
What happens when zinc granules are treated with a dilute solution of H 2 SO4 HCl HNO 3 NaCl and NaOH also write the chemical equations if a reaction occurs. Acetaldehyde acetic acid.
Always use test tube holder while heating the test tube.
Anhydrous copper sulphate crystals. Anhydrous copper sulfate is 3981 percent copper and 6019 percent sulfate by mass and in its blue hydrous form it is 2547 copper 3847 sulfate 1282 sulfur and 3606 water by mass. Four types of crystal size are provided based on its usage. Large crystals 1040 mm small crystals 210 mm snow crystals less than 2 mm and windswept powder less than 015 mm.
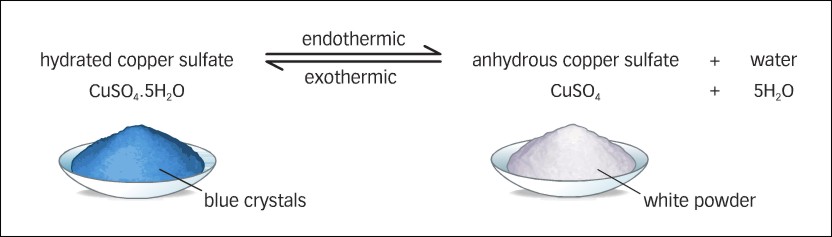
On adding water anhydrous copper sulphate changes to hydrated copper sulphate. It is a reversible chemical change. Keep the mouth of the test tube away from your face and also from other classmates.
Always use test tube holder while heating the test tube. Take a small quantity of copper sulphate crystals. Go to List.
Copper Sulphate is blue not because of air but because it has been oxidised to the Cu2 ion which is a d-block metal ion. The electrons in the metal ion can transition between different energy states and therefore the ion absorbs light energy and can be seen as being BLUE. Why is the Colour of copper sulphate blue.
Absorption of Light As it happens the difference in energy for the copper. Answer 1 of 5. All the answers here sound perfectly reasonable until you look at the video and see rapid evolution of bubbles in the solution.
That has nothing to do with the redox reaction with copper sulfate because that reaction would involve evolution of Cu0 ie. Copper metal MgSO4. Granular Crystals Copper Sulfate.
Sulfuric acid copper2 salt. CopperII sulfate 98 for analysis anhydrous. Tobacco States Brand Copper Sulfate.
Phelps Triangle Brand Copper Sulfate. Sulfuric acid copper salt. Sulfuric acid copper2 salt 1.
Ferrous sulphate crystals contain water molecules FeSO 4. On heating ferrous sulphate crystals lose water and anhydrous ferrous sulphate FeSO 4 is formed. So their colour changes from light green to white.
On further heating anhydrous ferrous sulphate decomposes to form ferric oxide Fe 2 O 3 sulphur dioxide SO 2 and sulphur. Magnesium sulfate or magnesium sulphate in British English is a chemical compound a salt with the formula MgSO 4 consisting of magnesium cations Mg 2 2019 by mass and sulfate anions SO 2 4It is a white crystalline solid soluble in water but not in ethanol. Magnesium sulfate is usually encountered in the form of a hydrate MgSO 4 nH 2 O for various values of n between 1 and 11.
Answer 1 of 17. Explanation - Zinc is more reactive than copper. So here on adding zinc to CuSO4 solution zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate forms zinc sulphate solution.
This is indicated by colour change from blue to colourless. CuSO4 solution has a blue colour while ZnSO4 solu. On heating copper sulphate crystals the blue colour of copper slowly changes to light blue and then colourless.
The water droplets are collected on the inner part of the test tube. It is regarded that each molecule of copper sulphate crystals at room temperature contains five water molecules as water of crystallisation. Do you see any difference in them.
Look at the. Anhydrous CuSO 4 has an orthorhombic crystal structure whereas CuSO 45H 2 O crystals have triclinic structures. The copper ions present in copper sulfate react with the chloride ions belonging to concentrated hydrochloric acid leading to the formation of tetrachlorocuprateII.
The chemical equation for this reaction is given by Cu 2 4Cl CuCl 4 2-When heated. Copper Sulphate is an odorless crystalline substance electric blue in color highly toxic and not safe to work with. It is produced industrially by treating copper metal with hot concentrated sulfuric acid or its oxides with dilute sulfuric acid.
For laboratory use copper sulfate is usually purchased. The anhydrous form occurs as a rare mineral known as chalcocyanite. The hydrated copper.
Blue crystals granules or powder. 2286 SG 156 C 4 C 148gkg 0 C 736gkg 100 C Basic copper sulfate. 3CuOH 2 CuSO 4.
Light blue green fine powder. Insoluble soluble in acids Mode of Action. The copper ion is the component of copper sulfate with toxicological implications.
The water molecules that are present in the crystals are called water of crystallisation. The molecular formula of blue vitriol is C u S O 4. 5 H 2 O It is called copper sulfate pentahydrate and It contains 5 moles of water of crystallisation.
Sodium carbonate monohydrate is called washing soda. Its molecular formula is N a 2 C O 3. Slowly effloresces in dry air or above 306 C with the formation of the trihydrate.
At 88-100 C the trihydrate is produced more quickly. Above 114 C the monohydrate is formed and between about 245 and 240 C the anhydrous product copperII sulfate results. Copper chlorophylls are obtained by addition of a salt of copper to the substance obtained by solvent extraction of strains of edible plant material grass lucerne and nettle.
The product from which the solvent has been removed contains other pigments such as carotenoids as well as fats and waxes derived from the source material. The principal colouring matters are the copper phaeophytins. C Copper sulphate on treatment with potassium iodide precipitates cuprous iodide Cu 2 I 2 liberates iodine gas and also for ms potassium sulphate.
A solution of potassium chloride when mixed with silver nitrate solution an insoluble white substance is for med. W rite the chemical. Taurine 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid.
75 mg 060 mmol and anhydrous CuCl 2 40 mg 030 mmol were dissolved in 03 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid in. Three beakers labelled as A B and C each containing 25 ml of water were taken. A small amount of NaOH anhydrous CuSO 4 and NaCl were added to the beakers A B and C respectively.
It was observed that there was an increase in the temperature of the solution contained in beakers A and B whereas in case of beaker C the temperature of the solution falls. PETG Chemical Resistance Chart. Acetaldehyde acetic acid.
1 mole of copper atoms will contain 602 x 1023 atoms. The water of crystallisation in calcium sulfate crystals can be removed as water vapour by heating as shown in the following equation. CaSO4xH2Os CaSO4s xH2Og Method.
Weigh an empty clean dry crucible and lid. Add 2g of hydrated calcium sulfate to the crucible and weigh again Heat strongly with a Bunsen for a. CWhen silver metal is added to Copper Sulphate solution there will not be any reaction as silver is non-reactive metal.
What happens when zinc granules are treated with a dilute solution of H 2 SO4 HCl HNO 3 NaCl and NaOH also write the chemical equations if a reaction occurs. Potassium AcetateCopper Sulfate 3c. To a mixture of 136 g 10 mol phenylacetic acid 70 g sodium or potassium acetate and 16 g 01 mol anhydrous cupric sulphate is introduced 2000 ml anhydrous acetic anhydride in 4000 ml flask.
The mixture is refluxed 24 h. After cooling 500 ml of solvent CCl 4 CHCl 3 CH 2 Cl 2 is added and the mixture is poured to a flask containing 2000 ml ice. Sulphate of ammonia 21 N 60 SO 3.
At one time as a fertiliser this was the main source of nitrogen. However sulphate of ammonia is seldom used now. It consists of whitish needle-like crystals and it is produced synthetically from atmospheric nitrogen.
Bacteria change the nitrogen in the compound to nitrate. It has a greater. Take about 2 ml of the given compound in a clean dry test-tube add 1 g of anhydrous calcium sulphate and shake well.
Filter and to the filtrate add 2 or 3 drops of acetyl chloride shakeand bring a glass rod dipped in ammonium hydroxide solution near the mouth of the test-tube. Formation of white fumes indicates the presence of alcoholic group. To characterize the product.
Copper Sulphate 1 Wine 1 Fining agent 1 In such quantity that the content of copper in the finished product shall not exceed 00001 2 Preserved duck eggs 2 In the alkaline soaking solution to assist in the preservation process 2 00005 calculated as copper in the edible portion of the.