Evaluation of mixed acid-base abnormalities requires an understanding of the anion gap the relationship between the change in serum sodium and chloride concentration and the limits of compensation for the primary acid-base imbalances Saxton and Seldin 1986. The ammonium ion NH4 in the body plays an important role in the maintenance of acid-base balance.

Urine becomes increasingly acidic as the amount of sodium and excess acid retained by the body increases.
Ammonium carbonate base or acid. Ammonium cation is found in a variety of salts such as ammonium carbonate ammonium chloride and ammonium nitrateMost simple ammonium salts are very soluble in water. An exception is ammonium hexachloroplatinate the formation of which was once used as a test for ammoniumThe ammonium salts of nitrate and especially perchlorate are highly explosive in these cases ammonium is the reducing. In acid base chemistry salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base.
Basic salts contain the conjugate base of a weak acid so when they dissolve in water they react with water to yield a solution with pH greater than 70. The product of the neutralization of a strong base and a weak acid. Its anion is the conjugate.
Ammonium bicarbonate decomposes above about 36 C into ammonia carbon dioxide and water in an endothermic process and so causes a drop in the temperature of the water. NH 4 HCO 3 NH 3 H 2 O CO 2. When treated with acids ammonium salts are also produced.
NH 4 HCO 3 HCl NH 4 Cl CO 2 H 2 O. Reaction with base produces ammonia. Ammonium chloride is produced as one of the products in the Solvay process for the production of sodium carbonate.
This compound can also be prepared on an industrial scale by reacting ammonia with hydrochloric acid or gaseous hydrogen chloride. Ammonium chloride is known to occur naturally in certain volcanic areas. An alternative to mixing the acid or base into the liquid is to soak strips of paper in the liquid and then place a drop of the acid or base onto the paper.
The experiment below also covers some other substances such as baking powder vanilla essence and onions. Baking powder fizzes in acids but not in bases. Onions and vanilla essence lose their characteristic smell when in a basic solution.
An acidbase reaction is a type of chemical reaction that involves the exchange of one or more hydrogen ions H between species that may be neutral molecules such as water H 2 O or electrically charged ions such as ammonium NH 4. Or carbonate CO 3 2. It also includes similar processes that occur in molecules and ions that are acidic but do not donate.
ClO 4 -Perchlorate ion. 32 10 9. 10 10 9.
13 10 6. 10 10 3. H 2 SO 4.
HSO 4-Hydrogen sulfate ion. 24 10 1. NO 3-Nitrate ion—–Hydronium ion.
An acid-base indicator changes its colour depending on the pH eg phenolphthalein. Redox indicators are also frequently used. A drop of indicator solution is added to the titration at the start.
At the endpoint has been reached the colour changes. It is an instrument that measures the electrode potential of the solution. These are used for titrations based on a redox.
Key Takeaways Key Points. A basic solution will have a pH above 70 while an acidic solution will have a pH below 70. Buffers are solutions that contain a weak acid and its a conjugate base.
As such they can absorb excess H ions or OH ions thereby maintaining an overall steady pH in the solution. PH is equal to the negative logarithm of the concentration of H ions in solution. When a strong base OH- is added to a buffer solution the hydroxide ions are consumed by the weak acid forming water and the weaker conjugate base of the acid.
The amount of the weak acid decreases while the amount of the conjugate base increases. This prevents the pH of the solution from significantly rising which it would if the buffer system was not present. Ammonium is also an endogenous substance that serves a major role in the maintenance of the acid-base balance.
Minor amounts of ammonium nitrogen are incorporated in the physiological N-pool. Sulfate is a normal intermediate in the metabolism of endogenous sulfur compounds and is excreted unchanged or in conjugated form in urine. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development.
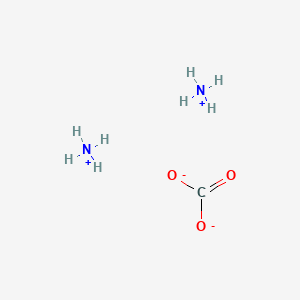
Carbonate ion. CO 3 2 ammonium ion. NH 4 ammonia.
IronIII ferric ion. FeH 2 O 6 3 pentaaquoironIII. FeH 2 O 5 OH 2 water.
OH hydronium ion. Strong acids and weak acids. We can look upon the generalized acid-base reaction.
As a competition of two bases for a proton. Definition of a strong acid. If the base H 2 O.
Evaluation of mixed acid-base abnormalities requires an understanding of the anion gap the relationship between the change in serum sodium and chloride concentration and the limits of compensation for the primary acid-base imbalances Saxton and Seldin 1986. Wilson and Green 1985. Clinical findings and history are also necessary to define the factors that may contribute to the development.
Acids and bases exist as conjugate acid-base pairs. Lets consider the relationship between the strength of the ammonium NH 4 and its conjugate base ammonia NH 3. The NH 4 ion is a weak acid because ammonia is a reasonably good base.
NH 4 aq H 2 Ol H 3 O aq NH 3 aq Weak acid. Use the acid-dissociation equilibrium constants. Ammonium sulfate is formed by adding finely divided gypsum to an ammonium carbonate solution.
NH 4 2 CO 3 CaSO 4 NH 4 2 SO 4 CaCO 3. Ammonium sulfate is also formed by treating ammonia with sulphuric acid. 2 NH 3 H 2 SO 4 NH 4 2 SO 4.
Chemical Properties of Ammonium Sulfate NH42SO4. Ammonium sulfate decomposes upon heating above 250 C forming ammonium. The use of conjugate acid-base pairs allows us to make a very simple statement about relative strengths of acids and bases.
The stronger an acid the weaker its conjugate base and conversely the stronger a base the weaker its conjugate acid. TABLE PageIndex1Important Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs. Table PageIndex1 gives a list of some of the more important.
The ammonium ion NH4 in the body plays an important role in the maintenance of acid-base balance. The kidney uses ammonium NH4 in place of sodium Na to combine with fixed anions in maintaining acid-base balance especially as a homeostatic compensatory mechanism in metabolic acidosis. The therapeutic effects of Ammonium Chloride depend upon the ability of the kidney to utilize ammonia.
The dilution of acid or base is exothermic. Thus acid or base is always added to water and water is never added to acid or base. If water is added to a concentrated acid or base a lot of heat is generated which may cause splashing out of acid or base and may cause severe damage as concentrated acid and base are highly corrosive.
Acid-base indicators indicators are natural or synthetic dyes which show a change of colour depending upon the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. The indicator like litmus is red in acidic and blue in basic medium. Methyl orange is red in acidic and yellow in basic medium.
Phenolphthalein is colourless in acidic and pinkish-red in basic medium. Answer 1 of 16. I assume you mean an aqueous solution of ammonia which is an equilibrium system of NH4OH ammonium hydroxide with NH3 ammonia gas.
The hydrochloric acid would react violently with the ammonia to form ammonium chloride which is a very slightly acidic salt generally harmless. For example with Regression minute concentrations of some acidic and basic components in acid rain samples titrated with strong base can be determined individually or grouped as follows. Strong acids H2SO4 HNO3 weak carboxylic acid formic acetic bicarbonate H2CO3HCO3-CO3 and ammonium ion NH4 NH3 FORNARO A.
GUTZ IGR Wet deposition and related atmospheric. Ammonium NH 4 nitrate NO 3 acetate C 2 H 3 O 2 or CH 3 COO hydrogen carbonate HCO 3 chlorate ClO 3 halides Cl Br I when combined with Ag Pb2 or Hg 2 2 sulfates SO 4 2 when combined with Ag Ca2 Sr2 Ba2 or Pb2 Ions That Form Insoluble Compounds Exceptions carbonate CO 3 2 when combined with Group 1 ions or ammonium NH 4. Indicators are used to determine whether a solution is acidic or alkaline.
Acids react with metals bases and carbonates to produce salts. Neutralisation is the reaction between an acid and a base. The kidneys maintain normal acid-base balance primarily through the reabsorption of sodium and the tubular secretion of hydrogen and ammonium ions.
Urine becomes increasingly acidic as the amount of sodium and excess acid retained by the body increases. Alkaline urine usually containing bicarbonate-carbonic acid buffer is normally excreted when there is an excess of base or alkali in the. We are a leading supplier to the global Life Science industry with solutions and services for research biotechnology development and production and pharmaceutical drug therapy development and production.