
Acid-base disturbances in gastrointestinal disease. 200 mg5 mL 473 mL BCF Tablet oral.
Clinical Physiology of Acid-Base and Electrolyte Disorders 5th ed McGraw-Hill New York 2001.
Acetazolamide acid base. Acetazolamide is also used for the treatment of acute mountain sickness. In the prevention or treatment of mountain sickness acetazolamide forces the kidneys to excrete bicarbonate the conjugate base of carbonic acid. Increasing the amount of bicarbonate excreted.
Acid-base disorders are a group of conditions characterized by changes in the concentration of hydrogen ions H or bicarbonate HCO 3- which lead to changes in the arterial blood pHThese conditions can be categorized as acidoses or alkaloses and have a respiratory or metabolic origin depending on the cause of the imbalance. Diagnosis is made by arterial blood gas interpretation. Acetazolamide is a sulfonamide derivative with diuretic antiglaucoma and anticonvulsant properties.
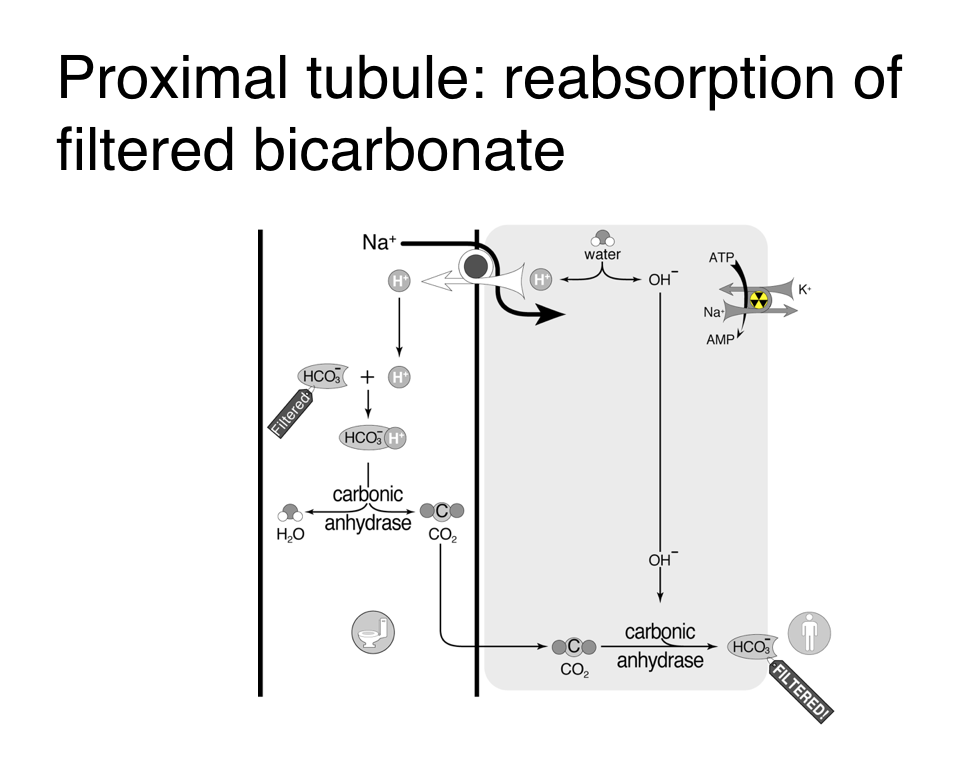
Acetazolamide is a non-competitive inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase an enzyme found in cells in the proximal tube of the kidney the eye and glial cells. Loss of base via the kidney. RTA type 1 2 and 4.
See Renal Tubular Acidosis. Gain of mineral acid. This should be easily established by history.
Normally 85 of filtered bicarbonate is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule and the remaining 15 is reabsorbed in the rest of the tubule. Acid-Base balance is an intricate concept which requires an intimate and detailed knowledge of. Cyanide Acetazolamide Hyperchloremic Acidosis Normal Anion Gap High Anion Gap Acidosis Normal Cl- Level RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS Airway Obstruction Lack of O2Hypoxia.
Living at High Altitudes 1 Emesis with Aspiration Lung Disease 2 Bronchospasm 1 Pneumonia 3. The underlying condition is treated. Oral or IV acetazolamide or hydrochloric acid is sometimes indicated.
See also Acid-Base Regulation Acid-Base Regulation Metabolic processes continually produce acid and to a lesser degree base. Hydrogen ion H is especially reactive. It can attach to negatively charged proteins and in high concentrations.
Read more and Acid-Base Disorders Acid-Base. Since the topic of the role of the kidneys in the regulation of acid-base balance was last reviewed from a teaching perspective Koeppen BM. Renal regulation of acid-base balance.
Adv Physiol Educ 20. 132141 1998 our understanding of the specific membrane transporters involved in H HCO3 and NH4 transport and especially how these transporters are regulated in response to. The underlying condition is treated.
Oral or IV acetazolamide or hydrochloric acid is sometimes indicated. See also Acid-Base Regulation Acid-Base Regulation Metabolic processes continually produce acid and to a lesser degree base. Hydrogen ion H is especially reactive.
It can attach to negatively charged proteins and in high concentrations. Read more and Acid-Base Disorders Acid-Base. Acetazolamide and Addisons.
GI causes diarrhoea vomiting fistulas pancreatic ureterostomies small bowel ileostomies Extras RTA. The disorder is maintained as long as the primary cause persists. In many cases the acid-base disturbance tends to increase in severity while the problem causing it persists though this is not absolute.
Gennari FJ Weise WJ. Acid-base disturbances in gastrointestinal disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol.
Weise WJ Serrano FA Fought J Gennari FJ. Acute electrolyte and acid-base disorders in patients with ileostomies. Am J Kidney Dis.
Kraut JA Madias NE. Acidemia arterial pH 735 results when acid load overwhelms respiratory compensation. Causes are classified by their effect on the anion gap Calculation of the anion gap Acid-base disorders are pathologic changes in carbon dioxide partial pressure Pco2 or serum bicarbonate HCO3 that typically produce abnormal arterial pH values.
Acidemia is serum pH 7. Base excess BE Metabolic acidosis or alkalosis may be determined by looking at the base excess. BE is the amount of required acid or base to bring the pH of the totally oxygenated blood to 740 at 37C and 40 mmHg PCO2.
It is the indicator of the metabolic status. If BE is 25 it is metabolic alkalosis. A negative base excess is equivalent to an acid excess.
A value outside of the normal range -2 to 2 mEq suggests a metabolic cause for the abnormality. The base excess is defined as the amount of H ions that would be required to return the pH of the blood to 735 if the pCO2 were adjusted to normal. Increased urine pH may be caused by acetazolamide bicarbonate or potassium citrate.
Causes of Acid or Alkaline Urine. Any urine pH can be normal. Urine pH is a crude index of acid-base balance and is not a reliable index of blood pH eg a vomiting patient with secondary hypochloremia may have aciduria despite systemic alkalosis because it.
Rose BD Post TW. Clinical Physiology of Acid-Base and Electrolyte Disorders 5th ed McGraw-Hill New York 2001. Palmer BF Alpern RJ.
J Am Soc Nephrol 1997. J Am Soc Nephrol 2000. Khanna A Kurtzman NA.
Seldin DW Rector FC Jr. Acid-base disorders including metabolic acidosis are disturbances in the homeostasis of plasma acidity. Any process that increases the serum hydrogen ion concentration is a distinct acidosis.
The term acidemia is used to define the total acid-base status of the serum pH. For example a patient can have multiple acidoses contributing to a net acidemia. Sales and upgrades.
Support and general queries. AHFS Drug Information AHFS DI is a leading source of evidence-based drug information. AHFS DI is a dependable comprehensive and objective database for FDA approved drug products.
Inclusion of evidence. It is because both concern acid base balance. Citrate is metabolized as citric acid taking up 3 protons per molecule metabolized which is the same as saying it provides 3 molecules of alkali like bicarbonate.
Loss of citrate is therefore loss of potential alkali. AcetaZOLAMIDE Outpatient Dosage Forms Capsule Extended Release 12 Hour Oral. 500 mg Tablet Oral.
125 mg 250 mg Acetic Acid Otic Outpatient Dosage Forms Solution Otic. 2 Acitretin Outpatient Dosage Forms Capsule Oral. 10 mg 25 mg Acyclovir Systemic Outpatient Dosage Forms Capsule Oral.
200 mg Suspension Oral. Effects as a function of altitude. The human body can perform best at sea level where the atmospheric pressure is 101325 Pa or 101325 millibars or 1 atm by definitionThe concentration of oxygen O 2 in sea-level air is 209 so the partial pressure of O 2 pO 2 is 21136 kPaIn healthy individuals this saturates hemoglobin the oxygen-binding red pigment in red blood cells.
250 mg Acetic Acid and Hydrocortisone Solution otic drops. Acetic acid 2 and hydrocortisone 1 10 mL contains benzethonium chloride Acyclovir Systemic Capsule oral. 200 mg BCF Suspension oral.
200 mg5 mL 473 mL BCF Tablet oral. 400 mg BCF 800 mg BCF Acyclovir Topical Ointment topical. 5 30 g Adalimumab Pen.
Acetate definition a salt or ester of acetic acid. Strong base handling Sodium metal hydride. Reactions with Lewis Acid.
Reactions with liquid andor gas ammonia and Chlorine. Friedel Crafts Alkylation Production facilities. Polpharma utilizes up-to-date technologies which ensure the safety of products employees and the natural environment.
We have the capabilities to provide customers. Excreting acid or alkaline urine helps maintain the bodys acid-base balance the balance between acidity and alkalinity. Video of the Day Diet What you eat can alter the pH of your urine although it doesnt change the pH of your blood.
Vegetarians generally have more alkaline urine than meat eaters because meat and dairy produce acidic urine and most vegetables and fruits a more alkaline. Wilderness Environmental Medicine WEM the official journal of the Wilderness Medical Society is a peer-reviewed international journal devoted to original scientific and technical contributions on the practice of medicine defined by isolation extreme natural environments and limited access to medical help and equipmentSampling of topics covered. High altitude and climbing.