4 At about the same time physicians began prescribing the purified compounds to relieve pain. The pH of a 01000 M solution of acetylsalicylic acid aspirin-HAsp was found to be 224.

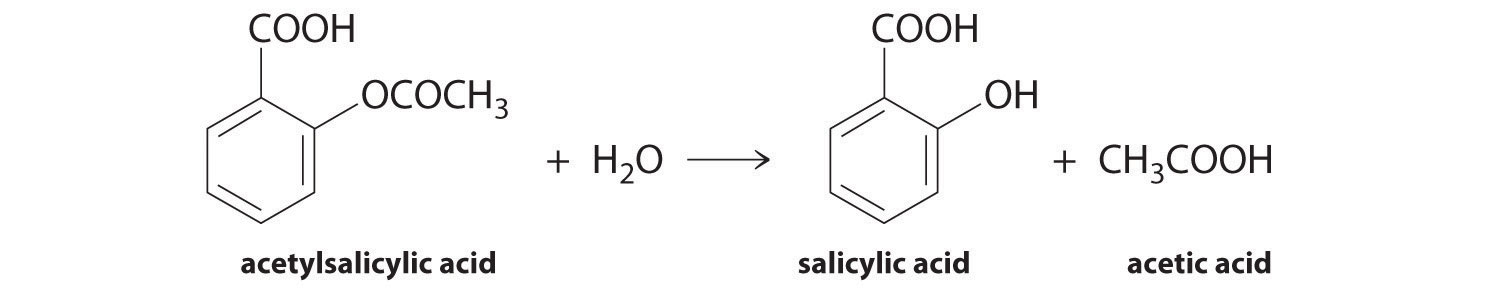
Aspirin 2-ethanoyloxybenzoic acid or acetylsalicylic acid hydrolyses to produce 2-hydroxybenzoic acid and ethanoic acid.
Acetylsalicylic acid solution. Synthesis of AspirinAcetylsalicylic acid C 9 H 8 O 4. Dry an Erlenmeyer flask and add 3 grams of salicylic acid to it. Put 5 to 8 drops of 85 phosphoric acid along with 6 mL of acetic anhydride to the flask.
Mix the solution and keep the flask in warm water for 15 minutes. To the warm solution add 20 drops of cold water drop wise. The pH of the complete solution of Acetylsalicylic acid is24 Its pKa dissociation constant is 297.
Also read - NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry. NCERT Solutions for All Subjects.
Chemical Properties of Acetylsalicylic acid Acetylsalicylic acid ReactionWhat is aspirin. Formulation of aspirin structure. In the field of medicine.
Aspirin also known as acetylsalicylic acid ASA is a medication used to reduce pain fever or inflammation. In solution with alkalis the hydrolysis proceeds rapidly and the clear solutions formed may consist entirely of acetate and salicylate. Like flour mills factories producing aspirin tablets must control the amount of the powder that becomes airborne inside the building because.
Also known as Aspirin acetylsalicylic acid ASA is a commonly used drug for the treatment of pain and fever due to various causesAcetylsalicylic acid has both anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. This drug also inhibits platelet aggregation and is used in the. Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC 6 H 4 CO 2 H.
A colorless bitter-tasting solid it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin acetylsalicylic acid. It is a plant hormone. The name is from Latin salix for willow treeIt is an ingredient in some anti-acne productsSalts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates.
Answer 1 of 3. Acetil salicylic acid is an organic acid having one carboxilic group which confers the acidity to the acetil salicylic acid and then we can write it as C8H7COOH then a neutralization reaction of the acid with soda NaOH will be C8H7COOH NaOH C8H7COONa H2O or C9H8O4 Na. The iron chloride solution FeCl 3.
If your solution turns purple it indicates starting material salicylic acid remains in your product and it needs to be further purified by recrystallization. Proceed to the step 5 below. If the FeCl 3 remains yellow even after stirring and waiting a few minutes skip step 5 and go on to the Analysis section.
A calibration curve was generated from a standard solution of acetylsalicylic acid. This curve was fit with Beers Law A εlc 1 where A is the absorbance arbitrary units ε is the molar absorptivity concentrationcm l is the path length of the cuvette cm and c is the concentration of the ironIIIsalicylate chromophore. Beers Law is the theory that connects the absorbance of.
This mechanism would cause the reaction to favor the product side aspirin and acetic acidThe solution was also heated in order to accelerate the approach to equilibrium It is important to consider that acetylsalicylic acid is not the only product that forms acetic acid is another byproduct of the reaction. The pH of a 01000 M solution of acetylsalicylic acid aspirin-HAsp was found to be 224. Determine the value of K a the ionization constant for acetylsalicylic acid K a.
The formula for acetylsalicylic acid is CH 3 CO 2 C 6 H 4 COOH but we use HAsp as an abbreviation. Write the equation for the equilibrium between aspirin and water. HAspaq H 2 Ol H 3 O aq Asp-aq.
The synthesis of the salicylic acid is done by creating the anion of the acid which is soluble in the aqueous solution. It is then protonated to crash the salicylic acid out of solution. If not enough acid was added to protonate all the product some will stay in the aqueous solution and will be lost.
Another source of product loss is during the recrystallization. Because it is impossible to. Acetylsalicylic acid will recrystallize and the solid impurities unreacted salicylic acid should remain dissolved in the solution.
The solid aspirin will again be collected using vacuum filtration and tested for purity. This aspirin should be more pure than the original aspirin. The final product will be dried and weighed and the theoretical and percent yields will be calculated.
Find the molar mass of aspirin and salicylic acid. From the periodic table. Molar Mass of C 12 grams Molar Mass of H 1 grams Molar Mass of O 16 grams MM aspirin 9 x 12 grams 8 x 1 grams 4 x 16 grams MM aspirin 108 grams 8 grams 64 grams MM aspirin 180 grams MM sal 7 x 12 grams 6 x 1 grams 3 x 16 grams MM sal 84 grams 6 grams.
Aspirin 2-ethanoyloxybenzoic acid or acetylsalicylic acid hydrolyses to produce 2-hydroxybenzoic acid and ethanoic acid. Here is the equation for the reaction. O O The rate at which this reaction happens is important for two reasons.
When administered aspirin hydrolyses in the body. Also if aspirin tablets are stored in a humid environment such as a bathroom they hydrolyse. The amount of.
The concentration of the acetylsalicylic acid stock solution then is. 222x10-3 mol C 9H 8O 4 01000 L 222x10-2 M This stock solution is used to prepare standards for the Beers Law curve by diluting aliquots of the stock solution into 1000 mL volumetric flasks and diluting to volume with ironIII chloride solution. The concentration of C 9H 8O 4 in the standards is calculated with.
Any of a class of substances whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste the ability to turn blue litmus red and the ability to react with bases and certain metals to form salts. A substance that yields hydrogen ions when dissolved in water. A substance that can act as a proton donor.
Although acetic acid is very soluble in water almost all of the acetic acid in solution exists in the form of neutral molecules less than 1 dissociates. Sulfuric acid is unusual in that it is a strong acid when it donates its first proton Equation ref438 but a weak acid when it donates its second proton Equation ref439 as indicated by the single and double arrows. In 1853 Charles Frederic Gerhardt created acetylsalicylic acid for the 1st time but he did not use or market this modified version of salicylic acid.
4 At about the same time physicians began prescribing the purified compounds to relieve pain. A Dundee physician Thomas Maclagan used salicin to treat patients who had rheumatism and he reported its beneficial effects in The Lancet in 1876. Citric Acid C7H5NO3S Saccharin C7H6O Benzaldehyde C7H6O2 Benzoic Acid C7H6O3 Vitamin S C7H8 Cycloheptatriene C8H10 Xylene C8H10N4O2 Caffeine C8H18 224-Trimethylpentane C8H8 Styrene C8H8O3 Vanillin C8H9NO2 Acetaminophen C9H20 Nonane C9H8O4 Acetylsalicylic Acid CaC2H3O22 Calcium Acetate CaHCO32 Calcium Bicarbonate CaNO32 Calcium Nitrate.
Preparation of Approximate Acid Solution 01M HCl 1. Put 100 mL distilled water into your other large bottle. Before performing this experiment ie in your prelab calculate the volume of concentrated HCl you will need to prepare 250 mL of 01M HCl.
Concentrated reagent grade HCl has a density of 1188 g mL1 and is 37 wt. Check your answer with your TA before making this. Ketorolac Tromethamine Ophthalmic Solution is a member of the pyrrolo-pyrrole group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs for ophthalmic use.
Its chemical name is -5-benzoyl-2 3-dihydro-1H pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid compound with 2-amino-2-hydroxymethyl-l3-propanediol11 and it has the following structural formula. The molecular formula of Ketorolac Tromethamine. There is the potential for cross-sensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid phenylacetic acid derivatives and other NSAIDs including bromfenac.
Use with caution in patients who have previously exhibited sensitivities to these drugs. There have been reports that ocularly applied NSAIDs may cause increased bleeding of ocular tissues including hyphemas in conjunction with ocular surgery. Acetylsalicylic acid Acetaminophen Caffeine Diphenhydramine hydrochloride O H N Cl.
4 Pour 50 mL of the amino acid developing solution into a 1000 mL beaker. The developing solvent is comprised of a four-to-one mixture of 1-butanol and glacial acetic acid that has been saturated with water. Position the cylinder inside the beaker with the bottom edge immersed in the solvent.
Make sure the. Group 1 cations includes those cations who selectively precipitates as chlorides by addition of diluted hydrochloric acid. We quickly bring the still hot solution in a centrifuge and separates the supernatant from the precipitate.
The treatment is repeated 3-4 times to avoid an undissolved residue of lead chloride on our precipitate of AgCl and Hg 2 Cl 2. The first two times you recover. There is the potential for cross-sensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid phenylacetic acid derivatives and other NSAIDs including BromSite.
Therefore caution should be used when treating individuals who have previously exhibited sensitivities to these drugs. Increased Bleeding Time of Ocular Tissue. With some NSAIDs including BromSite there exists the.