
On their own this group of drugs may raise potassium levels beyond the normal range termed hyperkalemia which risks potentially fatal arrhythmias. 2 Causes potassium wasting and hypokalemia.
FDA-approved indications include glaucoma idiopathic intracranial hypertension congestive heart failure altitude sickness periodic paralysis and epilepsy.
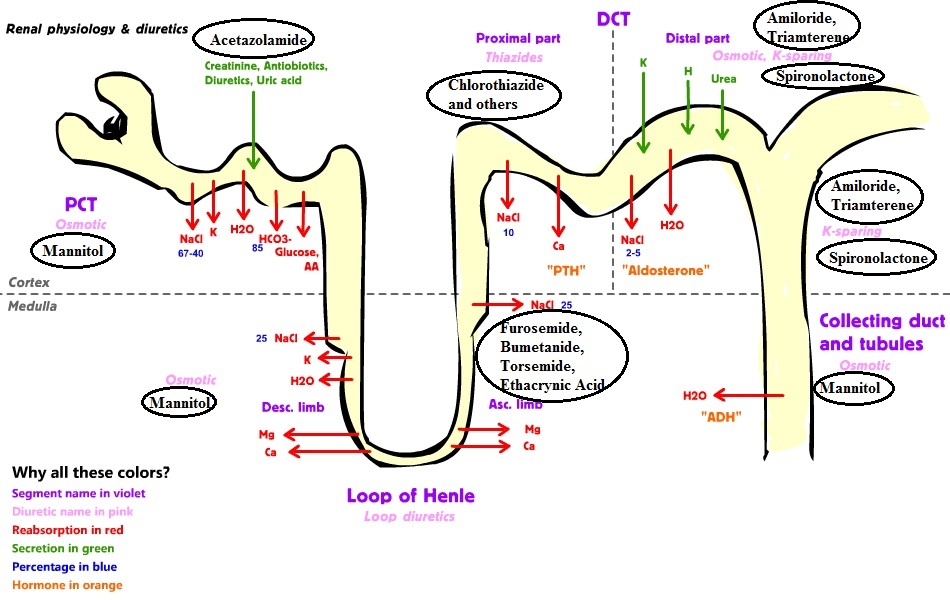
Acetazolamide and potassium levels. Acetazolamide sold under the trade name Diamox among others is a medication used to treat glaucoma epilepsy altitude sickness periodic paralysis idiopathic intracranial hypertension raised brain pressure of unclear cause urine alkalinazation and heart failure. It may be used long term for the treatment of open angle glaucoma and short term for acute angle closure glaucoma until. Sevelamer decreases levels of acetazolamide by increasing elimination.
Either increases levels of the other by Other see comment. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors CAIs and salicylates inhibit each others renal tubular secretion resulting in increased plasma levels. CAIs also shift salicylates.
An electrolyte imbalance such as acidosis or low levels of potassium or sodium in your blood. An allergy to sulfa drugs. To make sure acetazolamide is safe for you tell your doctor if you have.
Acetazolamide can work less well over time. This drug may reduce the potassium levels in your blood. Your doctor may recommend that you eat foods rich in potassium eg bananas or orange.
Acetazolamide is a diuretic and carbonic anhydrase inhibitor medication that is used to treat several illnesses. FDA-approved indications include glaucoma idiopathic intracranial hypertension congestive heart failure altitude sickness periodic paralysis and epilepsy. This activity outlines the indications contraindications interactions monitoring and other therapeutic information.
Acetazolamide is contra-indicated in situations in which sodium andor potassium blood levels are depressed in cases of marked kidney and liver disease or dysfunction suprarenal gland failure and hyperchloremic acidosis. DIAMOX tablets should not be used in patients with hepatic cirrhosis as this may increase the risk of hepatic encephalopathy. Long-term administration of DIAMOX tablets is.
If you take Acetazolamide 250mg Tablets for a long time it can occasionally affect the amount of potassium or sodium in your blood. Your doctor will probably take blood tests to check that this does not happen. You might also experience bone thinning or the risk of kidney stones with long-term therapy.
High or low blood sugar levels may occasionally occur. Potassium is available in different supplemental forms including potassium chloride potassium citrate potassium gluconate potassium bicarbonate potassium aspartate and potassium orotate. Because of the potential for serious side effects one should seek medical advice before deciding to use a potassium supplement see Safety.
Acetazolamide is a sulfonamide and cross reactivity to sulfonamide reactions have been reported. The liver injury typically arises after a few days to weeks of therapy and the pattern of serum enzyme elevations is usually hepatocellular or mixed. Immunoallergic features rash fever eosinophilia are common but autoantibody formation is not.
Acetazolamide or Diamox is the standard medical prophylaxis agent for high altitude illness. The medication is effective in preventing acute mountain sickness AMS high altitude pulmonary edema HAPE and high altitude cerebral edema HACE. Its mechanism is via inhibition of the carbonic anhydrase enzyme which counteracts the respiratory alkalosis which occurs during ascent to altitude.
Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor which prevents reabsorption of sodium bicarbonate in the proximal tubule. 1 Stimulates secretion of sodium bicarbonate. 2 Causes potassium wasting and hypokalemia.
3 Increased delivery of sodium to the macula densa which may induce tubuloglomerular feedback thereby reducing the renal blood flow. Potassium Balance Oxidative Stress and Disease. Oxidative stress OS is known to adversely affect health outcomes in humans.
It influences the activities of inflammatory mediators and other cellular processes involved in the initiation promotion and progression of human neoplasms and pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimers disease Huntingtons disease Lou Gehrig. An electrolyte imbalance such as acidosis or low levels of potassium or sodium in your blood. An allergy to sulfa drugs.
To make sure Diamox is safe for you tell your doctor if you have. If you also take aspirin in high doses. It is not known whether this medicine will harm an unborn baby.
Tell your doctor if. Typically the potassium citrate salts have a potassium on each of the three anion sites on the citrate molecule. The MW of citrate anion is 1891.
Urocit K a common commercial version is a crystalline monohydrate sal t so it has a MW of 339 for 3 potassium ions 1891 for citrate 18 for the one water molecule or 3241 in all. Potassium-sparing diuretics refers to drugs that cause diuresis without causing potassium loss in the urine. On their own this group of drugs may raise potassium levels beyond the normal range termed hyperkalemia which risks potentially fatal arrhythmias.
Triamterene specifically is a potential nephrotoxin and up to half of the patients on it can have crystalluria or urinary casts. Hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemiaandor low vitamin D levels. Ascending limb of loop of Henle LoH and DCT.
Hypovolemia and hypotension via Ang II andor hyperkalemia. Collecting duct CD Increased sodium uptake and potassium excretion into the urine. Causes net fluid retention.
Antidiuretic hormone ADH Hypovolemia and hypotension via Ang II. Renal potassium loss. Secondary to another electrolyte abnormality.
Polyuria with increased distal delivery of sodium and water to the tubule. Potassium wasting diuretics eg. Thiazides loop diuretics acetazolamide mannitol.
Lower than normal levels of potassium in the circulating blood. Definition NCI_CTCAE A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate a low concentration of potassium in the blood. Definition MSH Abnormally low potassium concentration in the blood.
It may result from potassium loss by renal secretion or by the gastrointestinal route as by vomiting or diarrhea. It may be. PP is classified as hypokalemic when episodes occur in association with low potassium blood levels or as hyperkalemic when episodes can be induced by elevated potassium.
Most cases of PP are hereditary usually with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Acquired cases of hypokalemic PP have been described in association with hyperthyroidism. The clinical features of these disorders.
Hypokalemia is generally defined as a serum potassium level of less than 35 mEqL 3. For You News Perspective. Wu et al reported that urinary levels of sodium Na and chloride Cl- were high and coupled Na.
Cl-ratio 1 in patients with renal tubular disorders and those using diuretics but urinary Na. Cl-ratios were skewed or uncoupled in patients with anorexiabulimia. Potassium nitrate is an inorganic salt with a chemical formula of KNO3.
It is a natural source of nitrate and has been used as a constituent for several different purposes including food preservatives fertilizers tree stump removal rocket propellants and fireworks. Potassium nitrate is a common active ingredient in toothpaste exerting an anti-sensitivity action. It provides increasing.
Keep all regular medical and laboratory appointmentsLaboratory andor medical tests such as vitamin B12 levels complete blood count blood potassium levels may be performed to monitor your progress or check for side effects. Consult your doctor for more detailsRemember that it is best to get your vitamins and minerals from food whenever possible. Eat a well-balanced diet and.
The channel becomes leaky when potassium levels fluctuate in the blood. This may occur with fasting followed by consumption of a high potassium feed such as alfalfa. Hyperkalemia which is an excessive amount of potassium in the blood causes the muscles in the horse to contract more readily than normal.
This makes the horse susceptible to sporadic episodes of muscle tremors or paralysis. Wilderness Environmental Medicine WEM the official journal of the Wilderness Medical Society is a peer-reviewed international journal devoted to original scientific and technical contributions on the practice of medicine defined by isolation extreme natural environments and limited access to medical help and equipmentSampling of topics covered. High altitude and climbing.
Acetazolamide 250 to 375 mg orally or IV once or twice a day increases HCO 3 excretion but may also accelerate urinary losses of K and phosphate PO 4. Volume-overloaded patients with diuretic-induced metabolic alkalosis and those with posthypercapnic metabolic alkalosis may especially benefit.