But once you move beyond benzene thats when things start getting really interesting. A 12-dimethylbenzene b 13-diethylbenzene c 13-dimethylbenzene d 14-diethylbenzene e 14-dimethylbenzene 15.
Today well describe the two main patterns by which substituents direct electrophilic aromatic substitution.
Alcohol on benzene ring. Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C 6 H 6The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon. Benzene is a natural constituent of crude oil and is one of the elementary petrochemicals.
The six-membered ring in benzene is a perfect hexagon all carbon-carbon bonds have an identical length of 140 Å. The cyclohexatriene contributors would be expected to show alternating bond lengths the double bonds being shorter 134 Å than the single bonds 154 Å. An alternative representation for benzene circle within a hexagon emphasizes the pi-electron delocalization in this.
Since there is only one substituent on the benzene ring we do not have to indicate its position on the benzene ring as it can freely rotate around and you would end up getting the same compound Figure 8. Example of simple benzene naming with chlorine and NO 2 as substituents. More complicated simple benzene naming examples - Note that standard nomenclature priority rules are.
A monosubstituted benzene with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of the benzene ring with the general formula C n H 2n1 C 6 H 5. A monosubstituted naphthalene with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of one of the aromatic rings with the general formula C n H 2n1 C 10 H 7. Some other groups of.
Supporting evidence that the phenolate negative charge is delocalized on the ortho and para carbons of the benzene ring comes from the influence of electron-withdrawing substituents at those sites. The additional resonance stabilization provided by ortho and para nitro substituents will be displayed by clicking the Resonance Structures button a second time. You may cycle through these.
Basic O-Ring chemical resistance compatibility information is based on isolated generic O-Ring material testing in optimal conditions at room temperature and pressure. Exposing rubber O-Ring materials to multiple chemicals and compounding application factors like temperature pressure and gland design can result in significantly different performance. Specific material compound formulations can.
Benzene is a clear colorless highly flammable and volatile liquid aromatic hydrocarbon with a gasoline-like odor. Benzene is found in crude oils and as a by-product of oil-refining processes. In industry benzene is used as a solvent as a chemical intermediate and is used in the synthesis of numerous chemicals.
Exposure to this substance. The benzene levels were particularly high in those that came on the market to fill a gap when supplies of the cleansers ran low at the start of the Covid-19 pandemic. Its possible the benzene in hand sanitizers may have been introduced during the manufacturing process when germ-killing alcohol is purified.
Alcohol is also sometimes used as a. A monosubstituted benzene with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of the benzene ring with the general formula C n H 2n1 C 6 H 5. A monosubstituted naphthalene with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of one of the aromatic rings with the general formula C n H 2n1 C 10 H 7.
Some other groups of. If the relative yield of the ortho product and that of the para product are higher than that of the meta product the substituent on the benzene ring in the monosubstituted benzene is called an ortho para directing group. If the opposite is observed the substituent is called a meta directing group.
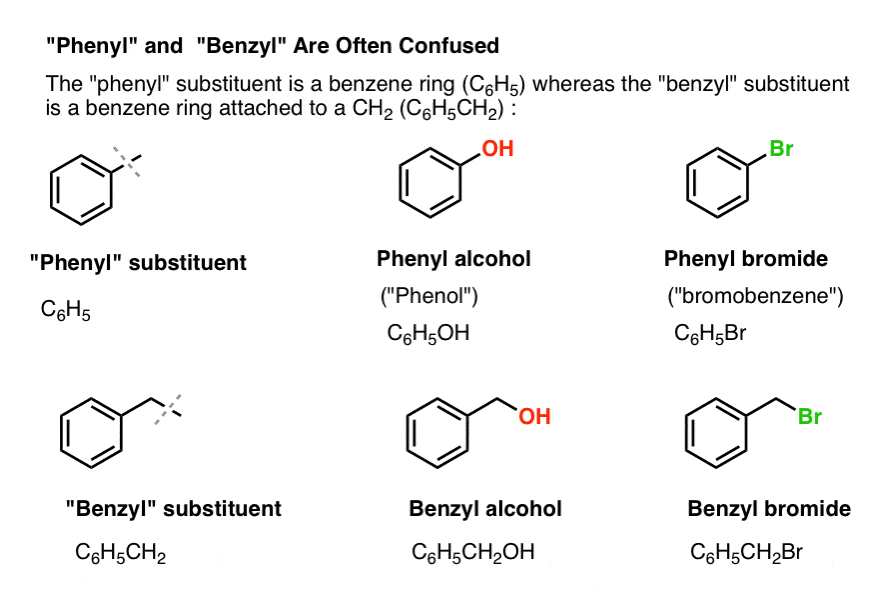
In organic chemistry the phenyl group or phenyl ring is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C 6 H 5Phenyl groups are closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring minus a hydrogen which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional groupPhenyl groups have six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring five of which are. The pi electrons in the benzene ring are delocalized due to resonance. Essentially the structure of a benzyl alcohol molecule is that of a toluene molecule in which one of the hydrogen atoms has been replaced by a hydroxyl group.
Properties of Benzyl Alcohol-C 6 H 5 CH 2 OH Chemical Data. Ethyl Alcohol Ethanol 64-17-5. Ethyl amine Monoethylamine Ethyl Benzene.
Ethyl Bromide Bromoethane 74-96-4. This is a compatibility table and compound from list to view comparability rating of the O-Ring. O-Ring Compatibility Chart JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser.
In their general structure heterocyclic compounds resemble cyclic organic compounds that incorporate only carbon atoms in the ringsfor example cyclopropane with a three-carbon-atom ring or benzene with a six-carbon-atom ringbut the presence of the heteroatoms gives heterocyclic compounds physical and chemical properties that are often quite distinct from those of their all-carbon. 4 - Includes organic compounds with more than one benzene ring and which have a boiling point greater than or equal to 100 ºC. 5 - A type of atom which spontaneously undergoes radioactive decay.
Modifications Pollutants removed from the list of hazardous air pollutants. Methyl Ethyl Ketone removed from the list of hazardous air pollutants in December 2005 - Federal Register - December 19. Two Important Reaction Patterns.
Ortho- Para-Directors and Meta-Directors Its one thing to learn about electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions of benzene itself. But once you move beyond benzene thats when things start getting really interesting. Today well describe the two main patterns by which substituents direct electrophilic aromatic substitution.
It is slightly soluble in water. Very soluble in ether benzene alcohol and acetone. It is used as a flavoring agent weathering agent in paints and plastics and as a fixative in perfumes also used in dyes.
Resin intermediates and in cosmetics and flavoring agent. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY. Chronic neurotoxic effects include vision disturbances.
Exposure to this chemical could result. So on the right heres an example of an arene or an aromatic ring and this right here this portion of the molecule would be a benzene. So lets write out that so benzenes a very famous organic chemistry molecule.
And then we have a methyl group coming off of our benzene ring. So one name for this would be methyl benzene. Thats not the name you would usually see normally you will hear.
Side chains which have pure hydrocarbon alkyl groups alkane branches or aromatic benzene rings are non-polar. Examples include valine alanine leucine isoleucine phenylalanine. The number of alkyl groups also influences the polarity.
The more alkyl groups present the more non-polar the amino acid will be. This effect makes valine more. Aromatic-cyclic based on benzene B.
Alcohol aldehyde ketone carboxyl amine organophosphate sulfhydral 1. Polar bonds between C and more electronegative atoms O and N 2. Combine two functional groups ester alcohol acid 3.
Amide amine acid C. Same chemical formula but differ in arrangement of atoms in space 2. How many actual double bonds does the benzene ring possess.
A None carbon-carbon bonds in benzene are delocalized around the ring b 1 double bond c 2 double bonds d 3 double bonds e 4 double bonds 14. Para-xylene is the same as. A 12-dimethylbenzene b 13-diethylbenzene c 13-dimethylbenzene d 14-diethylbenzene e 14-dimethylbenzene 15.
Which of the following formulas. Benzene là một hợp chất hữu cơ có công thức hoá học C 6 H 6Benzen là một hyđrocacbon thơm trong điều kiện bình thường là một chất lỏng không màu mùi dịu ngọt dễ chịu dễ cháyBenzen tan kém trong nước và rượu Vì chỉ chứa carbon và hydro nên benzene là một hydrocarbon. Benzen là thành phần tự nhiên của dầu thô.
For example the 18-crown-6 complex of potassium permanganate KMnO 4 dissolves in benzene to give purple benzene with a bare MnO 4 ion acting as a powerful oxidizing agent. Similarly the bare OH ion in sodium hydroxide NaOH made soluble in hexane C 6 H 14 by 15-crown-5 is a more powerful base and nucleophile than it is when solvated by polar solvents such as water or. Amines are organic derivatives of ammonia in which one two or all three of the hydrogens of ammonia are replaced by organic groups.
Compounds RNH 2 are called primary amines R 2 NH secondary amines and R 3 N are tertiary amines. The designation of amines as primary secondary and tertiary is different from the usage of these terms in.