
This process is called nitrification. Digestion- the decomposition of nitrogen in organic samples utilizing a concentrated acid solution.
This is accomplished by boiling a homogeneous sample in concentrated sulfuric acid.
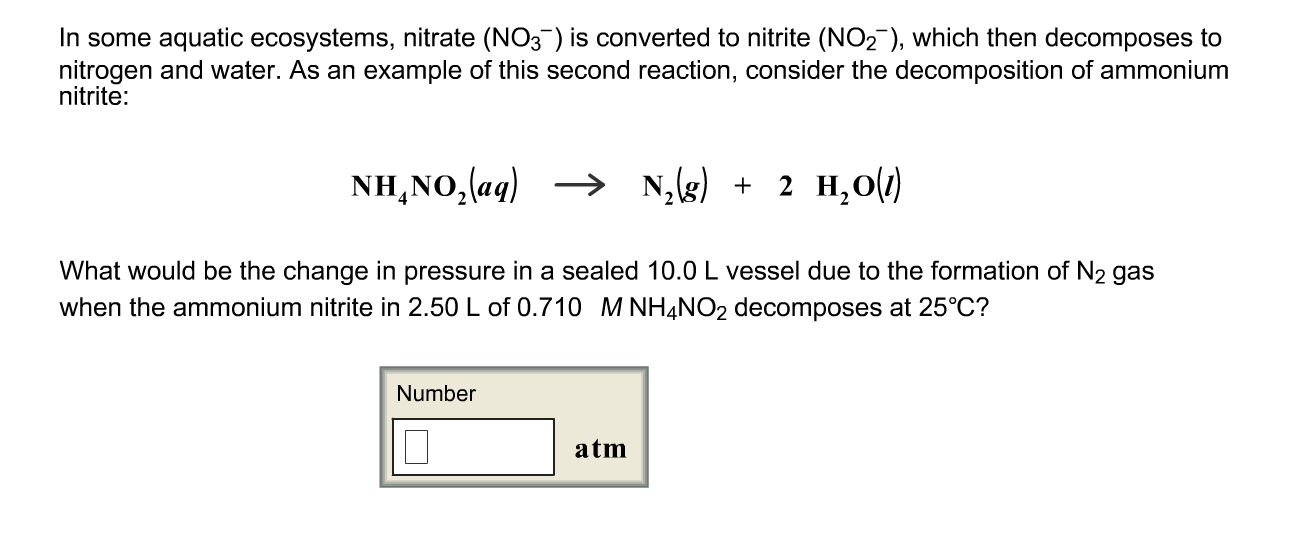
Ammonium nitrite decomposition. Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula NH 4 NO 3It is a white crystalline solid consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrateIt is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid although it does not form hydratesIt is predominantly used in agriculture as a high-nitrogen fertilizer. Global production was estimated at 216 million tonnes in 2017. Thermal decomposition or thermolysis is a chemical decomposition caused by heat.
The decomposition temperature of a substance is the temperature at which the substance chemically decomposes. The reaction is usually endothermic as heat is required to break chemical bonds in the compound undergoing decomposition. If decomposition is sufficiently exothermic a positive feedback.
Signs and symptoms of nitrite poisoning include methemoglobinemia nausea dizziness increased heart rate hypotension fainting and possibly shock. P-1 Safety Data Sheet SDS. 03242017 Page 3 7 Chronic Symptoms.
May cause irritation to the respiratory tract. Indication of Any Immediate Medical Attention and Special Treatment Needed. Sodium nitrite is sold as the salt and in solution.
The finely crystalline slightly yellowish salt is marketed in untreated form and also after treatment with aryl alkyl sulfonates. The salt contains ca. 990 sodium nitrite 06 sodium nitrate 01 sodium chloride and sodium sulfate and 01 water.
Ammonium sulfate is an inorganic sulfate salt obtained by reaction of sulfuric acid with two equivalents of ammoniaA high-melting decomposes above 280 white solid which is very soluble in water 706 g100 g water at 0. 1038 g100 g water at 100 it is widely used as a fertilizer for alkaline soils. It has a role as a fertilizer.
Mass flow is the movement of dissolved nutrients into a plant as the plant absorbs water for transpiration. The process is responsible for most transport of nitrate sulfate calcium and magnesium. Diffusion is the movement of nutrients to the root surface in response to a concentration gradient.
When nutrients are found in higher concentrations in one area than another there is a net. Answer 1 of 5. When you get questions like this it helps a lot if you can see the general sorts of patterns.
I will give the lowest level of explanation and then follow up with a high level explanation. In this case both of the reactants are salts. They are each made of a ca.
This decomposition produces ammonia which can then go through the nitrification process. Nitrifying bacteria in the soil convert ammonia into nitrite NO 2- and then into nitrate NO 3-. This process is called nitrification.
Compounds such as nitrate nitrite ammonia and ammonium can be taken up from soils by plants and then used in the formation of plant and animal proteins. Nitrite ion NO 2-3 Nitrogen dioxide NO 2 4 Nitric acid HNO 3 5 Nitrate ion NO 3 -5 Nitrogen is of concern to agriculture both as an essential plant nutrient for building proteins and amino acids and as a potential water pollutant. Nitrogen as nitrate or ammonium is highly soluble and moves rapidly in runoff and in soil solutions.
Buildup of nitrate in groundwater is a health concern. Total nitrogen TN total phosphorus TP total dissolved nitrogen TDN total dissolved phosphorus TDP ammonium NH 4 nitrate NO 3 nitrite NO 2 and chlorophyll a Chl-a concentrations were measured using Chinese standard methods for observation in lake eutrophication Jin and Tu 1990. NO x was the sum of NO 3.
Le nitrate dammonium est un composé ionique du cation ammonium et de lanion nitrate de formule N H 4 N O 3Il correspond au corps minéral anhydre naturel de maille orthorhombique nommé par les minéralogistes nitrammite 8. Il sagit aussi de lancien nitrate dammoniaque obtenu industriellement depuis le XX e siècle par un mélange dammoniaque et dacide nitrique deux. Nitrite is an intermediate product when ammonium is nitrified into nitrate and as nitrate denitrifies to nitrogen gas.
Nitrite levels are higher in plant effluents with partial nitrification or denitrification occurring. Nitrite is tested and reported as nitrite-nitrogen mgL. Organic nitrogen Org-N Organic nitrogen is nitrogen bonded with carbon and is found in proteins amino acids.
The effects of anammox on N isotopes must depend on the organism-scale isotope effects the sources of nitrite and ammonium substrates for the reaction and the degree to which these substrates are consumed. For instance if nitrate reduction by denitrifiers is the source of the nitrite remineralization processes are the source of the ammonium and both the nitrite and ammonium are completely. En général lammonium se forme sous leffet de la décomposition naturelle des matières organiques.
La présence dammonium est souvent liée à celle du nitrate et du nitrite. Dans leau il peut apparaître à cause de déchets issus dactivités agricoles industrielles ou domestiques. Lammonium nest pas néfaste pour la santé à condition que son absorption via l.
Rapid decomposition of dead algae reduces the dissolved oxygen concentration and pH and increases ammonia and carbon dioxide concentrations. After the crash of an algae bloom ammonia concentration can increase to 6 to 8 mgL and the pH can decline to 78 to 80. The 4-day chronic criterion the appropriate criterion to apply following the crash of an algae bloom ranges from about.
Google Scholar Citations lets you track citations to your publications over time. However ammonia- and nitrite-oxidizers also play a very important role in wastewater treatment facilities by removing potentially harmful levels of ammonium that could lead to the pollution of. Nitrification Ammonia or Ammonium Ions Nitrite Nitrate.
Ammonification Dead Matter Animal Waste Urea Uric Acid Ammonia or Ammonium Ions. Most of the ammonia escapes into the atmosphere. Rest is Nitrified Step 2 to nitrates.
Some of the nitrates is available for plants. Rest is Denitrified Step 4. Denitrification Nitrate.
Quaternary ammonium compounds QACs mainly represent cationic surfactants. They are the most used antiseptics and disinfectants 149. QACs may be considered as organically-substituted ammonium compounds wherein the nitrogen atom has a valence of five.
Whereas four of the substituent radicals R1 to R4 which are alkyl or heterocyclic radicals and the fifth X- is a small anion. Digestion- the decomposition of nitrogen in organic samples utilizing a concentrated acid solution. This is accomplished by boiling a homogeneous sample in concentrated sulfuric acid.
The end result is an ammonium sulfate solution. Distillation- adding excess base to the acid digestion mixture to convert NH 4 to NH 3 followed by boiling and condensationof the NH 3 gas in a receiving. Decomposition and mineralisation Plant and microbial uptake Nitrification Nitrogen fixation Leaching to groundwater Denitrification Soil nitrogen gas.
Nitrogen in the atmosphere N 2 About 80 of the atmosphere is dinitrogen gas which is more or less unavailable to most plants. Nitrogen gas in the atmosphere is basically unusable by most of biology plants and animals but there are a. Ammonium perchlorate can decompose at high temperatures forming toxic gases such as chlorine hydrogen chloride and nitrogen oxides.
Closed containers or tanks may rupture and explode if heated. It does not burn but is a powerful oxidizer and explosive when mixed with combustible materials. It is highly reactive and impact or high temperatures can cause violent decomposition or explosion.
NH3 is subsequently converted to nitrite and nitrate by bacteria known as nitrifying bacteria. Plants obtain nitrogen from the soil by absorbing ammonium NH4-. We will be publishing Issue 1 of The School STEM Technician at noon on the 1st December 2021 via the SSERC website.
This is our newest publication and has been created to support the school technician profession in Scotland. Some of the ammonium produced by decomposition is converted to nitrate NO 3- via a process called nitrification. The bacteria that carry out this reaction gain energy from it.
Nitrification requires the presence of oxygen so nitrification can happen only in oxygen-rich environments like circulating or flowing waters and the surface layers of soils and sediments. The process of nitrification.