This reaction takes place at a temperature of 900-1100C. CAS No 1302-74-5 constitutes a high temperature form and is formed on heating aluminium hydroxide AlOH 3 at a temperature of 1000 C or above.
The result is that the aluminum oxide present in the ore gets converted to sodium aluminate which is soluble.
Aluminum hydroxide to aluminum oxide. Aluminium hydroxide AlOH 3 is found in nature as the mineral gibbsite also known as hydrargillite and its three much rarer polymorphs. Bayerite doyleite and nordstranditeAluminium hydroxide is amphoteric ie it has both basic and acidic properties. Closely related are aluminium oxide hydroxide AlOOH and aluminium oxide or alumina Al 2 O 3 the latter of which is also amphoteric.
Uses Of Aluminum Sulfate. Aluminum is one of the most widely used metals in the world. On the periodic table it has the symbol Al and the atomic number 13.
Unalloyed aluminum is a silvery-white color. Refined from an ore called. Aluminium oxide Al 2 O 3 occurs in two major forms.
α-Al 2 O 3 corundum. CAS No 1302-74-5 constitutes a high temperature form and is formed on heating aluminium hydroxide AlOH 3 at a temperature of 1000 C or above. The concentrations of aluminum in tissues of female New Zealand rabbits exposed to aluminum oxide dust at a concentration of 056 mg Alcu m for 5 months 8 hrday 5 daysweek were determined.
The amount of aluminum in the brains of the animals was nearly two and a. Aluminum hydroxide aluminum phosphate and alum constitute the main forms of aluminum used as adjuvants. Among these aluminum hydroxide is the most commonly used chemical as adjuvant.
In spite of its wide spread use surprisingly the mechanism of how aluminum hydroxide-based adjuvants exert their beneficial effects is still not fully understood. Current explanations for the. The gel-like aluminum hydroxide AlOH 3 also called alumina trihydrate ATH is converted via a second reaction step usually slowly over a few hours at room temperature more rapidly in a few minutes at higher temperatures into aluminum oxide Al 2 O 3.
2 AlOH 3 2 AlOOH 2 H 2 O Al 2 O 3 3 H 2 O. The aluminum oxide serves as dielectric and also protects the metallic. Metallic aluminum and its oxide and hydroxide are nontoxic.
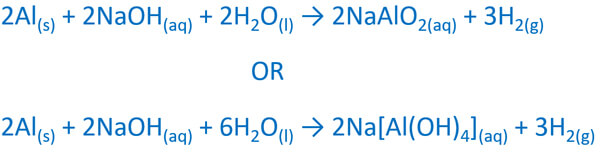
Aluminum is slowly attacked by most dilute acids and rapidly dissolves in concentrated hydrochloric acid. Concentrated nitric acid however can be shipped in aluminum tank cars because it renders the metal passive. Even very pure aluminum is vigorously attacked by alkalies such as sodium and potassium hydroxide to yield hydrogen and.
Alumina also called aluminum oxide synthetically produced aluminum oxide Al 2 O 3 a white or nearly colourless crystalline substance that is used as a starting material for the smelting of aluminum metal. It also serves as the raw material for a broad range of advanced ceramic products and as an active agent in chemical processing. The result is that the aluminum oxide present in the ore gets converted to sodium aluminate which is soluble.
The sodium aluminate when dissolved in alkaline water is converted to aluminum hydroxide. This compound is then calcined in other words aluminum hydroxide is heated to a very high temperature of around 980 degrees Celsius. The corrosion resistance of aluminum relies on the inactivity of this surface film of aluminum or hydrated oxide.
Its when this surface film dissolves that corrosion occurs. When the film suffers localized damage and self-healing cannot occur localized corrosion follows. This surface film is generally stable in a pH range of about 45 to 8.
The film can stay stable in other cases depending. Aluminum can burn in oxygen dazzling white flame to form aluminum oxide Al2O3. Reaction of aluminum with oxygen.
4Al 3O 2 2Al 2 O 3. Aluminum reacts with water according to the following reactions 2. 2Al 6H 2 O 2AlOH 3 3H 2 1 2Al 4H 2 O 2AlO OH 3H 2 2 2Al 3H 2 O Al 2 O 3 3H 2 3 As a result of these reactions are formed respectively.
Bauxite is an ore that contains a large amount of aluminum hydroxide Al 2 O 3 3H 2 O along with other compounds. Karl Joseph Bayer an Austrian chemist developed this process in 1888. The Hall-Héroult and Bayer processes are still used today to produce nearly all of the worlds aluminum.
With an easy way to extract aluminum from aluminum oxide and an easy way to extract large amounts of. The filtered alumina solution aluminium hydroxide is then transferred or pumped into precipitator tanks where it cools and starts to seed. These seeds stimulate a precipitation process allowing solid aluminium hydroxide crystals to be formed.
All the aluminium hydroxide that settles at the bottom of the tank is removed. The remaining caustic soda is washed away from aluminium hydroxide. The most abundant aluminum compounds are aluminum oxide and aluminum hydroxide and these are water insoluble.
Aluminum oxide may be present in water both in alkalic form 2Al 2 O 3 s 6H aq - Al 3 aq 3H 2 O l and in acidic form 2Al 2 O 3 s 2OH-aq - AlO 2-aq H 2 O l. An example of a water soluble aluminum compound is aluminum sulphate with a water solubility of. Aluminum hydroxide and hydrogen is the following.
O 2AlOH 3 3H. The gravimetric hydrogen capacity from this reaction is 37 wt and the volumetric hydrogen capacity is 46 g H. Although this reaction is thermodynamically favorable it does not proceed due to the presence of a coherent and adherent layer of aluminum oxide which forms on the surface of aluminum.
Aluminum hydroxide decomposes to produce aluminum oxide and water. A 2 Al OH. Aluminum metal reacts with oxygen gas to form solid aluminum oxide.
4 Al 3 O2 g 2 Al2O3 s 5. Liquid carbonic acid hydrogen carbonate decomposes into carbon dioxide gas and water. H2CO 3 CO 2 g H2O 6.
Lead II nitrate solution reacts with iron III chloride solution to form solid lead II. Caustic soda sodium hydroxide is used to dissolve the aluminum compounds found in the bauxite separating them from the impurities. Depending on the composition of the bauxite ore relatively small amounts of other chemicals may be used in the extraction Aluminum is manufactured in two phases.
The Bayer process of refining the bauxite ore to obtain aluminum oxide and the Hall-Heroult. Sodium Hydroxide in Aluminum Ore Processing. Sodium hydroxide is used to extract alumina from naturally occurring minerals.
Alumina is used to make aluminum and a variety of products including foil cans kitchen utensils beer kegs and airplane parts. In building and construction aluminum is used in materials that enable building facades and window frames. Sodium Hydroxide in Other.
Aluminum oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide to produce sodium aluminate and water. This reaction takes place at a temperature of 900-1100C. A salt and water is obtained in this reaction in which.
Some of the present aluminium corrosion challenges are the ramifications from the elimination of chromates as inhibitors in protection schemes the tolerance of higher impurity levels due to the increased use of recycled metal the integration of lithium into alloys while retaining corrosion resistance and the sensitisation of non-heat treatable aluminium-alloys. Bauxite is a weathered rock containing two forms of hydrated aluminum oxide either mostly a monohydrate AlOOH in caustic bauxite or mostly a trihydrate AlOH 3 in lateric bauxite. Besides these compounds bauxite contains iron oxide which usually gives it a reddish-brown colour as well as silicates clay quartz and titanium oxide.
The crys-tal structure also contains 1220 by. The levels of aluminum fluoride personal sampling were measured during these two years and the mean concentrations were 3-6 mgcu m. In 1977 improvements were made at this plant thereby reducing the mean levels of aluminum fluoride to 04-10 mgcu m.
During the years 1978-1980 only two cases of asthma occurred. All aluminum alloys form an oxide layer in the presence of airwater which protects the chemically-active aluminum from further reacting with the outside environment. The amount of corrosion resistance is dependent upon temperature airborne chemicals and the proximal working environment.
However under ambient circumstances 5052 aluminum holds up exceptionally well. The oxide of aluminum known as bauxite Al 2 O 3 nH2O provides a convenient source of uncontaminated ore. Aluminum can be selectively leached from rock and soil to enter any water source.
Al3 is known to exist in groundwater in concentrations ranging from 01 ppm to 80 ppm. Aluminum can be present as aluminum hydroxide a residual from the municipal feeding of alum aluminum sulfate.