135 Causes Ingestion of large amounts of Na fluid deprivation lack of fluid consumption hyperventilation burns corticosteroid use Signs Symptoms Dry tongue. An essential pediatric and neonatal drug lookup continually updated.
28-Dialysis Renal Failure 31-Overdose Toxic Ingestion 60-Ped OD Toxic Ingestion 83-Marine Envenomations 88-Crush Syndrome.
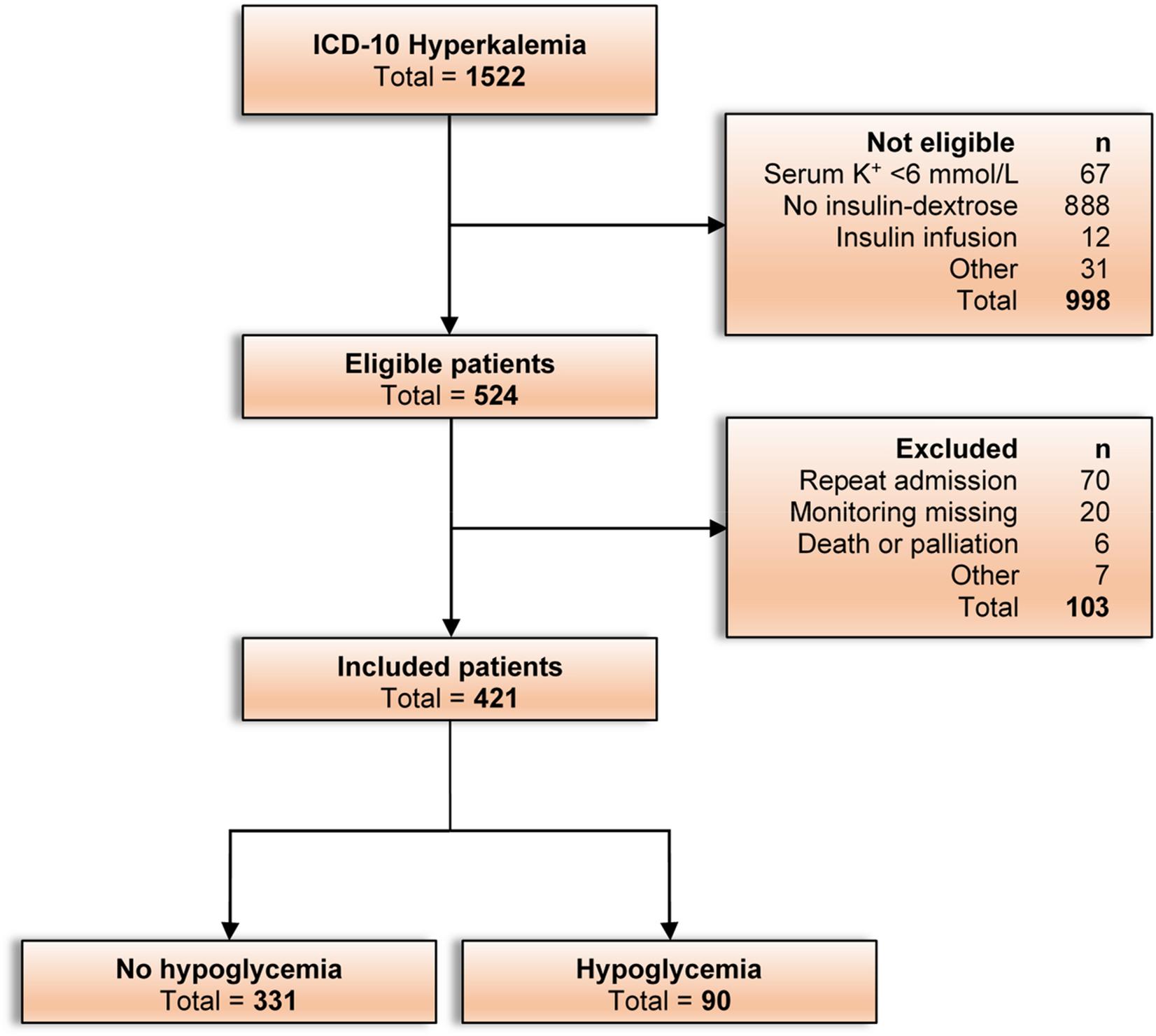
Antidote for hyperkalemia. Dextrose antidote is used for acute alcohol intoxication sulfonylurea overdose insulin overdose high blood potassium hyperkalemia and insulin-induced hypoglycemia in pediatric patients. Learn about side effects dosages drug interactions and more. Presence of hyperkalemia.
Given that isoproterenol causes vasodilation it has actually been tested in animal models an antidote to treat extravasation reactions. Several references state that isoproterenol can be given peripherally eg. The Alfred ICU Critical Care Study Guide by Criner GJ et al and Critical Heart Disease in Infants and Children by Nichols DG et al.
Calcium gluconate is a medication used to manage hypocalcemia cardiac arrest and cardiotoxicity due to hyperkalemia or hypermagnesemia. It is classified as a calcium salt. This activity outlines the indications action and contraindications for calcium gluconate as a valuable agent in managing hypocalcemia cardiac arrest cardiotoxicity due to hyperkalemia or hypermagnesemia and.
An essential pediatric and neonatal drug lookup continually updated. Propofol infusion syndrome is a rare but extremely dangerous complication of propofol administration. Certain risk factors for the development of propofol infusion syndrome are described such as appropriate propofol doses and durations of administration carbohydrate depletion severe illness and concomitant administration of catecholamines and glucocorticosteroids.
May cause hyperkalemia particularly with high doses renal insufficiency or when combined with other drugs that cause hyperkalemia. Alpelisib will decrease the level or effect of trimethoprim by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C910 metabolism. Trimethoprim increases levels of amantadine by decreasing elimination.
The other complication is hyperkalemia which occurs in 5 to 10 of patients receiving heparin and is the result of heparin-induced aldosterone suppression. The hyperkalemia can appear within a few days after the onset of heparin therapy. More rarely the side-effects alopecia and osteoporosis can occur with chronic use.
As with many drugs overdoses of heparin can be fatal. In September 2006. Renal replacement therapy may be indicated in the context of renal failure and hyperkalemia.
Note that the some of the indications for digibind differ see here for indications Seek and treat underlying cause inter-current illness. Medical clearance at 6h if. Falling serial serum digoxin levels.
No evidence of cardiotoxicity. LisinoprilHydrochlorothiazide is therefore a valuable therapy in the field of internal medicine. Zestoretic is a good 2-in-1 blood pressure medication that also protects kidney function long-term.
Lisinopril Hydrochlorothiazide is therefore a valuable therapy in the field of internal medicine is a prescription medication used to treat high blood pressure. Replaces calcium in hypocalcemia increases myocardial contractile force increases ventriular automaticity antidote for mag. Sulfate minimizes side efects of calcium channel blockers.
Calcium Chloride - Indications. Hypocalcemia hyperkalemia calcium channel blocker toxicity mag. Calcium Chloride - Contraindications.
Hyperkalemia may occur especially in patients with impaired renal function. Induce vomiting or evacuate the stomach by lavage. There is no specific antidote.
Treatment is supportive to maintain hydration electrolyte balance and vital functions. Patients who have renal impairment may develop hyperkalemia. In such cases discontinue.
Calcium gluconate is a mineral supplement and medication. As a medication it is used by injection into a vein to treat low blood calcium high blood potassium and magnesium toxicity. Supplementation is generally only required when there is not enough calcium in the diet.
Supplementation may be done to treat or prevent osteoporosis or rickets. It can also be taken by mouth but is not. Consider more antidote if there is a persistent metabolic acidosis.
Bicarbonate can be used cautiously. Correct metabolic acidosis with bicarbonate when blood pH falls below 720 and be sure to correct electrolyte imbalance for example hyperkalemia hypercalcemia. Oxygen requirement would be expected to decrease after successful administration of the antidote.
Calcium Gluconate is used in patients experiencing hyperkalemia calcium channel blocker overdose as an anti-dote to hypermagnesemia and for patients with hypocalcemia. It is very important you monitor and review your patients electrolyte levels prior to and after administration. A serious contraindication includes patients with V-fib digitalis toxicity and hypercalcemia.
Ensure a patent. Malignant hyperthermia MH is a life-threatening clinical syndrome of hypermetabolism involving the skeletal muscle. It is triggered in susceptible individuals primarily by the volatile inhalational anesthetic agents and the muscle relaxant succinylcholine though other drugs have also been implicated as potential triggers.
MH is not an allergy but an inherited disorder that is found both. Serious digoxin toxicity can cause hyperkalemia. Administration of potassium supplements in these patients may be hazardous.
After treatment with DIGIFab serum potassium concentration may decrease rapidly and must be monitored frequently especially during the first several hours of administration. The answer is A. Protamine sulfate is the antidote for Heparin.
Youre providing care to a patient who has been receiving long-term doses of Heparin. What finding in this patient demonstrates the patient may be experiencing a complication that can occur due to long-term use of this drug. Treatment of Thromboembolism Adult.
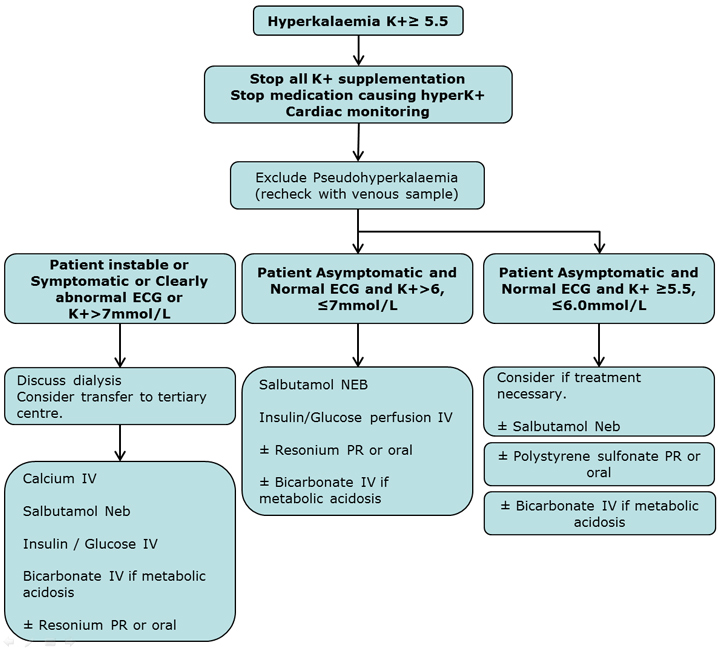
IV 5000-U bolus dose then 2000040000 U infused over 24 h dose adjusted to maintain desired APTT or 500010000 U IV piggyback q46h SC 1000020000 U followed by 800020000 U q812h Child. IV 50 Ukg bolus then 20000 Um 2 24 h or 50100 Ukg q4h or 1525 Ukgh Open Heart Surgery. The major sign of hyperkalemia or high serum potassium is taller and peaked T-waves.
Also a widening of the QRS-wave may be seen. This can be treated in a number of ways which include sodium bicarbonate IV glucoseinsulin calcium chloride IV Kayexalate dialysis and possibly albuterol. All of these will help reduce serum potassium levels.
Read more about hyperkalemia with cardiac. NURS 452 FLUID ELECTROLYTES STUDYGUIDE Sodium Na. 135 145 mEqL Most abundant in ECF Function.
Maintains water balance transmits nerve impulse contract muscles HYPERNATREMIA. 135 Causes Ingestion of large amounts of Na fluid deprivation lack of fluid consumption hyperventilation burns corticosteroid use Signs Symptoms Dry tongue. Antidote for Nerve Agents or Organophosphate Overdose One auto-injector then per medical control See Color Coded List One pediatric auto-injector then as per medical control Calcium Chloride NCCEP Protocol.
28-Dialysis Renal Failure 31-Overdose Toxic Ingestion 60-Ped OD Toxic Ingestion 83-Marine Envenomations 88-Crush Syndrome. Some other severe symptoms due to this hypermetabolism in malignant hyperthermia are tachycardia respiratory and metabolic acidosis and cardiac arrest impairment of blood coagulation kidney failure other organ failures and very high levels of potassium hyperkalemia which is critical to the function of nerve cells. Severe Metabolic Acidosis Hyperkalemia.
1 mEqkg slow IV bolus Max. Support ventilation Not recommended in cardiac arrest. 10 mcgkg SQ q 10-15 min until IV access 01-10 mcgkgmin IV.
Use with cautioun in hypokalemia. Cardiac Arrest Septic Shock. 04-1 unitkg IV bolus Max Dose.
Reducing the likelihood of fibrillation Indications. Hyperkalemia hypocalcemia hypermagnesemia beta blocker and calcium channel blocker overdose. Syncope cardiac arrest dysrhythmia bradycardia asystole N V metallic taste tissue necrosis at injection site.