
Click Start Quiz to begin. 4 Oxalate ion.
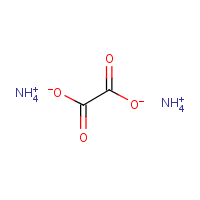
It is also called oxalate diammonium or salt diammonium.
Ammonium oxalate formula. Ammonium oxalate C 2 H 8 N 2 O 4 more commonly written as NH 4 2 C 2 O 4 is an oxalate salt with ammonium sometimes as a monohydrate. It is a colorless white salt under standard conditions and is odorless and non-volatile. It is the ammonium salt of.
Oxalic acid diammonium salt. Ethanedioic acid diammonium salt. The ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula NH 4.
It is formed by the protonation of ammonia NH 3. Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations NR 4 where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups indicated by R. Ammonium oxalate is a chemical formula inorganic compound C2H8N2O4.
It is also called oxalate diammonium or salt diammonium. Ammonium Oxalate is an ammonium-rich oxalate salt. Ammonium oxalate is a highly active dicarboxylic acid.
Test your knowledge on ammonium sulfate. Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click Start Quiz to begin.
C 2 K 2 O 4. Ethanedioic acid dipotassium salt. CID 971 Oxalic acid Component Compounds.
CID 971 Oxalic acid CID 5462222 Potassium Dates. Potassium oxalate is an odorless white. Ammonium oxide formula NH 4 2 O.
Ammonium phosphate formula NH 4 3 PO 4. Ammonium sulfate formula NH 4 2 SO 4. Ammonium sulfide formula NH 4 2 S.
C 6 H 8 O 6. BaC 2 H 3 O 2 2. Names Formula Names Formula ammonium NH4 acetate CH3COO-C2H3O2-bromate BrO3-carbonate CO3 2-chlorate ClO3-chlorite ClO2-chromate CrO4 2-cyanide CN-dichromate Cr2O7 2-hydrogen carbonate bicarbonate HCO3-hydrogen sulfate bisulfate HSO4-hydrogen phosphate biphosphate HPO4 2-hydroxide OH-hypochlorite ClO-iodate IO3-nitrate NO3-nitrite NO2-oxalate C2O4 2-perchlorate ClO4.
You can calculate molar mass by finding the number of atoms in the molecular formula then adding the atomic mass of each element together to find the molecular weight. The atomic mass can be found on the periodic table. For example lets find the molar mass of water H 2 O.
H 2 O is composed of two parts hydrogen H and one part oxygen O. The atomic mass of hydrogen is 100794 and. 4 Ammonium ion F Fluoride ion.
4 Oxalate ion. Most Common Formula Representations All represent ethanol Example C 2H 6O CH 3CH 2OH Name Molecular Formula Condensed Molecular Formula Structural Formula Line Formula. Microsoft Word - Chem 1 Compound Sheet FS08 Author.
Terry Bone Created Date. 922008 15513 PM. Formula writing rules to write the correct chemical formulas for each compound.
Compound Name Type of Compound. Ionic or Covalent Chemical Formula 1 copper II chlorite 2 sodium hydroxide 3 nitrogen dioxide 4 cobalt III oxalate 5 ammonium sulfide 6 aluminum cyanide 7 carbon disulfide 8 tetraphosphorous pentoxide 9 potassium permanganate 10 manganese III chloride Compound. Students enrolled in Dr.
Draganjacs Introduction to Chemistry CHEM1003 General Chemistry I CHEM1013 and General Chemistry II CHEM1023 classes are responsible for learning the names and formulae for the common acids and common reagents and for learning the names formulae and the charges for the common cations and anions listed below. We are a leading supplier to the global Life Science industry with solutions and services for research biotechnology development and production and pharmaceutical drug therapy development and production. Were to begin the goat throat is the best pump we have used every time i push the plunger down i feel pure ecstacy with each pump that feeling only gets stronger and when i turn the nozzle on and that crystal clear liquid of my choosing flows so effortlessly from the goat throat and in the blink of a eye i can stop the flow with no drips.
What do you think is the formula for bisulfate. Finally in some ions sulfur replaces one of the oxygen atoms and then thio is added as a prefix to the name. Thus SCN- is called thiocyanate after the cyanate ion CNO- and thiosulfate is S2O32- after sulfate.
The anion gap AG is a mathematical construct that compares the blood sodium concentration with the sum of the chloride and bicarbonate concentrations. It is a helpful calculation that divides the metabolic acidoses into 2 categories. High AG metabolic acidosis HAGMA and hyperchloremic metabolic acidosisand thereby delimits the potential etiologies of the disorder.