As noted p-toluenesulfonic acid pK a -2 is often the catalyst for such reactions. Subsequent nucleophilic attack of an alcohol substrate on the activated sulfoxonium intermediate leads to alkoxysulfonium salt formation.

Multiple sheet sizes are available from stock.
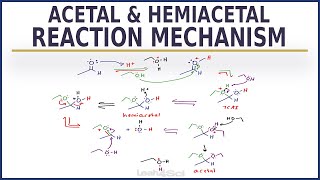
Acetal to alcohol mechanism. The acetal group protects aldehydes and ketones in basic conditions during for example LiAlH 4 or NaBH 4 reduction or Grignard reactions after which it is removed by hydrolysis. Remember the hydrolysis is in equilibrium with the alcohol reaction and to move the process forward a large excess of water is used. The question is the mechanism of the hydrolysis of acetals and thats what we.
Loss of the proton from the attached alcohol gives the acetal. Aldehyde to acetal conversion. Ketone to ketal conversion.
Acetals are stable compared to hemiacetals but their formation is a reversible equilibrium as with esters. As a reaction to create an acetal proceeds water must be removed from the reaction mixture for example with a DeanStark apparatus lest it hydrolyse the product. Mechanism for Hemiacetal and Acetal Formation.
The mechanism shown here applies to both acetal and hemiacetal formation. 1 Protonation of the carbonyl. 2 Nucleophilic attack by the alcohol.
3 Deprotonation to form a hemiacetal. 4 Protonation of the alcohol. 5 Removal of water.
6 Nucleophilic attack by the alcohol. 7 Deprotonation by water. The mechanism involves the intermediacy of vinyl alcohol.
This can cause confusion as acetal is more commonly used to describe compounds with the functional groups RCHOR 2 or RRC OR 2 rather than referring to this specific compound in fact 11-diethoxyethane is also described as the diethyl acetal of acetaldehyde. Precursor to vinylphosphonic acid. Acetaldehyde is a.
The mechanism shown here applies to both acetal formation and acetal hydrolysis by the principle of microscopic reversibility. Some examples of acetal formation are presented in the following diagram. As noted p-toluenesulfonic acid pK a -2 is often the catalyst for such reactions.
Two equivalents of the alcohol reactant are needed but these may be provided by one equivalent of a diol. Out the whole mechanism of acetal formation from aldehyde or ketone plus alcohol through the hemiacetal to the acetal preferably without looking at the fragments of mechanism above or the answer below. When you look at our version of this complete mechanism you should notice a remarkable degree of similarity in the two halves.
The reaction starts with a protonation on carbonyl oxygen and. If we bubble HCl gas through the solution or add a small quantity of concentrated H 2 SO 4 we get an acid-catalyzed reaction that occurs by a mechanism analogous to that described in the previous section. Acid-catalyzed reaction of an alcohol with a carbonyl.
The product of this reaction is known as a hemiacetal literally half of an acetal. Acid Catalyzed Hydration in Alcohol. As with any solvolysis reaction this reaction can be carried out in an alcohol solvent instead of water to yield an entirely different product.
The reaction mechanism is exactly the same the only difference is that the additional -R group on the alcohol gives an -OR instead of -OH as the final. Acetal and Ketal Protecting Groups Synthetic Applications of the Acetal Protecting Group 20 Because of resonance stabilization the carbonyl of the ab-unsaturated ketone is less electrophilic and therefore less reactive to nucleophiles compared to an isolated ketone. The Wieland-Miescher ketone is a common intermediate in the.
The addition of acid to the hemiacetal creates an acetal through the following mechanism. The proton produced by the dissociation of hydrochloric acid protonates the alcohol molecule in an acidbase reaction. An unshared electron pair from the hydroxyl oxygen of the hemiacetal removes a proton from the protonated alcohol.
The oxonium ion is lost from the hemiacetal as a molecule of. Benzyl alcohol appears in many flower and herb GC and headspace analyses and appears to act as a natural fixative and blending agent in flower scents. It can be used in a similar way in fragrance creation.
This is fragrance grade material of high purity. When benzyl alcohol develops a distinct almond note it is due to the formation of benzaldehyde if this happens discard it and buy fresh. Upon further reaction with another molecule of the alcohol an acetal is obtained.
Since alcohols are weak nucleophiles the reaction requires an acid catalyst for the activation of the carbonyl group towards nucleophilic attack. Since the hemiacetals can undergo hydrolysis to yield the reactants the alcohol and carbonyl compound the water formed during the reaction must be removed. The hydrohalogenation of alkenes involves breaking a carbon to carbon double bond followed by the electrophilic addition of a hydrogen atom and halogen.
The halide will add to the more substituted carbon following Markovnikovs rule. The product is a haloalkane also called an alkyl halide. Summary of Hydrohalogenation Mechanism Nucleophilic pi bond reaches.
The mechanism of alkali-catalyzed transesterification is described elsewhere 21. The first step involves the attack of the alkoxide ion to the carbonyl carbon of the triglyceride molecule which results in the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate. The reaction of this intermediate with an alcohol produces the alkoxide ion in the second.
Acetal formation is a reversible reaction with an equilibrium coefficient of about 09 Misselhorn 1975. Thus if the alcohol content is between 40 and 50 by volume as is the case for many strong spirits only 1520 of the total amount of acetaldehyde combines with ethanol. Hence acetal formation does not reduce the free aldehyde content of strong spirits markedly even after.
These ethers again are formed by Williamson-type reactions. However the chloromethyl acetal must be converted in situ to the iodide 111 or activated with Ag. 116 Further methods for MTM introduction consist of a Pummerer rearrangement with dimethyl sulfoxide DMSO and acetic anhydride 117a or treatment of the respective alcohol with dimethyl sulfide in the presence of dibenzoyl peroxide.
Reactions include references to chapters and pages of the following textbooks. If you wish to limit the reactions to only one of these textbooks check it specifically. Searchable text includes all words found in reactants products conditions or comments.
Shown below are some of the more. The mechanism can be considered generally as shown where the initial step involves electrophilic E attack on the sulfoxide oxygen atom. Subsequent nucleophilic attack of an alcohol substrate on the activated sulfoxonium intermediate leads to alkoxysulfonium salt formation.
This intermediate breaks down under basic conditions to. Follows the mechanism of Williamson ether synthesis. Under DDQ conditions the oxidation of PMB through the charge transfer complex is followed by hydrolysis releasing the deprotected compound and p-methoxybenzaldehyde.
By reducing a benzylidene or p-methoxybenzylidene acetal with DIBAL a mono-protected diol can be. The S N 1 Mechanism. Kinetics Thermodynamics Curved Arrows and Stereochemistry with Practice Problems.
The Substrate and Nucleophile in S N 2 and S N 1 Reactions. Carbocation Rearrangements in S N 1 Reactions with Practice Problems. When Is the Mechanism S N 1 or S N 2.
Reactions of Alcohols with HCl HBr and HI Acids. SOCl 2 and PBr 3 for Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl Halides. Mechanism of action.
Aminoglycosides like kanamycin irreversibly bind to specific 30S-subunit proteins and 16S rRNA. Specifically Kanamycin binds to four nucleotides of 16S rRNA and a single amino acid of protein S12. This interferes with decoding site in the vicinity of nucleotide 1400 in 16S rRNA of 30S subunit.
This region interacts with the wobble base in the anticodon of tRNA. Polysaccharides where the ratio of hemiacetals to acetal linkages is very low eg. Saccharides That Lack A Hemiacetal Are Not Reducing Sugars.
We saw at the top of the post that hemiacetals are in equilibrium with an aldehyde or ketone. In contrast acetals ketals are locked in place and can only be converted back to the aldehyde or ketone with aqueous acid. Thats why they.
The mechanism of anti-inflammatory activity of topical corticosteroids is unclear. Various laboratory methods including vasoconstrictor assays are used to compare and predict potencies andor clinical efficacies of the topical corticosteroids. There is some evidence to suggest that a recognizable correlation exists between vasoconstrictor potency and therapeutic efficacy in man.
The term mechanism of action. Carbohydrates are formed by combining sugar monomers together with glycosidic bonds hemiacetal alcohol acetal. Proteins are formed by combining amino acids together in peptide bonds carboxylic acid amine amide.
Nucleic Acids DNARNA are formed by linking nucleotides together in phosphodiester bonds phosphoric acid alcohol à phosphoester. We stock a complete selection of clear UV resistant Plexiglas clear and colored Plexiglass infra-red transmitting UV filtering UV transmitting and plastic plexiglass mirror acrylic plastic sheetsFeaturing Plexiglas brand clear acrylic sheets. Multiple sheet sizes are available from stock.
4x8 4x10 4x12 6x10 8x10 in clear.