30 31 Acidosis is frequently exacerbated by seizure activity tissue hypoperfusion and hypovolemia secondary to vomiting. The efficacy of acetylcysteine.
A high TSH result often means an underactive thyroid gland caused by failure of the gland hypothyroidismVery rarely a high TSH result can indicate a problem with the pituitary gland such as a tumour in what is known as secondary hyperthyroidismA high TSH value can also occur in people with underactive thyroid glands who have been receiving too little thyroid hormone medication.
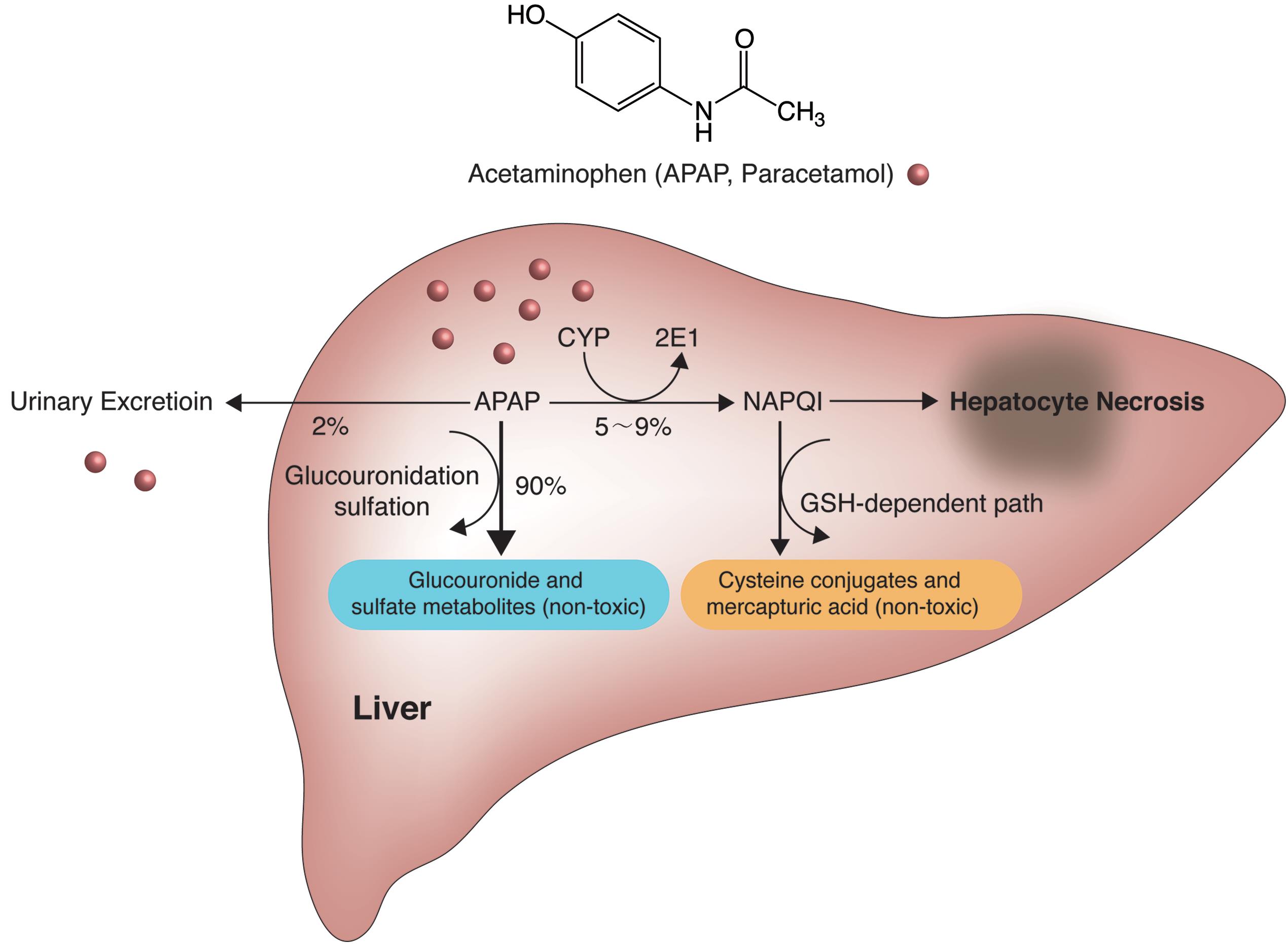
Acidosis paracetamol overdose. Acidosis is the most important single indicator of probable mortality and the need for transplantation. Paracetamol overdose results in more calls to poison control centers in the US than overdose of any other pharmacological substance accounting for more than 100000 calls as well as 56000 emergency room visits 2600 hospitalizations and 458 deaths due to acute liver failure per year. Paracetamol Overdose Protocol and Shortened NAC Administration Chart PILOT March June 2020 NOTE.
This protocol differs from advice on TOXBASE however the general paracetamol overdose guidance still applies. Please ensure the EDLsIDLs are given a diagnosis of paracetamol overdose to allow auditing of this pilot. Pilot V12 Jan 2020 Mar-June 2.
Pilot V12 Jan 2020 Mar. Rarely massive overdose may initially present with coma and severe metabolic acidosis. Presentation with coma may also occur if a combination preparation of paracetamol and opioid is taken in overdose or after an overdose of multiple drugs.
Hepatotoxicity is extremely rare in patients treated with acetylcysteine within 8 hours of an acute paracetamol overdose. The efficacy of acetylcysteine. Coma and severe metabolic acidosis in patients who have extremely high plasma paracetamol concentrations usually greater than 800 mgL.
Drowsiness in the first 1-2 days after a single paracetamol overdose is unlikely to be due to liver failure so consider other causes. In those presenting late loin pain haematuria and proteinuria after 24 hours suggest incipient renal failure. From these the EXTRIP panel concluded that paracetamol was dialysable and suggested extracorporeal treatments could be considered in cases of severe paracetamol poisoning defined by paracetamol level acidosis or coma and also depending on antidote availability.
They concluded that intermittent haemodialysis is the preferred extracorporeal treatment in people with paracetamol. Paracetamol is widely used for its analgesicanti-pyretic effects. It is also common to see accidental paediatric ingestion unintentional self-administered supratherapeutic ingestions or intentional self-poisoning in the Emergency Department.
While paracetamol is safe in normal doses it is hepatotoxic and potentially fatal in overdose. Fortunately N-acetylcysteine NAC. P Paracetamol Propylene glycol used as an inactive stabilizer in many medications.
Historically the P also stood for Paraldehyde though this substance is not commonly used today I Infection Iron Isoniazid which can cause lactic acidosis in overdose Inborn errors of metabolism an especially important consideration in pediatric patients L Lactic acidosis. E Ethylene. Staggered overdose 8 hours eg.
4g at 1pm 4g at 2pm and 4g at 3pm and its now 4pm use the paracetamol concentration to 1pm. This allows for the worst-case scenario. If you time anchor to 3pm you may have a lower concentration and underestimate the overdose.
The paracetamol concentration should be repeated at 6 pm 2 h after the. Raised anion gap metabolic acidosis is recognized in acute NSAID overdose and this occurs as a result of accumulation of acidic metabolites. 30 31 Acidosis is frequently exacerbated by seizure activity tissue hypoperfusion and hypovolemia secondary to vomiting.
14 16 17 31 35 Acidosis has been reported following overdose of ibuprofen 11 14 16 30 31 39 diclofenac 29 mefenamic. Adults including the elderly and children over 16 years. One to two tablets every 4-6 hours as required to a maximum of 8 tablets daily in divided doses.
One tablet every 4-6 hours as necessary to a maximum of 4 doses in 24 hours. Children under 10 years. Not recommended for children under 10 years of age.
Alternative presentations of paracetamol are. Immediate medical advice should be sought in the event of an overdose even if the child seems well. Do not give with any other Paracetamol-containing products Leaflet.
Immediate medical advice should be sought in the event of an overdose even if the child seems well because of the risk of delayed serious liver damage 45 Interaction with other medicinal products and. Iron overdose can have local gastrointestinal effects as well as characteristic systemic toxicity metabolic acidosis liver failure shock and multi-organ failureRisk assessment is based on the amount of elemental iron ingested. Paracetamol acetaminophen Lactulose Propylene glycol Epinephrine norepinephrine.
Some drugs and toxins that can cause lactic acidosis. Metabolism of ethanol is associated with increased NADHNAD ratio favoring conversion of pyruvate to lactate 2. Gluconeogenesis is also inhibited so that the combination of moderate hyperlactatemia and hypoglycemia is a not infrequent finding.
Koulouris Z Tierney MG Jones G Metabolic acidosis and coma following a severe acetaminophen overdose Ann Pharmacother 33 1999. 1191-4 Ann Pharmacother 33 1999. Paracetamol is the most common single agent involved in poisonous ingestions in young children.
While there is potential for serious liver damage if a large dose is ingested in practice it is rare for a child to achieve toxic blood levels by ingesting paracetamol elixir syrup. I Early-onset lactic acidosis following massive ingestion within 24 hours. Ii Later-onset lactic acidosis due to hepatic failure 48 hours after ingestion.
Acetaminophen level Marked hyperbilirubinemia 10 mgdL may cause a false-positive acetaminophen level usually in. The first report of the adverse effects of tricyclic overdose was in 1959 and came within two years of their clinical usefulness having been recognised. 1 Now tricyclics are identified as one of the most frequently ingested substances in self poisoning along with paracetamol benzodiazepines and alcohol.
2 They are second only to analgesics as the commonest. The authorised dose regimen for acetylcysteine in paracetamol overdose is 3 consecutive intravenous infusions given over a total of 21 hours. Continued treatment given at the dose and rate as used in the third infusion may be necessary depending on the clinical evaluation of the individual patient.
Asthma see Side-effects for management of asthma but do not. Sodium bicarbonate is given to treat possible acidosis because of Amitriptyline overdose. Patients with arrhythmias and QRS prolongation may also meed sodium bicarbonate.
Intravenous diazepam may be given in order to control the seizures or convulsions. Phenytoin is not to be given even if it is an anticonvulsant drug because it may lead to further blocking. Paracetamol level in case of co-ingestion.
Glucose level if reduced GCS. Blood gas looking for acidosis. No antidote treatment is supportive 1.
Standard procedures and supportive care. Consider intubation early in reduced GCS. Decontamination Charcoal is generally contraindicated due to risk of aspiration however patients with ingestion of doses 10-15 mg.
A high TSH result often means an underactive thyroid gland caused by failure of the gland hypothyroidismVery rarely a high TSH result can indicate a problem with the pituitary gland such as a tumour in what is known as secondary hyperthyroidismA high TSH value can also occur in people with underactive thyroid glands who have been receiving too little thyroid hormone medication. Diagnostic Specificity and diagnostic sensitivity Often a pathology test is used to diagnose a particular disease. However sometimes not all patients with that disease will have an abnormal test result false negative and sometimes a patient without the disease will have an abnormal test result false positive.