
An organic acid anhydride citation needed is an acid anhydride that is an organic compoundAn acid anhydride is a compound that has two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. PhosphorusIII oxide reacts to form phosphorous acid in water.
Let suppose hydrochloric acid HCl a strong acid is taken as an analyte and sodium hydroxide NaOH strong base is taken as a titrant.
Acid anhydride examples. An organic acid anhydride citation needed is an acid anhydride that is an organic compoundAn acid anhydride is a compound that has two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common type of organic acid anhydride is a carboxylic anhydride where the parent acid is a carboxylic acid the formula of the anhydride being RCO 2 O. Symmetrical acid anhydrides of this type are named by.
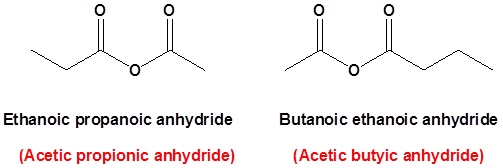
In symmetrical acid anhydride carboxylic acid the only constituent used to form the compound so the prefix is carboxylic and suffix anhydride is used. In asymmetrical acid anhydride two different carboxylic acids are used like the dehydration of benzoic acid and propanoic acid so the prefix is benzoic propanoic and anhydride is a suffix. Ethanoic acid forms ethanoic anhydride propanoic.
Carbonic acid is an illustrative example of the lewis acidity of an acidic oxide. Silicon dioxide is the anhydride of silicic acid. PhosphorusIII oxide reacts to form phosphorous acid in water.
P 4 O 6 6 H 2 O 4 H 3 PO 3. PhosphorusV oxide reacts with water to give phosphoric v acid. P 4 O 10 6 H 2 O 4 H 3 PO 4.
Phosphorus trioxide is. Perchloric Acid Acetic anhydride alcohols bismuth and its alloys paper wood grease oils or any organic materials and reducing agents. Peroxides organic Acid inorganic or organic.
Also avoid friction and store cold. Phosphorus white Air oxygen. Phosphorus pentoxide Alcohols strong bases water.
Potassium Air moisture andor oxygen or water carbon tetrachloride carbon dioxide. Sulfuric acid sulfuric also spelled sulphuric H 2 SO 4 also called oil of vitriol or hydrogen sulfate dense colourless oily corrosive liquid. One of the most commercially important of all chemicalsSulfuric acid is prepared industrially by the reaction of water with sulfur trioxide see sulfur oxide which in turn is made by chemical combination of sulfur dioxide and oxygen either by.
Acid halides such as Acetyl chlorideBenzenesulfonyl bromide Propanoyl chloride Phosphorous pentoxide also called Phosphoric anhydride when mixed with water may boil from the heat generated Non-Hazardous or non-regulated chemicals Buffers Surfactants Ion exchange resins Alumina Silica Culture media Agarose Albumin Pump oil. Acid definition a compound usually having a sour taste and capable of neutralizing alkalis and reddening blue litmus paper containing hydrogen that can be replaced by a metal or an electropositive group to form a salt or containing an atom that can accept a pair of electrons from a base. Acids are proton donors that yield hydronium ions in water solution or electron-pair acceptors that.
Ethanoic acid also commonly known as the Acetic acid is a two-carbon acid and hence is the second member of the carboxylic acid family after methanoic acid which is a one-carbon carboxylic acid. Ethanoic acid has the second simplest possible structure of a carboxylic acid after Methanoic acid. It comprises of a methyl group attached to the carboxylic acid functional group.
Examples of equivalence point. The reaction of a strong acid with a strong base. Let suppose hydrochloric acid HCl a strong acid is taken as an analyte and sodium hydroxide NaOH strong base is taken as a titrant.
If we plot a graph between analyte pH and a titrant NaOH which can be added from the burette a titration graph will be formed. Some examples of both nomenclatures are provided below. Simple dicarboxylic acids having the general formula HO 2 CCH 2 n CO 2 H where n 0 to 5 are known by the common names.
Oxalic n0 Malonic n1 Succinic n2 Glutaric n3 Adipic n4 and Pimelic n5 Acids. Common names such as these can be troublesome to remember so mnemonic aids which take the form of a catchy. Store concentrated Nitric acid Store in a corrosive cabinet labeled Acid or on shelving using a secondary containment Do not store under the sink Oxidizers Ammonium preferably with ventilation corrosive cabinet or storage area Calcium potential water sources Chemical Segregation and Storage Table Chemical Segregation Class of Chemicals Common Chemical Examples Additional Concerns and.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR DISTRIBUTING DEA FORM 486. For Import Declaration distribute as follows. Copy 1 must be retained on file by the regulated person as the official record of import.
Import declaration forms must be retained for two years. Copy 2 is a DEA copy. This form must be received at 8701 Morrissette Drive Springfield VA 22152 at least 15 days prior to importation.
Non-halogenated solvent-acid mixtures non-halogenated organic acids such as acetic acid trichloroacetate acetic anhydride. Organic waste - Non-halogenated plus water Examples. Non-halogenated solvent-water mixtures or non-halogenated solvents with greater than 20 water such as 80 ethanol.
Organic waste - Non-halogenated Examples. Acetone toluene acetonitrile ethyl acetate. When two molecules of acetic acid undergo a condensation reaction together the product formed is acetic anhydride.
Acetic Acid as a Solvent. In its liquid state CH 3 COOH is a hydrophile readily dissolves in water and also a polar protic solvent. A mixture of acetic acid and water is in this manner similar to a mixture of ethanol and water.
Acetic acid also forms miscible mixtures with. Synthesis of AspirinAcetylsalicylic acid C 9 H 8 O 4. Dry an Erlenmeyer flask and add 3 grams of salicylic acid to it.
Put 5 to 8 drops of 85 phosphoric acid along with 6 mL of acetic anhydride to the flask. Mix the solution and keep the flask in warm water for 15 minutes. To the warm solution add 20 drops of cold water drop wise.
Acetic acid vinegar hydrocyanic acid hydrogen sulfide formic acid and trichloracetic acid are some of the most common examples of weak acids. In fact they are a common substance in everyday life they may be in the vitamins you take the food you eat or in the cleaning supplies you use. Determination of the Concentration of Acetic Acid in Vinegar Lab Exercise 4 CHEM 1106 91912.
Standardize a sodium hydroxide solution using a primary standard acid. Determine the molarity and the percent by mass of acetic acid in vinegar by titration with the standardized sodium hydroxide solution. Vinegar is a dilute.
The cards are data sheets intended to provide essential safety and health information on chemicals in a clear and concise way. The primary aim of the cards is to promote the safe use of chemicals in the workplace. The main target users are workers and those responsible for occupational safety and health.
The ICSC project is a common undertaking between the World Health Organization WHO and. Dehydration Reaction Examples. Reactions that produce acid anhydrides are dehydration reactions.
For example acetic acid CH 3 COOH forms acetic anhydride CH 3 CO 2 O and water by the dehydration reaction 2 CH 3 COOH CH 3 CO 2 O H 2 O Dehydration reactions are also involved in the production of many polymers. C Draw acetic anhydride. D Draw the two d Draw the two Convert the line structures in the figure below to their condensed formulas eg CH3CH22CH3 for butane.
If the amine and carboxylic acid functional groups in amino acids join together to form amide bonds a chain of amino acid units called a peptide is formed. A simple tetrapeptide structure is shown in the following diagram. By convention the amino acid component retaining a free amine group is drawn at the left end the N-terminus of the peptide chain and the amino acid retaining a free.