of organic chemical compound which is also be called as arenes or aromatics. It contains conjugated planar ring system instead of alternating single and double bonds. This aromatic compounds are cyclic in nature but they are unsaturated and have scent of their own for example Benzede which is used as a solvent.