Phytohemagglutinins PHA metabolites the carcinogens derived from tobacco cause p53 mutations at codons 156 and 157 as well as at 245 248. Treatment of cancer that begins in other parts of the body and spreads to the liver is not covered in this summary.
Treatment is guided by staging and prognosis.
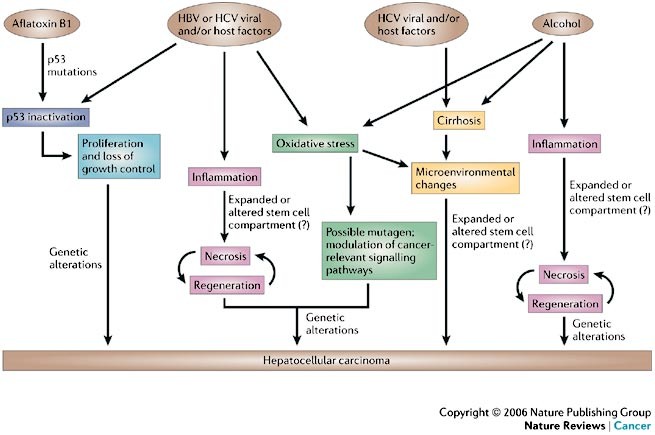
Aflatoxin hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. It occurs in the setting of chronic liver inflammation and is most closely linked to chronic viral hepatitis infection hepatitis B or C or exposure to toxins such.
Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC is the most common primary liver malignancy and is a leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. In the United States HCC is the ninth leading cause of cancer deaths. Despite advances in prevention techniques screening and new technologies in both diagnosis and treatment incidence and mortality continue to rise.
Cirrhosis remains the most. People who have it may develop hepatocellular carcinoma. This harmful substance which is made by certain types of mold on peanuts corn and other nuts and grains can cause.
Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC usually arises in patients with cirrhosis of the liver due to any cause. A significant number of patients may be asymptomatic and are diagnosed following screening. Patients at risk of HCC should receive surveillance with an ultrasound of the liver at 6-month intervals.
Treatment is guided by staging and prognosis. Treatment options include resection. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Primary liver cancer is the fourth most common tumor worldwide.
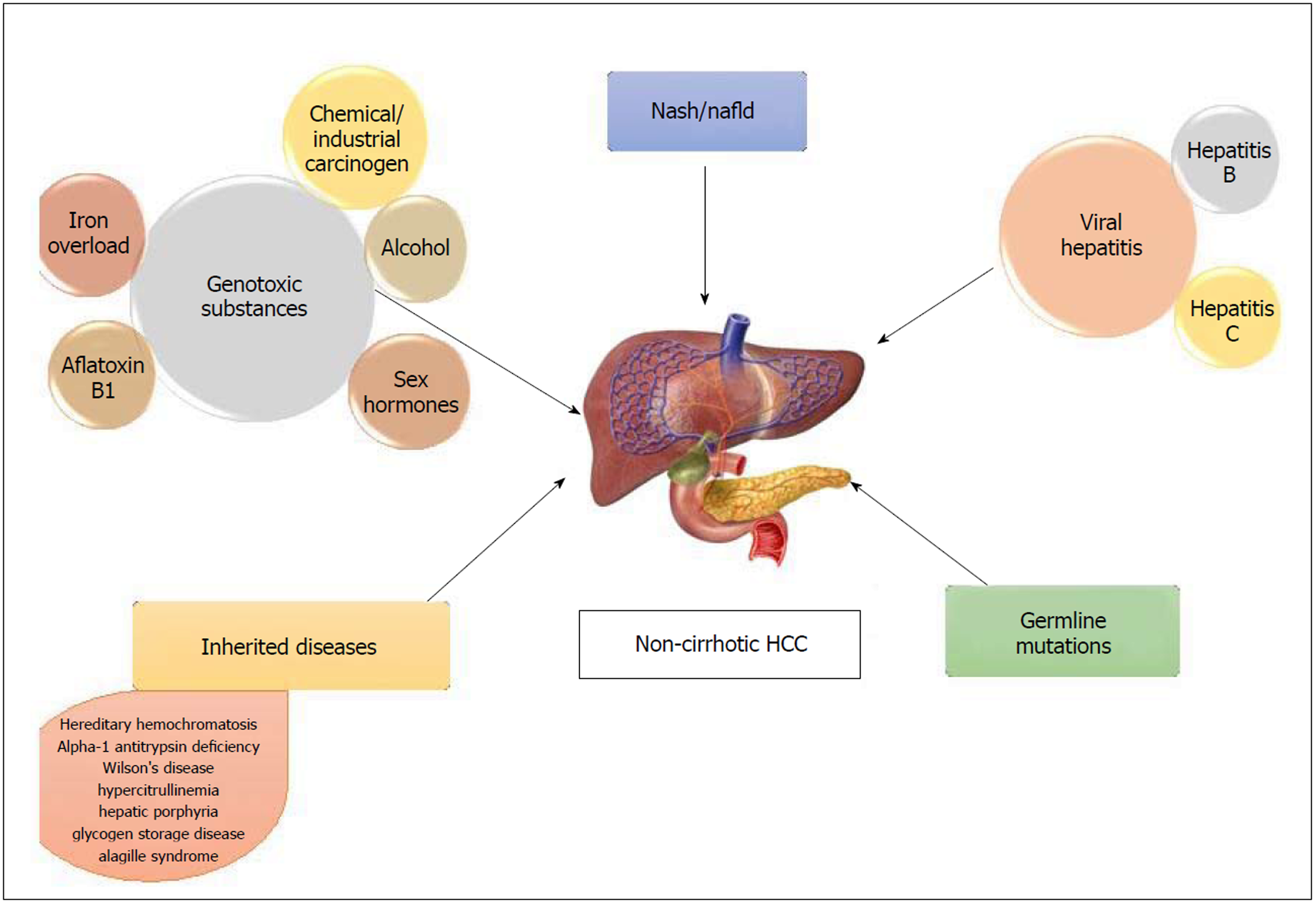
Hepatocellular carcinoma occurs mainly in the context of cirrhosis hepatitis B or. Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC is the most common type of liver cancer accounting for approximately 90 of all liver cancers with average survival rates between 6 and 20 months. Infections such as chronic hepatitis B andor hepatitis C are the main causes of HCC worldwide.
Hepatitis B vaccination reduces the risk for HCC. Other causes include alcohol consumption and food containing aflatoxin. Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC is the most common form of liver cancer and accounts for 90 of cases.
Infection by hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus are the main risk factors for HCC. Aflatoxin B1 reacts with DNA to form mutagenic adducts leading to codon 249 mutation of TP53 Liver Cancer International 2020141. Diagnostic features for hepatocellular carcinoma include hyperenhancement during arterial phase and washout in the venous or delayed phase due to alteration in blood supply during malignant transformation as benign hepatocytes receive blood supply from.
As the principal histologic type of liver cancer hepatocellular carcinoma HCC accounts for the great majority of liver cancer diagnoses and deaths. Hepatitis B virus HBV and hepatitis C virus HCV remain at present the most important global risk factors for HCC but their importance will likely decline in the coming years. The effect of HBV vaccination of newborns already seen in.
Other causes include aflatoxin non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver flukes. The most common types are hepatocellular carcinoma HCC which makes up 80 of cases and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. The diagnosis may be supported by blood tests and medical imaging with confirmation by tissue biopsy.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most frequent primary liver cancer and is an important medical problem. With 782 000 cases diagnosed and 746 000 deaths in 2012 and an age-adjusted worldwide incidence of 101 cases per 100 000 person-years hepatocellular carcinoma is ranked as the sixth most common neoplasm and the third leading cause of cancer death. The genomic landscape of liver hepatocellular carcinoma and mutational signatures.
Top panel shows individual tumor mutation rates while the middle panel details ethnicity tumor grade age gender hepatitis C virus HCV and hepatitis B virus HBV infection status and cirrhosis for 363 HCC. Bottom panel shows genes with statistically significant levels of mutation MutSig suite false. Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC is an aggressive disease with a poor clinical outcome.
The cancer stem cell CSC model states that tumour growth is powered by a. Long-term exposure to aflatoxin is a major risk factor for cancer of liver called hepatocellular carcinoma which causes liver scarring loss of nutrients inflammation of the digestive tract and other serious problems that can lead to death. Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC is the sixth most common and the second most deadly cancer worldwide.
The most important risk factors for HCC remain to be hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection aflatoxin B exposure alcohol consumption inborn meta-bolic diseases and diabetes 1. Although the development of modern medicine and the combined use of various therapeutic. Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC is the fourth most common cause of cancer-related death worldwide.
Chronic liver inflammation due to hepatitis virus infection and other major effectors is a major risk factor of HCC. Indoleamine 23-dioxygenase 1 IDO1 a heme enzyme highly expressed upon stimulation with proinflammatory cytokines such as interferon-γ IFN-γ is activated to modulate the. Such a mutation has been associated with hepatocellular carcinoma a type of cancer whereby aflatoxin B 1 promotes AGGAGT ArgSer transversion point mutation of p53 gene at codon 249 that alters p53 gene which is responsible for DNA repair.
Apart from GT transversions GC transversions and GA transitions have also been reported. Point mutation of G T at codon. Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC primary liver cancer is associated with aflatoxin B1 consumption.
Individuals with increased risks of developing aflatoxin associated Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC have chronic Hepatitis B and C which synergically interacts with aflatoxin B1 increasing the development of HCC. Colonization of plants by Aspergillus flavus is. Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC.
Aflatoxin is a toxin thats produced by mold that grows on nuts and grains. Malignant liver lesions are diagnosed in a myriad of ways. If your healthcare provider suspects you have liver cancer any of these may be ordered.
Blood tests like alpha-fetoprotein AFP tumor marker and liver function tests LFTs Imaging tests like. Hepatocellular carcinoma is a cancer that arises in the liver. It is also known as hepatoma or primary liver cancer.
HCC is the fifth most common cancer in the world. Recent data shows that HCC is becoming more common in the US. This rise is thought to be because of chronic hepatitis C an infection that can cause HCC.
In the United States most cancers that are found in the liver are ones. Positive for hepatocyte markers HepPar1 arginase glypican 3 pCEA and CD10 with canalicular staining pattern Usually negative for CK7. Histologic evidence of both hepatocellular and biliary differentiation by HE morphology and supported by immunohistochemistry WHO 2019.
The most common type of adult primary liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma. This type of liver cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. This summary is about the treatment of primary liver cancer cancer that begins in the liver.
Treatment of cancer that begins in other parts of the body and spreads to the liver is not covered in this summary. Aflatoxin-B1 AFB1 is associated with increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cancer because its metabolized to a carcinogen that causes cellular mutations. In animal studies supplementing with chlorophyllin at the same time as consuming high amounts of dietary AFB1 significantly reduced the amount of DNA damage that developed.
This is especially important for. Similarly it is well established that preferential selection of a p53 mutation at codon 249 in hepatocellular carcinoma HCC is tightly linked to exposure to a high dose of the carcinogen aflatoxin B1. Smoking also results in signature p53 mutations.
Phytohemagglutinins PHA metabolites the carcinogens derived from tobacco cause p53 mutations at codons 156 and 157 as well as at 245 248. Mutational spectra of aflatoxin B 1 in vivo establish biomarkers of exposure for human hepatocellular carcinoma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the USA 11415E3101E3109.
Abstract Chawanthayatham S Valentine CC 3rd Fedeles BI Fox EJ Loebd LA Levine SS Slocum SL Wogan GN Croy RG Essigmann JM. Mutational spectra of aflatoxin B 1 in.