The stratum corneum is the outermost layer of the epidermis and the rate-limiting barrier in absorption of an agent. Leaves spinach beet greens are reported to have far greater oxalate content than stalks rhubarb or roots beets carrots.

Poison a substance natural or synthetic that damages living tissues and has injurious effects on the body whether it is ingested inhaled or absorbed or injected through the skin.
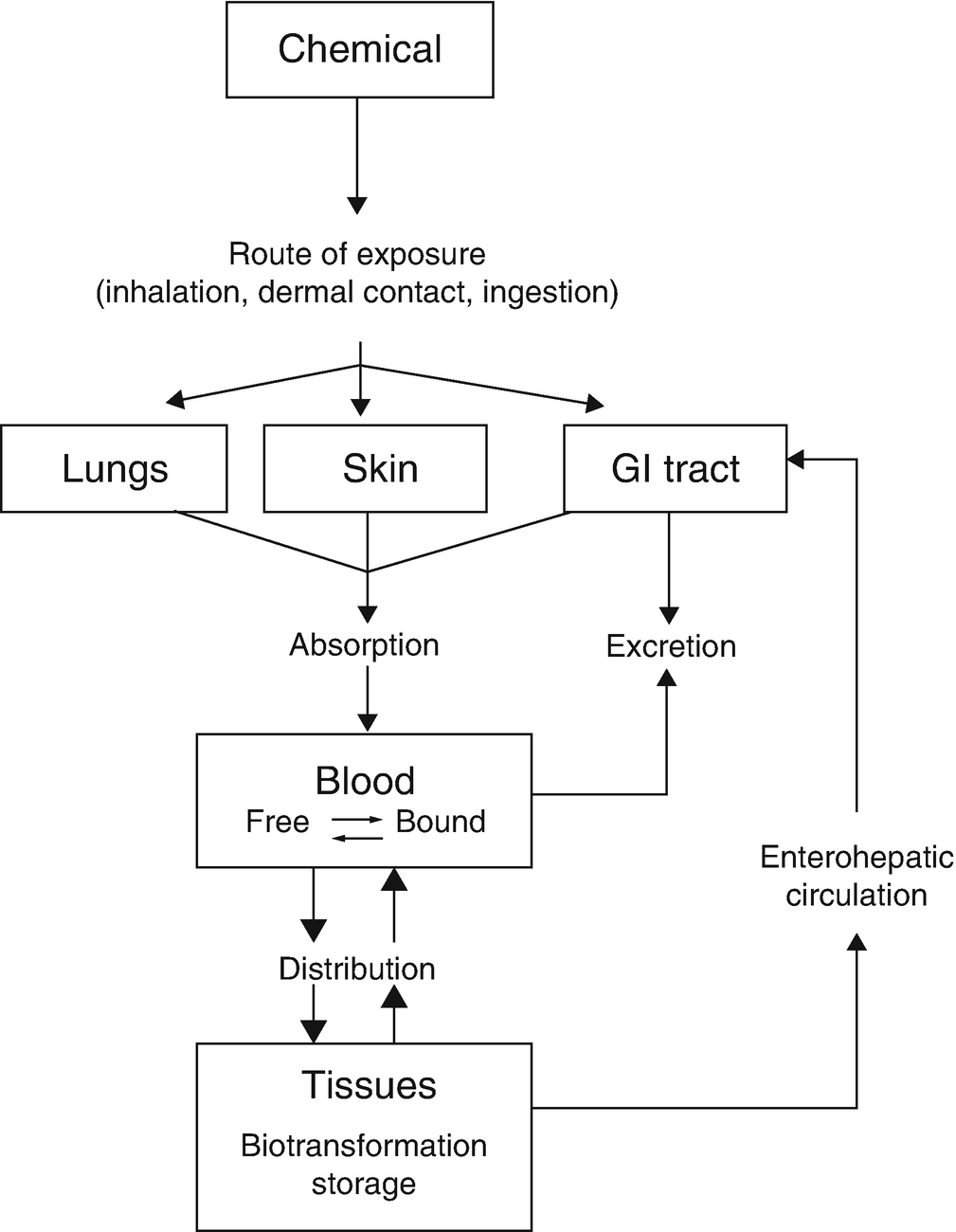
Absorption distribution and excretion of toxicants. Toxins and toxicants can move through the layers by passive diffusion. The stratum corneum is the outermost layer of the epidermis and the rate-limiting barrier in absorption of an agent. Thus how quickly something passes through this thicker outer layer determines the overall absorption.
The stratum corneum is primarily composed of lipophilic cholesterol cholesterol esters and ceramides. Phytic acid is a six-fold dihydrogenphosphate ester of inositol specifically of the myo isomer also called inositol hexakisphosphate IP6 or inositol polyphosphateAt physiological pH the phosphates are partially ionized resulting in the phytate anion. The myo phytate anion is a colorless species that has significant nutritional role as the principal storage form of phosphorus in.
As already mentioned the distribution and elimination of most toxicants occur by first-order processes. Under first-order elimination kinetics the elimination rate constant apparent volume of distribution clearance and half-life are expected not to change with increasing or decreasing dose ie. Urinary excretion clearance volume of distribution half- life.
Urinary excretion is similar in men and women. Clearance is greater in men. Prolonged drug duration due to higher fat content and lower organ blood flow in women.
Increased rates of absorption in women than men. The concentration in the organis dependent on the absorption distributionbiotransformation and excretion ofthe substance. Chemical Hazards and Controls.
Cause blood system damage. Hydrocarbons propane isopropyl ethers. Chemical Hazards and Controls.
Form and innate chemical. Absorption of methimazole after oral administration is rapid and extensive 351 with an absolute bioavailability of approximately 093 1 and a T max ranging from 025 to 40 hours. 31 C max is slightly but not significantly higher in hyperthyroid patients and both C max and AUC are significantly affected by the oral dose administered.
3 Volume of distribution. 76 primarily to serum albumin. Metabolized rapidly by ester hydrolysis to inactive metabolites.
Route of elimination. Approximately 75 of the administered dose is excreted in the urine during the first day after injection. Drug clearance from the body is the result of elimination by renal excretion and by extrarenal pathways nonrenal clearance usually hepatic metabolism.
Because RRT replaces renal function it is clear that drug clearance during RRT is clinically relevant only with those drugs for which renal clearance is normally dominant ie 30 of the total body clearance. This is usually the case. A absorption metabolism distribution and excretion studies that indicate the likelihood the substance would be present in potentially toxic levels in breast milk.
Andor b results of one or two generation studies in animals which provide clear evidence of adverse effect in the offspring due to transfer in the milk or adverse effect on the quality of the milk. Ca and Zn absorption were not affected by alginate. Absorption of Fe Cr and Co were significantly reduced in the alginate group.
Joint FAOWHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. WHO Food Additive Series 30. Toxicological evaluation of ceratin food additives and naturally occurring toxicants.
Alginic acid and its ammonium calcium potassium and sodium salts 1993. 45 absorption tissue distribution metabolism excretion and the other molecular and biochemical 46 processes that ultimately lead to particular responses. Interspecies extrapolation of such a dose 47 metric may be possible by the use of a PBTK model.
While this more sophisticated approach. Distribution of oxalate within a plant can vary. Leaves spinach beet greens are reported to have far greater oxalate content than stalks rhubarb or roots beets carrots.
A distinction should be made between total oxalate soluble and insoluble oxalate as excess soluble oxalate has more of an effect on bioavailability and kidney stone formation. Poison a substance natural or synthetic that damages living tissues and has injurious effects on the body whether it is ingested inhaled or absorbed or injected through the skin. If the toxicity is severe enough death may result.
Learn about different types of poisons and their effects on the body. Academiaedu is a platform for academics to share research papers. 93 Absorption Distribution and Excretion.
Zinc is absorbed in the small intestine by a carrier-mediated mechanism. Under regular physiologic conditions transport processes of uptake do not saturate. The exact amount of zinc absorbed is difficult to determine because zinc is secreted into the gut.
Zinc administered in aqueous solutions to fasting subjects is absorbed. Fertility and Sterility is an international journal for obstetricians gynecologists reproductive endocrinologists urologists basic scientists and others who treat and investigate problems of infertility and human reproductive disorders. Includes the history and scope of the field.
Absorption distribution metabolism and excretion of toxicants. Mechanisms of toxic action. Ecotoxicology as well as specific examples important toxicants.
Introduces regulatory toxicology and human and ecological risk assessment. Offered by Environmental Science Policy. Limited to three attempts.
This session will begin with a general background on traditional DART testing and the state of the science in regard to regulatory needs for DARTDNT screening followed by presentations covering alternative models and approaches to screen for reproductive toxicants to predict teratogenicity the to understand and predict DNT using behavioral assessments in zebrafish. These presentations will. A route of exposure by which substances enter the body through the skin.
Read more at USGBC. According to the World Health Organization dioxins are some of the most potent toxins known to humans with no known safe limit for exposure and a strong propensity for bioaccumulation. In addition dioxins are highly persistent in the environment.
Read more at WHO.