
Molar Mass ¼ Molecular Weight M gmol v T cK P c bar z c Methane 16043 0012 1906 4599 0286 Ethane 3007 01 3053 4872 0279 Propane 44097 0152 3698 4248 0276 n-Butane 58123 02 4251 3796 0274 n-Pentane 7215 0252 4697 337 027 n-Hexane 86177 0301 5076 3025 0266 n-Heptane 100204 035 5402 274 0261 n-Octane 114231 04 5687 249 0256 n-Nonane 128258. The molar heat of combustion of methane gas is given in the table as a positive.
The molar heat of combustion of methane gas is given in the table as a positive.
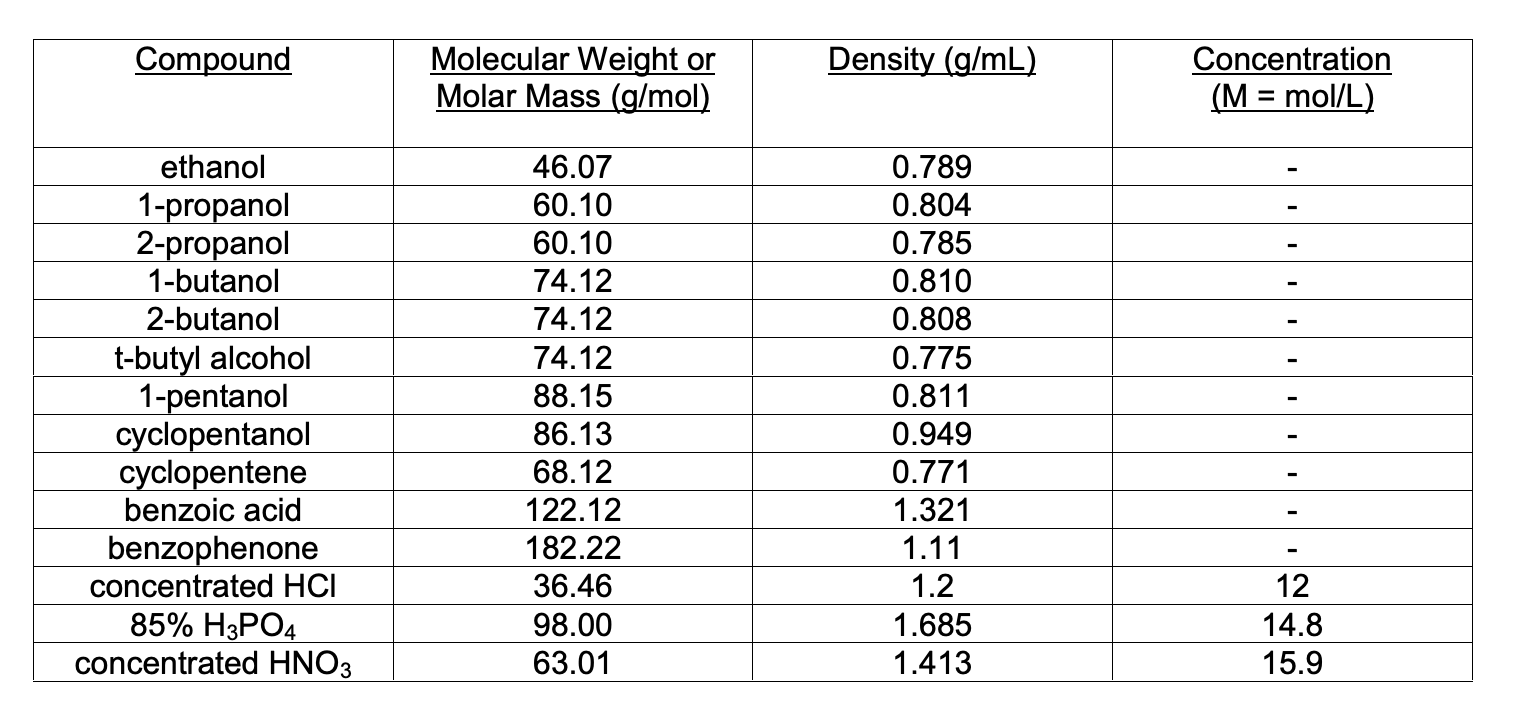
1 propanol molar mass. As molar mass increases the AT value of a molecule with similar types of intermolecular forces 7. The presence of an alcohol group -OH methyl group -CH3. The AT value of a molecule compared to the presence of a 82-propanol had a AT value compared to 1-propanol because 9.
Kinetic energy is related to the temperature of a substance. As liquid molecules are converted to gas molecules. 1-Propanol is a primary alcohol with the formula CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 OH and sometimes represented as PrOH or n-PrOHIt is a colorless liquid and an isomer of 2-propanolIt is formed naturally in small amounts during many fermentation processes and used as a solvent in the pharmaceutical industry mainly for resins and cellulose esters and sometimes as a disinfecting agent.
Structure properties spectra suppliers and links for. 1-Propanol Propan-1-ol 71-23-8 71-31-8 109-78-4 927-74-2 36294-23-2. Jump to main content Jump to site nav.
Membership. Journals books. C 3 H 7 OH l 9 2 O 2g 3CO 2g 4H 2 O l ΔH -2021.
C 4 H 9 OH l 6O 2g 4CO 2g 5H 2 O l ΔH -2671. From the table we see that 1 mole of methane gas CH 4g undergoes complete combustion in excess oxygen gas releasing 890 kJ of heat. The molar heat of combustion of methane gas is given in the table as a positive.
Isoamyl alcohol is a colorless liquid with the formula C 5 H 12 O specifically H 3 C 2 CHCH 2 CH 2 OH. It is one of several isomers of amyl alcohol pentanol. It is also known as isopentyl alcohol isopentanol or in the IUPAC recommended nomenclature 3-methyl-butan-1-olAn obsolete name for it was isobutyl carbinol.
Isoamyl alcohol is an ingredient in the production of. Propan-1-ol is the parent member of the class of propan-1-ols that is propane in which a hydrogen of one of the methyl groups is replaced by a hydroxy group. It has a role as a protic solvent and a metabolite.
It is a short-chain primary fatty alcohol and a member of propan-1-ols. Intermolecular forces in 1 propanol. I would find this using n massmolar mass.
To convert from kJmol to kJL do I multiply by molL ie. The number of moles in 1L. If so how do I find that value.
I have to do this for ethanol 1-propanol 1-butanol 1-hexanol 1-heptanol and 1-octanol. The larger 1-propanol molecules have stronger London forces between them. Lower than 298 K.
Ethyl acetate is a polar molecule therefore dipole-dipole interaction will be present there. These contain information you will need to answer more less Dipole-dipole attractions Higher polarity molecules attract more strongly and have a higher boiling point propane 1-propanol 13-propanediol least. Isobutanol appears as a clear colorless liquid with a sweet odor.
Flash point 85 - 100F. Less dense than water. Vapors heavier than air.
Isobutanol is an alkyl alcohol that is propan-1-ol substituted by a methyl. Molar Mass ¼ Molecular Weight M gmol v T cK P c bar z c Methane 16043 0012 1906 4599 0286 Ethane 3007 01 3053 4872 0279 Propane 44097 0152 3698 4248 0276 n-Butane 58123 02 4251 3796 0274 n-Pentane 7215 0252 4697 337 027 n-Hexane 86177 0301 5076 3025 0266 n-Heptane 100204 035 5402 274 0261 n-Octane 114231 04 5687 249 0256 n-Nonane 128258. The table above shows the structural formulas and molar masses for three different compounds.
Which of the following is a list of the compounds in order of increasing boiling points. Butane 1-propanol acetone B. Butane acetone 1-propanol C.
1-propanol acetone butane DAcetone butane 1-propanol. A particle-level diagram of a metallic element is shown above. Compare the boiling points of carboxylic acids with alcohols of similar molar mass.
Compare the solubilities of carboxylic acids in water with the solubilities of comparable alkanes and alcohols in water. Many carboxylic acids are colorless liquids with disagreeable odors. The carboxylic acids with 5 to 10 carbon atoms all have goaty odors explaining the odor of Limburger cheese.
Here M 2 is the molar mass of the solvent. Aquamolality Solvomolality of substance 1 in a mixed solvent with components 2 3 12 m 1 3. Here the average molar mass of the solvent is.
And x 2 is the solvent mole fraction of component 2. This term is used most frequently in discussing comparative. 1-propanol CH 3 OCH 2 CH 3 methyl ethyl ether amide O O C OH O C O O C NH N O C O CH 3 CH 2 C H propanal O R R C NH R R N R O R C OH ketone organic acid ester amine O CH 3 CH 2 C OH propanoic acid O CH 3 CH 2 COCH 3 methyl propanoate CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 NH 2 1-propanamine O CH 3 CH 2 C NH propanamide Note.
R represents a bonded atom or. On the basis of dipole moments andor hydrogen bonding explain in a qualitative way the differences in the boiling points of acetone 562 C and 1-propanol 974 C which have similar molar masses. The melting point of H 2 Os is 0 C.
Would you expect the melting point of H 2 Ss to be 85 C 0 C or 185 C. Four representative primary alkanolamines were selected named 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol AMP two methyl. Im as an example AMP and KIm were mixed with a molar ratio of 21 then stirred for 12 h at T 3232 K and the obtained KAMP 2Im was dried for 24 h under vacuum at T 3332 K to remove a possible trace of moisture.
The preparation methods of other DFILs were the same as. This can be converted to kJ per mass units. The molweight of ethanol is 21201 6101 11600 4608 gmol.
The heat of combustion of ethanol ΔH c C 2 H 6 O l 136691kJmol 1000gkg 4808 gmol 29664 kJkg ethanol 297 MJkg 12754 BTUlb 7086 kcalkg. The table below shows values of heat of combustion calculated after the above described method. The ideal gas law treats the molecules of a gas as point particles with perfectly elastic collisions.
This works well for dilute gases in many experimental circumstances. However gas molecules are not point masses and there are many cases gases need to be treated as non-idealJohannes D. Van der Waals suggested a modification to take into account molecular size and molecular interaction forces.
Temperature K A B C Reference Comment. Ambrose Sprake et al 1975. Coefficents calculated by NIST from authors data.