
Students could carry out test-tube reactions of solutions of the halogens Cl 2 Br 2 I 2 with solutions containing their halide ions eg KCl KBr. Ammonium carbonate NH 4 2 CO 3.
Essentially all alkali metal Li Na K Rb Cs and ammonium NH 4 salts are soluble.
Ammonium chlorate solubility. Ammonium chlorate Ammonium chloride. Potassium perchlorate Sodium perchlorate Lithium perchlorate. Except where otherwise noted data are given for materials in their standard state at 25 C 77 F 100 kPa.
What is Infobox references. Ammonium perchlorate AP is an inorganic compound with the formula NH 4 ClO 4. It is a colorless.
Ammonium cation is found in a variety of salts such as ammonium carbonate ammonium chloride and ammonium nitrateMost simple ammonium salts are very soluble in water. An exception is ammonium hexachloroplatinate the formation of which was once used as a test for ammoniumThe ammonium salts of nitrate and especially perchlorate are highly explosive in these cases ammonium is the reducing. Ammonium chlorate NH4ClO3 287 Ammonium chloride NH4Cl 294 332 372 414 458 504 553 602 656 712 773 Ammonium hexachloroplatinate NH42PtCl6 0289 0374 0499 0637 0815 144 216 261 336 Ammonium chromate NH42CrO4 25 292 34 393 453 519 590 712 761 Ammonium dichromate NH42Cr2O7 182 255 356 465 585 714 860 115 156 Ammonium dihydrogen arsenate.
Metal chlorates are oxidants in the presence of strong acid. Liberates explosive chlorine dioxide gas. Liberates chlorine dioxide and carbon dioxide by heating a moist metal chlorate and a dibasic organic acid.
Mixtures of perchlorates with sulfur or phosphorus are explosives Bretherick 1979 p. Mixtures of the chlorate with ammonium salts powdered metals silicon sulfur or sulfides. CID 222 Ammonia CID 123351 Perchlorate CID 24247 Perchloric acid Dates.
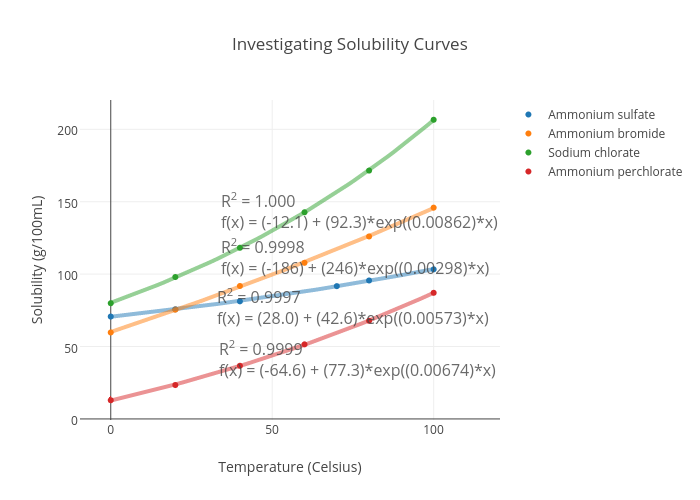
Ammonium perchlorate appears as a white crystalline solid or powder. Classified as a division 11 explosive if powdered into particles smaller than 15 microns in diameter or if powdered into. Remember solubility depends on the temperature of the water.
Compounds that dont dissolve around room temperature may become more soluble in warm water. When using the table refer to the soluble compounds first. For example sodium carbonate is soluble because all sodium compounds are soluble even though most carbonates are insoluble.
A simple set of rules known as solubility rules allows us to predict when a precipitation reaction will occur. These vary in detail according to different sources but broadly speaking the rules provide a quick qualitative check on the solubility of combinations of ions in water. The solubility rules presented below are from Oxtoby et al.
Solubility of ionic compounds. All nitrate NO 3 nitrite NO 2 chlorate ClO 3 and perchlorate ClO 4 salts are soluble. Silver nitrite and potassium perchlorate are considered slightly soluble.
Essentially all alkali metal Li Na K Rb Cs and ammonium NH 4 salts are soluble. Some Li are insoluble with Li 3 PO 4 being the most. Ammonium NH 4 Lithium Li Sodium Na Potassium K Magnesium Mg2 Calcium Ca2 Barium Ba2 Iron II Fe2 Iron III Fe3 Copper II Cu2 Silver Ag Zinc Zn2 Lead II Pb2 Aluminum Al3 Fluoride F- SOLUBLE SLIGHTLY SOLUBLE SOLUBLE SOLUBLE INSOLUBLE INSOLUBLE SLIGHTLY SOLUBLE SLIGHTLY SOLUBLE SLIGHTLY SOLUBLE SOLUBLE SOLUBLE SOLUBLE.
AN is an inorganic salt with colorless and odorless crystals that are soluble in most organic solvents. The salt is hardly found in nature for its high water solubility. It was first described in 1659 and currently is the most commercially important ammonium compound in production volume and usage terms.
Its great importance comes from the fact that the salt. To easily determine solubility memorize the most popular soluble chemicals and compounds. Remember that elements such as lithium sodium potassium or other alkali metals as well as chloride bromide and iodide are all soluble.
Additionally any compounds that contain nitrate acetate nitrite chlorate or perchlorate are soluble. When a solute is mixed with a solvent there are three possible outcomes. If the solution has less solute than the maximum amount it is able to dissolve the solubility it is a dilute solutionIf the amount of solute is exactly the same as the solubility it is saturated.
If there is more solute than is able to be dissolved the excess separates from the solution and. Remember salts are compounds which consist of metal cations like Na Ca 2 Cu 2 or the one nonmetal molecular ion that we have discussed ammonium - NH 4 ionically bonded to nonmetal anions such as Cl- including molecular anions such as hydroxide - OH- sulfate - SO 4 2 Solubility Of A Salt Lab Answer Key Effect of Temperature on the Solubility of a Salt lab April 3rd 2019 - View. Ammonium NH 4 nitrate NO 3 acetate C 2 H 3 O 2 or CH 3 COO hydrogen carbonate HCO 3 chlorate ClO 3 halides Cl Br I when combined with Ag Pb2 or Hg 2 2 sulfates SO 4 2 when combined with Ag Ca2 Sr2 Ba2 or Pb2 Ions That Form Insoluble Compounds Exceptions carbonate CO 3 2 when combined with Group 1 ions or ammonium NH 4.
Boiling point - the temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas. Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. See Standard state and enthalpy of formation Gibbs free energy of formation entropy and heat capacity for thermodynamic data for the same compounds.
For full table with Density Liquid Denity at Melting Point and Water Solubility-rotate the screen. Solubility And Temperature Lab Answers Free Books FREE Solubility And Temperature Lab Answers PDF Book is the book you are looking for by download PDF Solubility And Temperature Lab Answers book you are also motivated to search from other sources SoluonsSolubility AndReaconTypesBrownLeMayCh4 APChemistry 1. Project the graph Solubility of Salt and.
Chemical formula plays an important role in understanding different concepts of chemistry. Chemistry is all about learning chemical elements and compounds and how these things work together to form several chemical equations that are hard to understand. Chlorate hypochlorite C 2 O 4 í SiO 3 í oxalate silicate MnO 4 í ClO 4 í ClO 3 í 6 7 Á I G Á G 6s 7s barium Ra francium ammonium NH 4 1 hydronium H 3 O 1 4d 4 5 4s potassium calcium 3910 5s rubidium 1 I A K 1s 2s 3s H Li od 1 2 3 15 V A 16 VI A 2 II A 3 III B 4 magnesium IV B B 7 VII B 8 VIII B 7p 6p 12 II B 9 VIII B 5p 10 VIII B Co 1401 18 VIII A 17 VII A He helium 1900 cobalt 58.
CH 3 COONH 4. Ammonium carbonate NH 4 2 CO 3. Ammonium dichromate NH 4 2 Cr 2 O 7.
NH 4 NO 3. Ammonium oxalate NH 4 2 C 2 O 4. We will be publishing Issue 1 of The School STEM Technician at noon on the 1st December 2021 via the SSERC website.
This is our newest publication and has been created to support the school technician profession in Scotland. Potassium sodium and ammonium salts. Chlorides bromides and iodides.
All are soluble except silver leadII and mercuryII salts eg. All are soluble except leadII sulphate barium sulphate and calcium sulphate. All are insoluble except those of potassium sodium and ammonium.
Hydrogen fluoride can be released when other fluoride-containing compounds such as ammonium fluoride are Acetic acid. A dilute approximately 5 percent by volume solution of acetic acid produced by fermentation and oxidation of natural carbohydrates is called vinegar. A salt ester or acylal of acetic acid is called acetate.
It Hch3co2 name NaOH is Ionic. In association with Nuffield Foundation. Try this demonstration to create a mini volcanic eruption illustrating the decomposition of ammonium dichromate.
Includes kit list and safety instructions. An equilibrium using copperII and ammonia. In association with Nuffield Foundation.
Try this practical to explore an equilibrium involving copperII ions with copper. Predict the solubility of common inorganic compounds by using solubility rules. Compute the oxidation states for elements in compounds.
Humans interact with one another in various and complex ways and we classify these interactions according to common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet.
The trend in solubility of the silver halides in ammonia. Students should be able to explain why. Silver nitrate solution is used to identify halide ions.
The silver nitrate solution is acidified. Ammonia solution is added. AT d and k.
Students could carry out test-tube reactions of solutions of the halogens Cl 2 Br 2 I 2 with solutions containing their halide ions eg KCl KBr.