Severe metabolic acidosis may result from inhibition of pyruvate carboxylase and mitochondrial damage 29. Acid-base disorders are a group of conditions characterized by changes in the concentration of hydrogen ions H or bicarbonate HCO 3- which lead to changes in the arterial blood pHThese conditions can be categorized as acidoses or alkaloses and have a respiratory or metabolic origin depending on the cause of the imbalance.

Hyperchloremic acidosis or hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
Acetazolamide hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Hyperchloremic acidosis is a form of metabolic acidosis associated with a normal anion gap a decrease in plasma bicarbonate concentration and an increase in plasma chloride concentration see anion gap for a fuller explanation. Although plasma anion gap is normal this condition is often associated with an increased urine anion gap due to the kidneys inability to secrete ammonia. Hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis is a pathological state that results from bicarbonate loss rather than acid production or retention.
Bicarbonate loss leading to hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis occurs in a variety of ways. Gastrointestinal GI causes renal causes and exogenous causes. GI loss of bicarbonate occurs through severe diarrhea pancreatic fistula nasojejunal tube suctioning.
Metabolic acidosis is a serious electrolyte disorder characterized by an imbalance in the bodys acid-base balance. Metabolic acidosis has three main root causes. Increased acid production loss of bicarbonate and a reduced ability of the kidneys to excrete excess acids.
Metabolic acidosis can lead to acidemia which is defined as arterial blood pH that is lower than 735. Metabolic acidosis is primary reduction in bicarbonate HCO 3 typically with compensatory reduction in carbon dioxide partial pressure P co 2. PH may be markedly low or slightly subnormalMetabolic acidoses are categorized as high or normal anion gap based on.
There have also been reports of symptomatic anion gap metabolic acidosis associated with acetazolamide therapy in elderly patients 26 and in those with impaired renal function 26 27 and diabetes mellitus 28. Severe metabolic acidosis may result from inhibition of pyruvate carboxylase and mitochondrial damage 29. Ocular solution of CA inhibitor-induced acidosis is rare but has been.
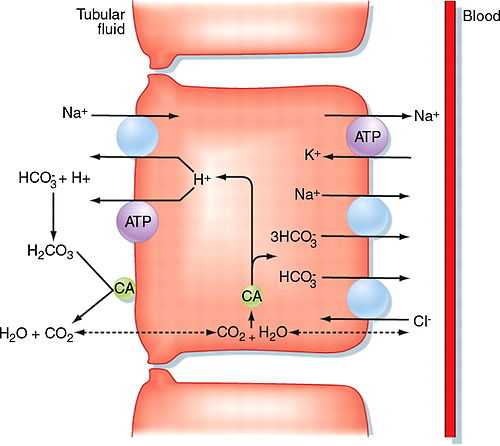
Acetazolamide is a reversible inhibitor of the carbonic anhydrase enzyme that results in reduction of hydrogen ion secretion at the renal tubule and an increased renal excretion of sodium potassium bicarbonate and water. It can be used as a diuretic or to treat glaucoma as it prevents excessive build up of aqueous humor. It also inhibits carbonic anhydrase in the central nervous system to.
As metabolic acidosis continues in some patients. Alkaline diuresis can be initiated by intravenous NaHCO 3 administration or by acetazolamide therapy. The goal is to maintain the urine pH at greater than 75 until the salicylate level falls below 30-50 mgdL.
Multiple dosing of activated charcoal at 025-1 gkg every 2-4 hours can also be used to increase the excretion of salicylate. Acetazolamide increases toxicity of metformin by Other see comment. Decreases serum bicarbonate and induce non-anion gap hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
Acetazolamide will increase the level or effect of mexiletine by passive renal tubular reabsorption - basic urine. Hyperchloremic acidosis or hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. The potential causes of too much acid being introduced to your blood include.
Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis is also called hyperchloremic acidosis because instead of reabsorbing HCO3- with Na the kidney reabsorbs Cl-. Many GI secretions are rich in bicarbonate eg biliary pancreatic and intestinal fluids. Loss from diarrhea tube drainage or fistulas can cause acidosis.
In ureterosigmoidostomy insertion of ureters into the sigmoid colon after obstruction. Acetazolamide is contra-indicated in situations in which sodium andor potassium blood levels are depressed in cases of marked kidney and liver disease or dysfunction suprarenal gland failure and hyperchloremic acidosis. DIAMOX tablets should not be used in patients with hepatic cirrhosis as this may increase the risk of hepatic encephalopathy.
Long-term administration of DIAMOX tablets is. Acid-base disorders are a group of conditions characterized by changes in the concentration of hydrogen ions H or bicarbonate HCO 3- which lead to changes in the arterial blood pHThese conditions can be categorized as acidoses or alkaloses and have a respiratory or metabolic origin depending on the cause of the imbalance. Diagnosis is made by arterial blood gas interpretation.
Acetazolamide is used to prevent and reduce the symptoms of altitude sickness. This medication can decrease headache tiredness nausea dizziness and shortness of breath that can occur when you. Metabolic acidosis or alkalosis may be determined by looking at the base excess.
BE is the amount of required acid or base to bring the pH of the totally oxygenated blood to 740 at 37C and 40 mmHg PCO2. It is the indicator of the metabolic status. If BE is 25 it is metabolic alkalosis.
Anion Gap AG The anion gap represents the difference between. Healthy subjects typically have a gap of 0 to slightly normal 10 mEqL. A urine anion gap of more than 20 mEqL is seen in metabolic acidosis when the kidneys are unable to excrete NH4 such as in renal tubular acidosis.
If the urine anion gap is zero or negative but the serum AG is positive the source is most likely gastrointestinal. Hyperchloremic acidosis Vomiting and diarrhea can cause a temporary state of acidosis called hyperchloremic acidosis which means your body has lost the base of sodium bicarbonate it uses to neutralize your blood. Lactic acidosis Too much lactic acid can result in acidosis.
According to Healthline Causes can include chronic alcohol. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - carbonic anhydrase inhibitors cause a decrease in serum bicarbonate and induce nonanion gap hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. This may increase the risk of lactic acidosis.
Examples of drugs that inhibit carbonic anhydrase include. Topiramate Topamax Acetazolamide Diamox Zonisamide Zonegran. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors frequently cause a decrease in serum bicarbonate and induce non-anion gap hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
Concomitant use of these drugs with metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets may increase the risk for lactic acidosis. Consider more frequent monitoring of these patients. Topiramate zonisamide acetazolamide or.
Plasma bicarbonate decreases and a relative transient metabolic acidosis may occur due to a disequilibrium in carbon dioxide transport in the red cell. Urinary citrate excretion is decreased by approximately 40 after doses of 100 mg every 8 hours. Uric acid output has been shown to decrease 36 in the first 24 hour period.
Acute or chronic metabolic acidosis including diabetic ketoacidosis with or without coma. Warnings and Precautions Lactic Acidosis. There have been postmarketing cases of Metformin-associated lactic acidosis including fatal cases.
These cases had a subtle onset and were accompanied by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise myalgias abdominal pain respiratory distress or. Acute or chronic metabolic acidosis including diabetic ketoacidosis with or without coma. Warnings and Precautions Lactic Acidosis.
There have been postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis including fatal cases. These cases had a subtle onset and were accompanied by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise myalgias abdominal pain respiratory distress or. Moderate Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors such as acetazolamide cause a decrease in serum bicarbonate and may induce non-anion gap hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
Use of topiramate with metformin may increase the risk for lactic acidosis. Consider more frequent monitoring. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors have rarely been described to alter blood sugar so routine.
Topiramate or other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors eg. Zonisamide acetazolamide or dichlorphenamide frequently cause a decrease in serum bicarbonate and induce non-anion gap hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Concomitant use of these drugs with Metformin hydrochloride tablet may increase the risk for lactic acidosis.
Consider more frequent monitoring of these patients. Normal saline causing hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis hyperglycemic hyperosmolar non-ketotic syndrome HHNS.
Tissue necrosis of other etiologies eg trauma infarction. Renal failure primarily if there is. Dysfunction of the renin-angiotensin.
Acetazolamide increases toxicity of metformin by Other see comment. Decreases serum bicarbonate and induce non-anion gap hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism.
Concurrent use may increase risk of.