
Liquid or spray mist can cause tissue damage especially to the mucous membranes of the eyes mouth and respiratory tract. Expectorant in cough syrups.
AMMONIA is a base.
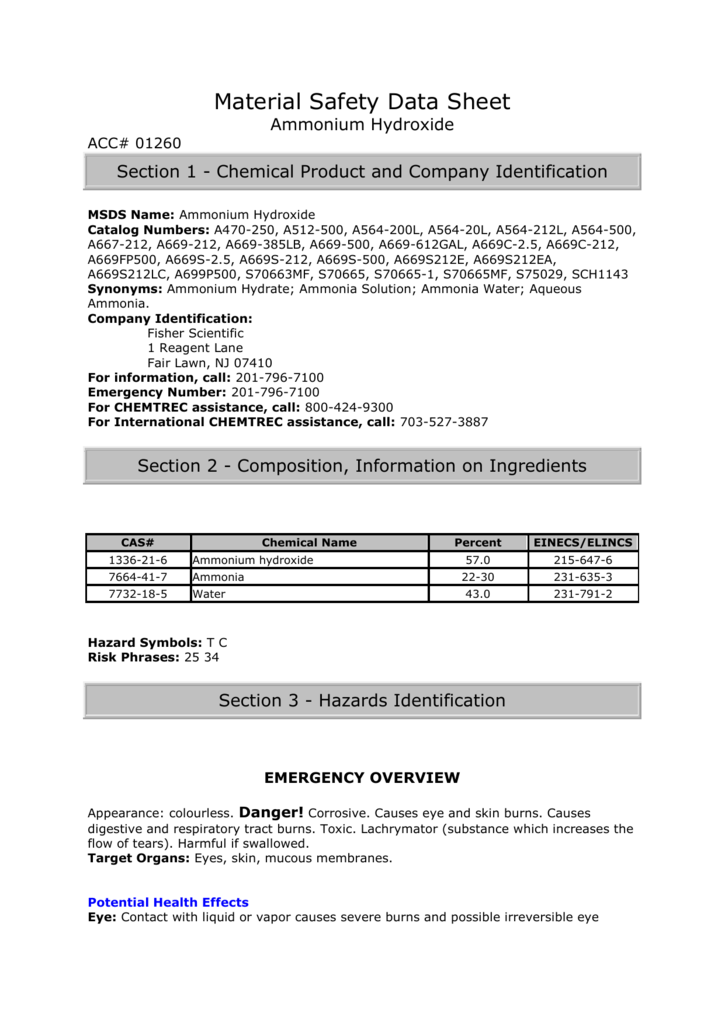
Ammonium hydroxide hazards. The major hazards encountered in the use and handling of ammonium hydroxide stem from its toxicologic properties. Toxic by all routes ie inhalation ingestion and dermal contact exposure to this colorless intensely pungent-smelling liquid may occur from its use in fertilizers dyes explosives plastics cleansing agents fibers and resins. Effects from exposure may include extreme.
Ammonia solution also known as ammonia water ammonium hydroxide ammoniacal liquor ammonia liquor aqua ammonia aqueous ammonia or inaccurately ammonia is a solution of ammonia in water. It can be denoted by the symbols NH 3 aq. Although the name ammonium hydroxide suggests an alkali with composition NH 4 OH it is actually impossible to isolate samples of NH 4 OH.
Ammonium Hydroxide is extremely dangerous in case of touch with the skin corrosive irritant permeator eye contact irritant swallowing etc. The eyes are non-corrosive. Non-corrosive to the lungs.
Liquid or spray mist can cause tissue damage especially to the mucous membranes of the eyes mouth and respiratory tract. Ammonium Hydroxide in contact with the. Expectorant in cough syrups.
The ammonium ion NH4 in the body plays an important role in the maintenance of acid-base balance. The kidney uses ammonium NH4 in place of sodium Na to combine with fixed anions in maintaining acid-base balance especially as a homeostatic compensatory mechanism in metabolic acidosis. The therapeutic effects of Ammonium Chloride depend upon the.
Tetramethylammonium hydroxide TMAH or TMAOH is a quaternary ammonium salt with molecular formula NCH 3 4 OH It is commonly encountered in form of concentrated solutions in water or methanolTMAH in solid state and its aqueous solutions are all colorless but may be yellowish if impure. We will be publishing Issue 1 of The School STEM Technician at noon on the 1st December 2021 via the SSERC website. This is our newest publication and has been created to support the school technician profession in Scotland.
Ammonium hexafluoroaluminate 7784-19-2. Aluminium hydroxide is used widely in non-prescription stomach antacids in buffered analgesics and other pharmaceuticals and in antiperspirants and dentifrices as a filler in cosmetics plastics rubber and paper and as a soft abrasive for brass and plastics ATSDR 1999. It is also used pharmaceutically to lower the plasma.
AMMONIA is a base. Reacts exothermically with all acids. Violent reactions are possible.
Readily combines with silver oxide or mercury to form compounds that explode on contact with halogens. When in contact with chlorates it forms explosive ammonium chlorate Kirk-Othmer 3rd ed Vol. Reacts violently or produces explosive.
Didecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride. Sodium hydroxide 1310-73-2. Causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
May cause respiratory irritation. Butyl rubber Natural rubber Neoprene rubber Nitrile rubber Polyvinyl chloride. Follow manufacturers recommendations in the product safety data sheet.
NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards respirator guidance. 0215 external icon AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE 10-35 solution Aqua ammonia Ammonium hydrate 0414 external icon AMMONIA ANHYDROUS R717 Refrigerant gas 717 1051 external icon AMMONIUM CHLORIDE Sal ammoniac 1234 external icon NITROGEN TRIFLUORIDE Nitrogen fluoride Trifluoroamine Trifluoroammonia Perfluoroammonia. Ammonium Hydroxide Facts and Formula.
List of the Strong Acids and Key Facts. Is It Ever Safe to Drink Bleach. How to Remove Rust Stains.
Molecular Formula for Common Chemicals. Setting Up a Home Chemistry Lab. Mosquito Bite Home Remedies.
How to Do the White Smoke Chemistry Demonstration. Ammonium Nitrate Facts and Uses. What Is Cream of Tartar or Potassium Bitartrate.