Its boiling point is 140. The aspirin molecule contains a total of 21 bonds There are 13 non-H bonds 8 multiple bonds 3 rotatable bonds 2 double bonds 6 aromatic bonds 1 six-membered rings 1 carboxylic acids aromatic 1 esters aliphatic and 1 hydroxyl groups.

But when used at the right concentrations acids are actually some of the most beneficial.
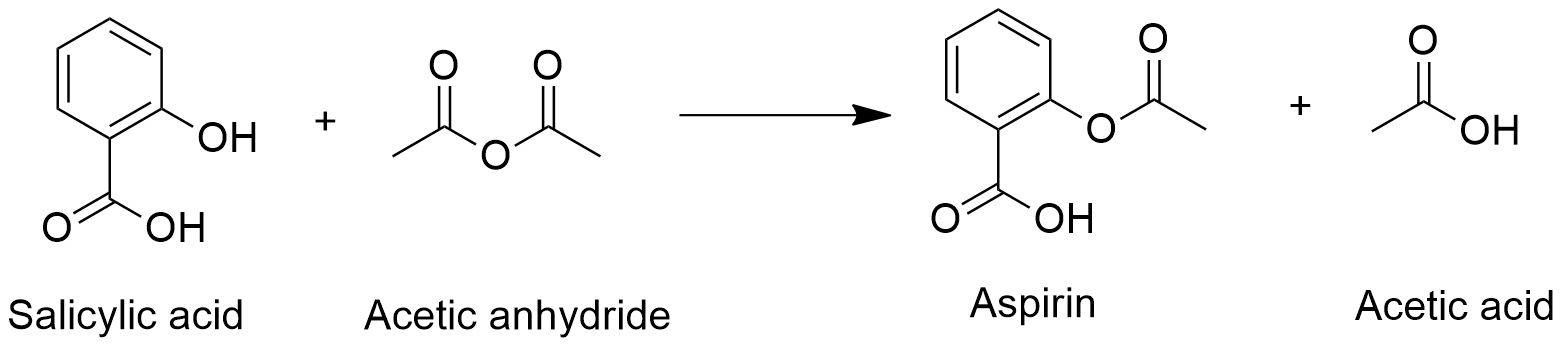
Acetylsalicylic acid chemical structure. Aspirin Acetylsalicylic acid- C9H8O4 - Acetylsalicylic Acid also called aspirin is one of the most widely used nonprescription drugs. Aspirin is one of the safest and most effective medicines in the world. Acetylsalicylic acid is derived from salicylic acid.
Visit BYJUS to understand the Properties Structure Synthesis Uses Health risk and FAQs of Aspirin or Acetylsalicylic acid. Acetylsalicylic acid is a small fragrant acid with its chemical name monohydroxy benzoic acid. It is naturally lipophilic.
It was first taken from the bark of the Willow Tree. It derives its common name from various related sources with the same name eg. It is available as a product of salicin β-glycoside alcohol found in plants and is an active metabolite produced from acetylsalicylic.
Structure of Acetylsalicylic Acid. Image will be uploaded soon. Properties of Aspirin.
Physical Properties of Aspirin It Shows Following Physical Properties Its molar mass is 18016 gmol. Its melting point is 136. Its boiling point is 140.
Its soluble in water. 3g of aspirin can dissolve in 1 liter of water. It is a white crystalline solid at room temperature.
It is weakly. Aspirin is a salicylate drug often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains as an anti-inflammatory compound that inhibits Cox-1Target. Cox-1Aspirin USAN also known as acetylsalicylic acid is a salicylate drug often used as ananalgesic to relieve minor aches and pains as an antipyretic to reduce fever and as an anti-inflammatory medication.
The active ingredient of. Aspirin is an orally administered non-steroidal antiinflammatory agent. Acetylsalicylic acid binds to and acetylates serine residues in cyclooxygenases resulting in decreased synthesis of prostaglandin platelet aggregation and inflammation.
This agent exhibits analgesic antipyretic and anticoagulant properties. Aspirin also known as acetylsalicylic acid ASA is a medication used to reduce pain fever or inflammation. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease pericarditis and rheumatic fever.
Aspirin given shortly after a heart attack decreases the risk of death. Aspirin is also used long-term to help prevent further heart attacks ischaemic strokes. A chemical structure of a molecule includes the arrangement of atoms and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together.
The aspirin molecule contains a total of 21 bonds There are 13 non-H bonds 8 multiple bonds 3 rotatable bonds 2 double bonds 6 aromatic bonds 1 six-membered rings 1 carboxylic acids aromatic 1 esters aliphatic and 1 hydroxyl groups. The first chapter introduces the product composition structure hazards storage toxicological ecological information etc. The second chapter focuses on.
Generic Name Acetylsalicylic acid Commonly known or available as Aspirin DrugBank Accession Number DB00945 Background. Also known as Aspirin acetylsalicylic acid ASA is a commonly used drug for the treatment of pain and fever due to various causesAcetylsalicylic acid has both anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. In the 1800s the Heyden Chemical Company was the first to mass-produce salicylic acid commercially.
It was not until 1899 when a modified version named acetylsalicylic acid was registered and marketed by Bayer under the trade name aspirin. Even though it has been available since the early 1900s its real mode of action was not known until the late 1970s. Some of the indications for aspirin.
Hoffmann a chemist in the pharmaceutical laboratory of the German dye manufacturer Friedrich Bayer Co in Elberfeld consulted the chemical literature and came across the synthesis of acetylsalicylic acid and then prepared the first sample of pure acetylsalicylic acid on 10 August 1897. This was marketed in 1899 under the registered trademark. In 1853 chemist Charles Frédéric Gerhardt treated acetyl chloride with sodium salicylate to produce acetylsalicylic acid for the first time.
4648 in the second half of the nineteenth century other academic chemists established the compounds chemical structure and devised more efficient methods of synthesis. In 1897 scientists at the drug and dye firm Bayer began investigating. Drug Food Interactions.
2D NMR Search. Drug Discovery Drug Repurposing Precision Medicine Machine Learning Telehealth Electronic Medical. Salicylic Acid is a small aromatic acid whose chemical name is monohydroxybenzoic acid.
It is lipophilic in nature. It was first derived from the bark of Willow Tree. Salicylic Acid exist as clear white or colourless and odourless needle-shaped crystals at room temperature.
Salicylic acid HOC6H4COOH or C7H6O3 CID 338 - structure chemical names physical and chemical properties classification patents literature biological. B01AC06 acetylsalicylic acid B01AC07 dipyridamole B01AC30 combinations eg. Acetylsalicylic acid and dipyridamole An important principle used more frequently in recent years as more rational combinations have been marketed is to assign separate ATC 3rd or 4th levels for combinations.
C10B Lipid modifying agents combinations. Acetylsalicylic acid commonly known as aspirin absorbs light in the UV region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The Spectronic 200 operates in the visible region.
Therefore we must perform a series of chemical reactions to convert acetylsalicylic acid to a colored complex as shown in Figure 5. In reaction 1 a base eg sodium. The structure of aspirin is given below.
Therapeutic Uses of Aspirin. Aspirin acetylsalicylic acid is a medical medication that is used to alleviate irritation or inflammation. It is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
It is also used for blood clots heart attacks strokes and bowel cancer prevention. However while some studies have. The word acid conjures up images of bubbling test tubes and thoughts of scary chemical burns.
But when used at the right concentrations acids are actually some of the most beneficial. The sum of the physical and chemical processes by which living organized substance is built up and maintained anabolism and by which large molecules are broken down into smaller molecules to make energy available to the organism catabolism. Essentially these processes are concerned with the.
The acid found in vinegar is A. The acid found in ants is A. The hydrolysis of an ester in the presence of a base is called _____.
Individual acetylsalicylic acid aspirin molecules are microscopic. Studying how the molecules change in the reaction between oxygen and methane is an example of a macroscopic process. Know the relationship between pure chemistry and applied chemistry.
Aspirin acetylsalicylic acid is one drug that any chemist would predict based on the chemical structure alone to be relatively unstable. This is because aspirin belongs to a class of organic molecules called esters. Esters are formed when alcohols react with carboxylic acids.
A molecule of water is lost in the process. Heres a simple example Figure 1. Acetic acid a carboxylic.